Benefit cap: number of households capped to November 2022
Published 21 March 2023
Applies to England, Scotland and Wales
The latest release of these statistics can be found in the collection of benefit cap statistics.
The benefit cap is a limit on the total amount of benefit that most working age people can get.
The amount of benefit a household receives is reduced to ensure claimants do not receive more than the cap limit. The benefit cap can be applied through either:
-
Universal Credit (UC)
-
Housing Benefit (HB)
The benefit cap was introduced in April 2013. It was initially applied to HB and subsequently to UC, as UC was gradually rolled out. UC replaces 6 means-tested benefits including HB and since December 2018, UC has been available across Great Britain (GB) to people applying for means-tested social security support. However, a small number of the population may still apply for HB. Read about who can get HB. DWP is in the process of moving all legacy benefit claimants to Universal Credit.
When the benefit cap was introduced in April 2013, the cap level set initially was:
-
£26,000 per year
-
£18,200 per year for single adults with no children
The Summer Budget 2015 announced changes to the level of the benefit cap to:
-
£20,000 per year (or £13,400 for single adults with no children) nationally
-
£23,000 per year (£15,410 for single adults with no children) in Greater London
These lower, tiered cap levels were introduced from 7 November 2016 and remain the current cap levels up to the period covered by this release (November 2022).
Figures relating to households with their UC capped are subject to retrospection. All figures in these statistics have been updated as at November 2022. For more information, see the Background Information and Methodology document. The timeseries detailing weekly cap amount does not include retrospection. Figures within this release have been rounded in line with our rounding policy. Figures may not sum due to rounding.
1. Main stories
The main stories are:
-
around 112,000 households had their benefit capped at November 2022
- 101,000 households were capped on UC at November 2022
- 11,000 households were capped on HB at November 2022
-
the total number of capped households has fallen by 7% (7,800) in the latest quarter to November 2022, when compared to the previous quarter (August 2022):
-
volumes of UC capped households have fallen by 6% (6,500) in the quarter to November 2022 since the previous quarter
-
volumes of HB capped households have continued to fall, with an 11% (1,300) decrease in the quarter to November 2022 since the previous quarter
-
-
1.8% of households claiming HB or UC had their benefits capped at November 2022, which is a decrease from 1.9% of all households capped at August 2022
-
the weekly average cap amount was £50 at November 2022 which compares to £51 at August 2022
-
in the quarter to November 2022, 9% (3,900) of households that left the UC benefit cap, left due to earning over the earning threshold. This compares to 10% (2,500) of households that left due to earning over the earning threshold in the quarter to August 2022
Between August 22 and November 22, there were more households that flowed off the cap than flowed on
The number of households that flowed on and off the cap between August 2022 and November 2022
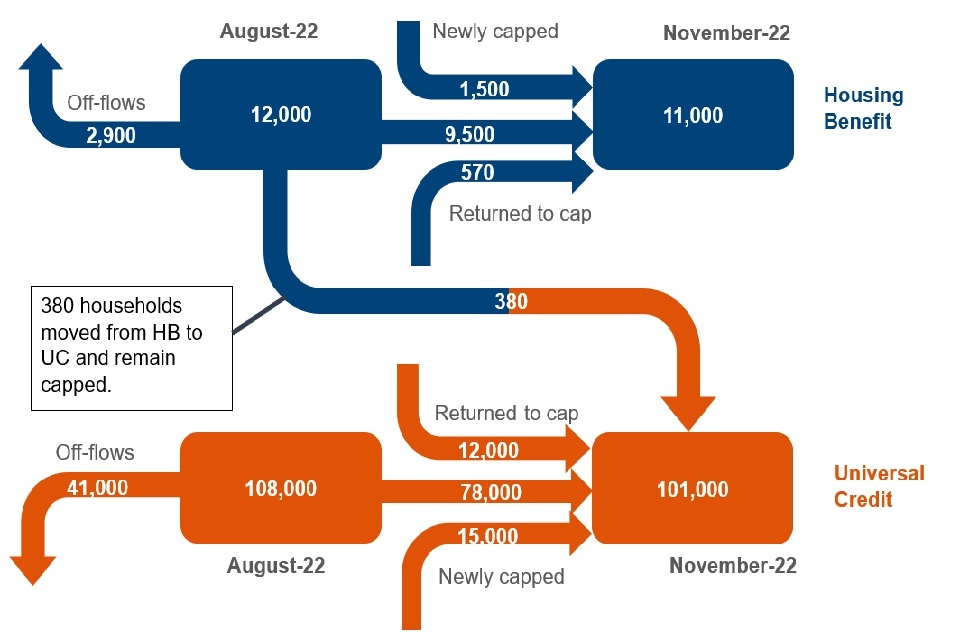
Source: DWP Universal Credit Quarterly Statistics and DWP Housing Benefit Caseload Statistics.
In the latest quarter for households capped on HB:
-
the number of households that had their HB capped decreased by 11% from August 2022 (12,000) to November 2022 (11,000)
-
9,500 households remained capped on HB at November 2022
-
2,900 households off-flowed from the benefit cap, which means no longer on the benefit cap (between August 2022 and October 2022). Of the 2,900 off-flows, 40% (1,200 households) were no longer claiming HB. Of the households no longer claiming HB, 78% (910) are now claiming UC
-
380 households moved from HB to UC and continued to be capped (between August 2022 and October 2022)
- 1,500 households were newly capped, which means they were on the HB benefit cap caseload for the first time (between August 2022 and October 2022):
- of the 1,500 newly capped HB households, 240 were also off-flows within the same time-period (August 2022 and October 2022)
- 570 households returned to the HB cap that had been capped prior to, but not at, August 2022
In the latest quarter for households capped on UC:
-
the number of households that had their UC capped at November 2022 was 101,000, which is 6,500 lower than at August 2022
-
78,000 remained capped at November 2022
-
there were 41,000 off-flows (between August 2022 and October 2022)
-
there were 380 on-flows from the HB cap (between August 2022 and October 2022) to the UC cap. An on-flow is a household that is capped for the first time on the respective benefit (HB or UC). In this case it is not the first time the household was on the benefit cap, rather the first time it was capped under UC
-
15,000 were newly capped (between August 2022 and October 2022)
-
12,000 returned to the UC cap that had been capped prior to, but not at, August 2022
Around 15,000 (14,900 newly capped and 380 on-flows from the HB cap) households flowed on to the UC cap. Of these, 5,500 also flowed off the cap within the same time period (between August 2022 and October 2022).
Note: Figures relating to on-flows, newly capped and off-flows refer to the time period August 2022 and October 2022. Figures relating to remaining capped or returning to the cap refer to the time period August 2022 and November 2022. The difference is due to the methodology used to obtain outcome at off-flow (including households that flow from the HB cap to the UC cap), as it is not possible to obtain outcome data for November 2022, at November 2022. Figures within this release have been rounded in line with our rounding policy. Figures may not sum due to rounding.
2. The number of capped households in GB
At November 2022, around 112,000 households had their benefits capped in GB:
-
101,000 were capped on UC
-
11,000 were capped on HB
The total number of capped households has fallen by 7% (7,800) when compared to the previous quarter (August 2022).
The number of households capped under HB at November 2022 continued to decrease, with an 11% (1300 households) decrease from August 2022.
The number of households capped under UC has decreased by 6% (6,500 households) at November 2022 when compared to August 2022. The volumes of households capped under UC are still high compared with pre-pandemic levels, however the volume sharply decreased in October 2021 which coincided with the withdrawal of the temporary £20 uplift to UC which ended on the 6 October 2021. The proportion of capped households on the overall UC caseload has remained fairly stable at 2.1% at November 2022, when compared to 2.2% at August 2022.
The total number of capped households on UC have fallen by 6% from August 2022 to November 2022
Monthly number of UC and HB capped households from April 2013 to November 2022
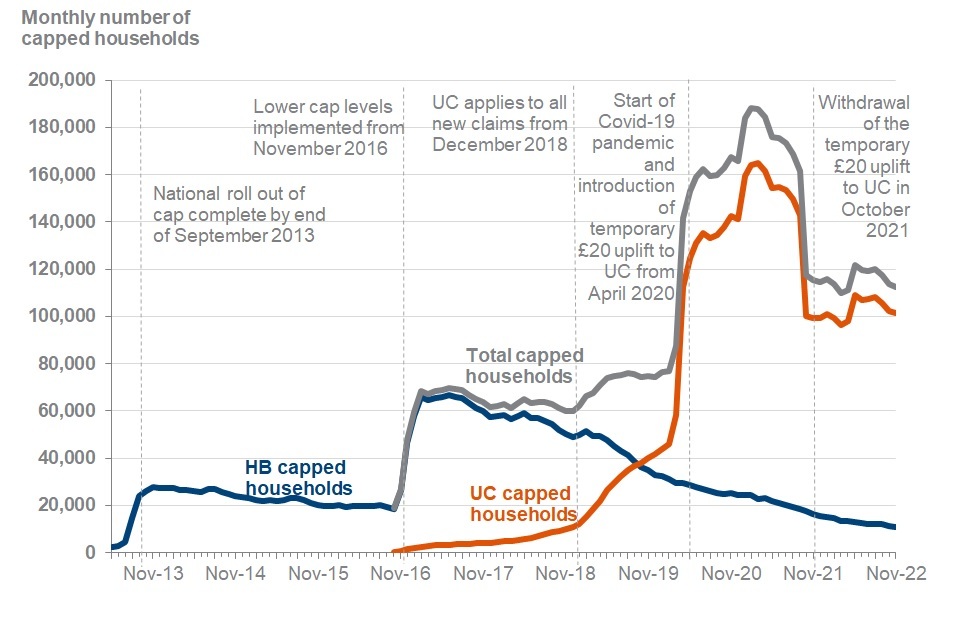
Source: Benefit Cap HB point in time caseload and UC point in time caseload statistics to November 2022, Stat Xplore
UC came into the scope of the benefit cap in October 2016 and capped households claiming UC steadily increased from 350 households (October 2016) to 11,000 households when UC was fully rolled out in December 2018. Up until this point, the changes to the overall capped caseload were driven by HB capped households which reached 67,000 households in June 2017, following the change to current cap levels. The HB capped caseload remained stable until August 2017 (65,000 households) when it started to slowly decrease.
Following the completion of GB-wide roll out of UC in December 2018, the households capped on UC increased due to:
-
the majority of new claimants no longer being able to apply for legacy benefits, only UC
-
HB claimants moving onto UC
The UC capped caseload overtook the HB capped caseload in October 2019, with 36,000 HB households capped and 38,000 UC households capped. Since then, HB capped households have continued to steadily decrease to 11,000 households at November 2022.
Between March 2020 and April 2020, at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the UC capped caseload increased by 92%, from 59,000 households to 110,000 households. From April 2020 until March 2021 the number of households capped on UC increased to a peak of 170,000. The number of households capped on UC decreased sharply from March 2021 to the quarter to November 2021, with a 40% (66,000 households) decrease to 100,000 households. This coincided with the withdrawal of the temporary £20 uplift which ended on the 6 October 2021. The number of UC capped households then remained stable to the quarter ending February 2022, but increased by 10% in the quarter to May 2022, to stand at 110,000 households capped on UC. This increase coincides with the annual uprating of benefit awards from April 2022. The number of households capped on UC remained relatively stable between May 2022 and August 2022, however there has been a decrease of 6% (6,500) between August 2022 and November 2022.
Whilst volumes of households capped on UC are greater than pre-pandemic levels, the proportion of capped households on the overall UC caseload is 2.1% at November 2022, which is more comparable to levels at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic.
See Stat-Xplore for full data.
Note: The UC caseload point in time data is used to source both UC Official Statistics and the UC data within these Benefit Cap Official statistics, however for the latter publication the full back series of data is refreshed for each release, whereas only the latest two years data are refreshed for the UC Official Statistics and the historic data are frozen. It is expected that the latest quarter’s overall provisional figures (for capped UC figures) will be around 2% of their revised figure in future releases, similar to UC Official Statistics.
16,000 households (UC and HB) were newly capped in the latest quarter.
The number of newly capped households has decreased at November 2022 when compared to the same quarter a year earlier
Quarterly number of newly capped UC and HB households from April 2013 to October 2022
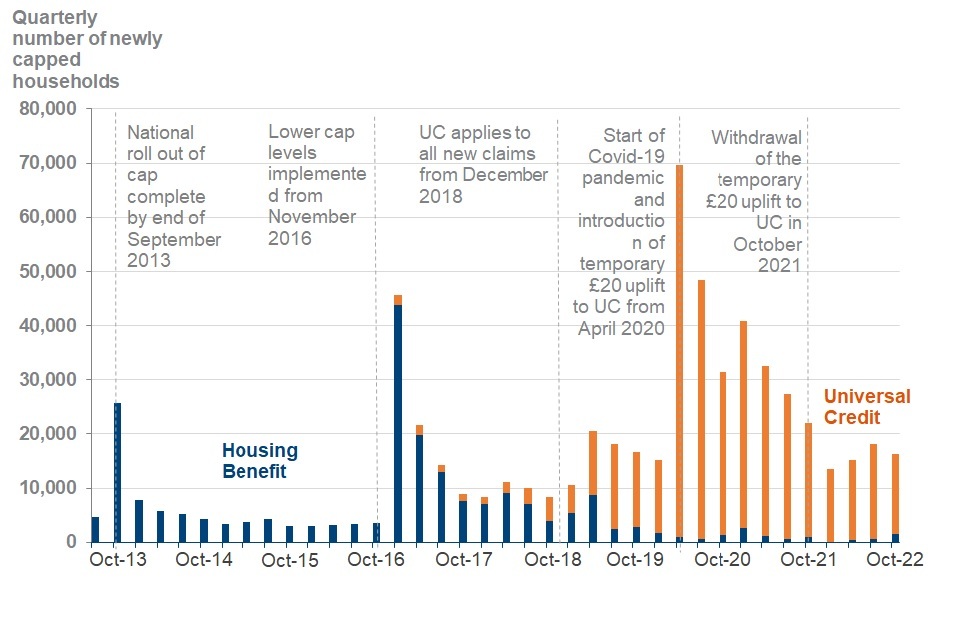
Source: Benefit Cap HB cumulative and UC cumulative caseload statistics to October 2022, Stat-Xplore
16,000 households had their benefits capped for the first time this quarter (August 2022 to October 2022). This is 10% (1,800) fewer households than last quarter (May 2022 to July 2022), when 18,000 households had their benefits capped for the first time.
Note: Newly capped households are those that have their benefits capped for the very first time. For UC, this excludes off-flows from the HB cap who then immediately become capped under UC. Due to the methodology used to obtain outcome at off-flow (including households that flow from the HB cap to the UC cap), it is not possible to obtain outcome data for November 2022, at November 2022.
The quarterly number of off-flows from the UC cap has continued to increase for the third consecutive quarter
Timeseries of number of households that have flowed off the UC and HB cap from November 2013 to November 2022
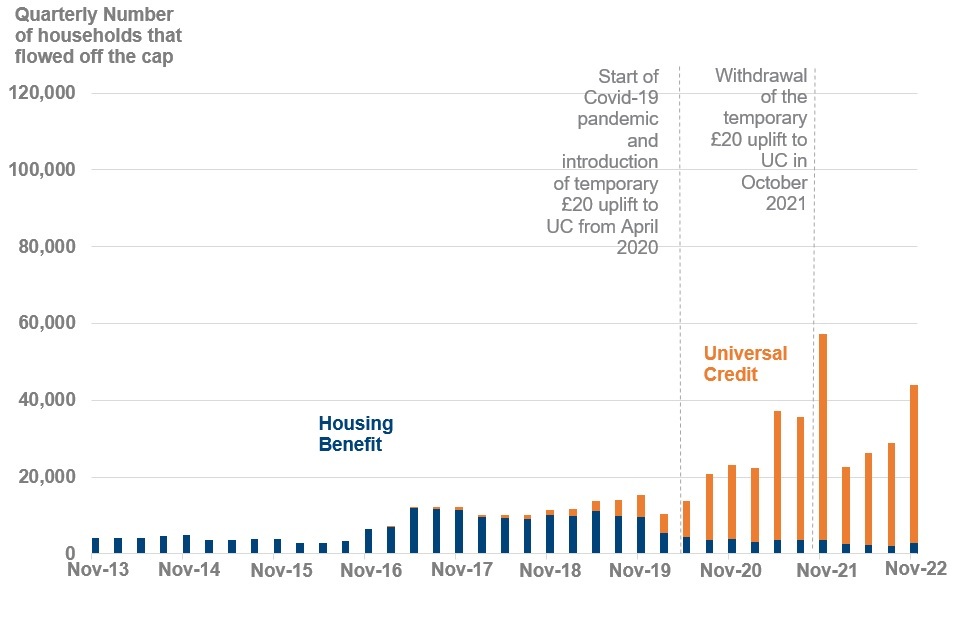
Source: Benefit Cap HB cumulative and UC cumulative caseload statistics to October 2022, Stat-Xplore
In the quarter to November 2022, 41,000 households left the UC cap. Of these off-flows, 13% (5,500 households) were also on-flows during this quarter. This means that these households had their UC capped for the first time and left the cap during this quarter.
The number of quarterly off-flows from UC, steadily increased from 200 at the quarter ending February 2017, to 5,700 at the quarter ending November 2019. The increase has been greater since the quarter ending February 2020, with the largest number of households that have left the UC benefit cap observed at November 2021 (54,000) which coincides with the withdrawal of the temporary £20 uplift to UC in October 2021. At November 2022, the number of quarterly off-flows from UC has increased to 41,000 households from August 2022 (27,000).
In the most recent quarter, (off-flows from August 2022 to October 2022), 9% (3,900) of UC households that flowed off the cap, left the cap due to having earnings at, or over, the earnings threshold of £658 per assessment period (from 12 April 2022). This compares to 10% (2,500) of UC households that left due to earning over the earnings threshold in the quarter to August 2022.
The earnings exemption threshold is subject to change each financial year. The earnings exemption threshold is £658 for the Financial Year Ending (FYE) 2023. Details of previous exemption threshold levels can be found in background information and methodology document. See Stat-Xplore for full data broken down by region.
Note: Outcome statistics for households no longer capped under UC have not currently been developed and are not comparable with statistics for outcomes of those that are no longer capped under HB. Outcomes figures related to moving into work have been presented separately for UC and HB. This is because under UC a household is exempt from the cap when earnings in each assessment period are at least the level of the earnings exemption threshold (for FYE 2023 this is £658). Under HB, a household becomes exempt from the cap if it is entitled to WTC, which depends on hours of paid work (at least 30 hours for those aged 25 to 59, at least 16 hours for single people with 1 or more children, and at least 24 hours between a couple with 1 or more children).
Off-flow outcomes are shown as at the end of the quarter in which a household moved off the benefit cap, meaning the outcomes are fixed at that point, unless a household is capped again at a later date. More detail on the way off-flow outcomes are determined is included in the background information and methodology document.
Quarterly off-flows from the HB cap were relatively stable between the quarter ending February 2014 until the quarter ending August 2016, remaining between 2,800 to 4,800. At November 2016, the quarterly off-flows began to increase each quarter until May 2017, where it stood at 12,000. The HB quarterly off-flows remained relatively stable once again until they decreased to 5,500 at February 2020. Since then, the HB quarterly off-flows have continued to gradually decrease.
In the most recent quarter (off-flows from August 2022 to October 2022), 2,900 households left the HB cap. Of the 2,900 off-flows, 40% (1,200 households) were no longer claiming HB. Of these, 78% (910) of households no longer claiming HB are now claiming UC.
Of the households which flowed off the HB cap in the latest quarter, 8% (240 households) left the HB cap with an open WTC claim. This is the same proportion as last quarter (August 2022) when 180 households (8%) left the HB cap with an open WTC claim.
See Stat-Xplore for full data.
Since December 2018, WTC has been replaced by UC with only a small number of the population able to apply for WTC, see the eligibility criteria and further information about WTC.
3. Characteristics of capped households
86% of households (HB and UC) that are currently capped include children.
At November 2022, 86% (97,000) of total capped households that had their benefits capped included children. In UC, 86% (87,000) of capped households included children and in HB, 87% (9,500) of capped households included children.
Of the households including children, capped at November 2022:
-
91% (88,000) had between 1 and 4 children
-
9% (8,600) had 5 or more children
UC capped households have fewer children per household than HB capped households
Proportion of UC and HB capped households by number of children at November 2022
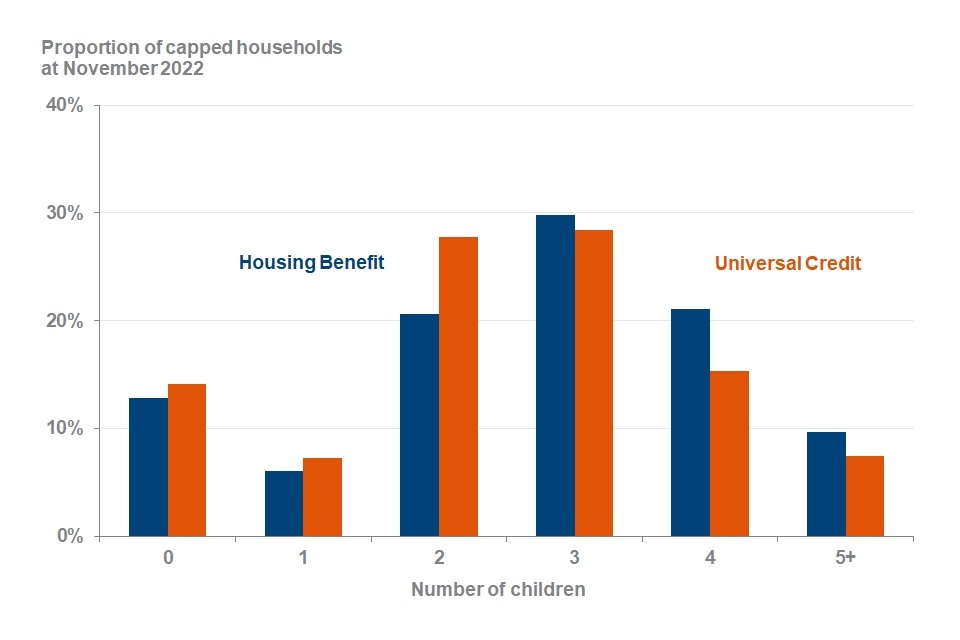
Source: Benefit Cap HB point in time caseload and UC point in time caseload statistics to November 2022, Stat Xplore
Since February 2020 (data at November 2019) a new methodology to determine the number of children was developed. Figures prior to this cannot be compared. Read further information in the Background Information and Methodology document.
Child Benefit (CHB) and Child Tax Credit (CTC) are legacy benefits which can be claimed alongside HB. UC claimants can get CHB and, where applicable, receive the UC child element instead of CTC. CHB, CTC and UC are all in scope for the benefit cap, so households in receipt of these benefits or elements are more likely to exceed the cap limit and be capped if they are not exempt.
See Stat-Xplore for full data on the family make-up of capped households.
See data table 1 and data table 6 for full data on the age of youngest child by family type at November 2022.
See data table 3 for full data on the cumulative HB cap caseload by family type and age of youngest child.
70% of households that have their benefits capped are single-parent families.
The majority of households capped continues to be single parents with children
Proportion of capped households by household type from February 2019 to November 2022
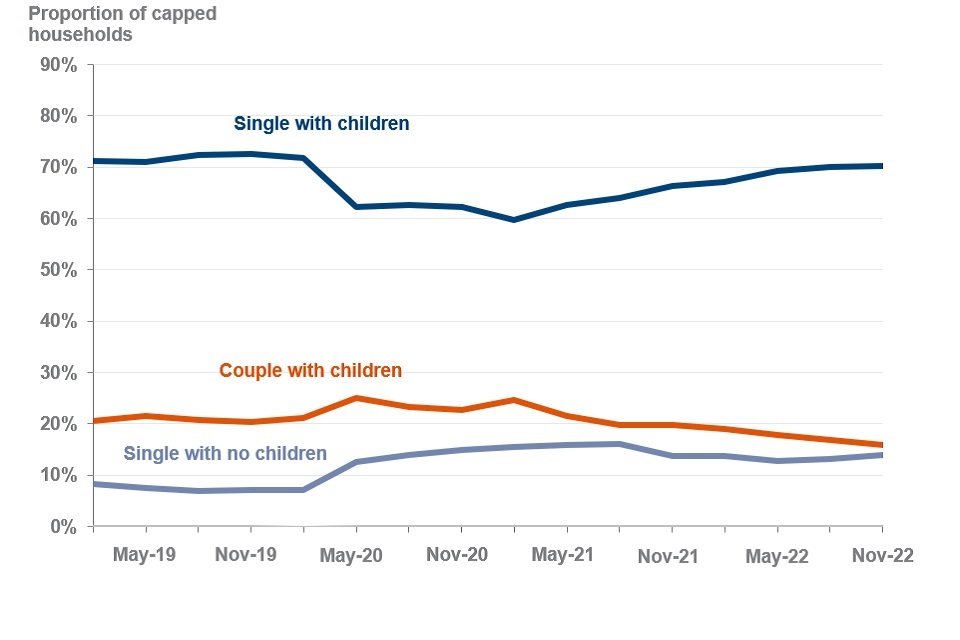
Source: Benefit Cap HB point in time caseload and UC point in time caseload statistics to November 2022, Stat Xplore
At the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a change in the characteristics of households capped on UC and HB, however, trends are now showing similar characteristics to those seen prior to the COVID-19 pandemic:
-
at November 2022, 70% (79,000) of households that had their benefits capped, were single-parent families, which is the same as at August 2022. Since February 2021, there was a continuous increase from 60%, quarter on quarter to 70% at August 2022. In the quarter to November 2022 this figure has remained stable
-
single-person households with no children steadily decreased from 16% at August 2021 to 13% at May 2022. After May 2022 the figure started to increase and at November 2022, it stands at 14%
-
households of couples with children has gradually decreased from 25% at February 2021 to 16% (18,000) at November 2022
-
households of couples with no children account for a negligible amount of the total capped caseload, continuously accounting for 0.1% since May 2020
Just over half of all single-parent capped households have a youngest child under the age of 5 at November 2022
Number of capped UC and HB single parent households (thousands) by age of youngest child at November 2022
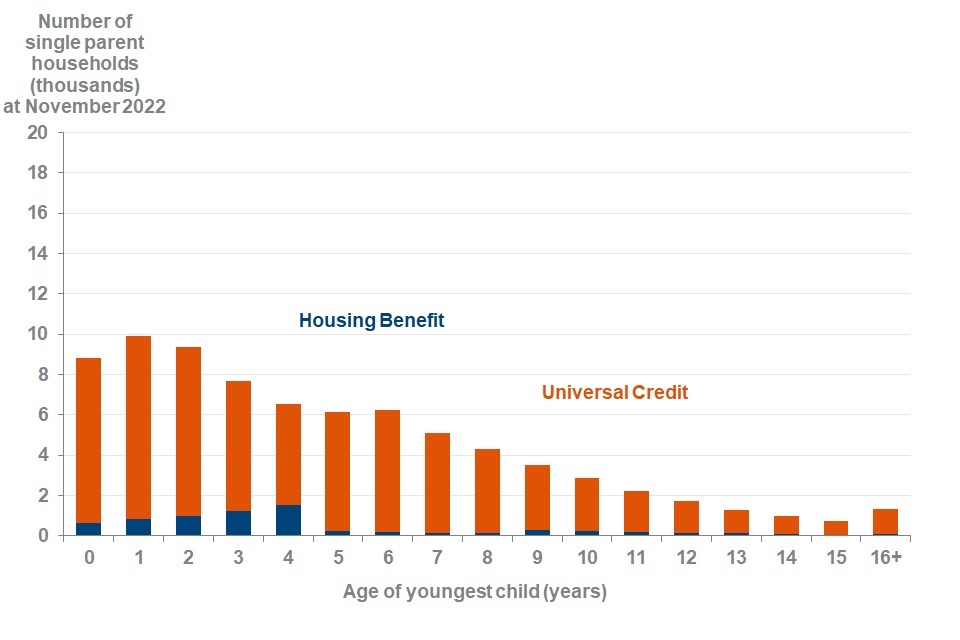
Source: DWP Universal Credit Quarterly Statistics, DWP Housing Benefit Caseload Statistics, HMRC child benefit data, Benefit Cap HB point in time caseload statistics to November 2022
At November 2022, 54% (42,000) of single-parent capped households have at least one child aged under 5 years, including 24% (19,000) with a child aged under 2 years.
Income Support (IS) is a legacy benefit which could be claimed alongside HB. When the youngest child reaches the age of 5 claimants are no longer eligible for IS on the grounds of being a lone parent and, unless they satisfy another condition of entitlement for IS, must claim UC. As the HB award will stop when the UC claim is made this may be the reason for a sudden decrease in the number of HB capped households with a youngest child aged 5 or over.
The proportion of households claiming benefits that have their benefit capped was 1.8% at November 2022, which is a decrease from 1.9% at last quarter (August 2022).
Note:
-
from June 2021 (data to February 2021) it has been possible to identify working age claimants for HB. Previously the proportion of benefit claiming households that were capped was calculated using all HB claimants. HB claimants that are of state pension age (and therefore not in scope for the benefit cap) are no longer included in this calculation so these statistics cannot be compared to prior releases. For more information, see the Background Information and Methodology document
-
the proportion capped figures have been calculated using HB and UC household figures obtained from Stat-Xplore. The total number of HB and UC capped households have been divided by the total number of households on HB and UC respectively to obtain these figures
The proportion of UC claiming households that are capped is greatest in the English Local Authorities.
Proportion of UC households capped at Local Authority level at November 2022
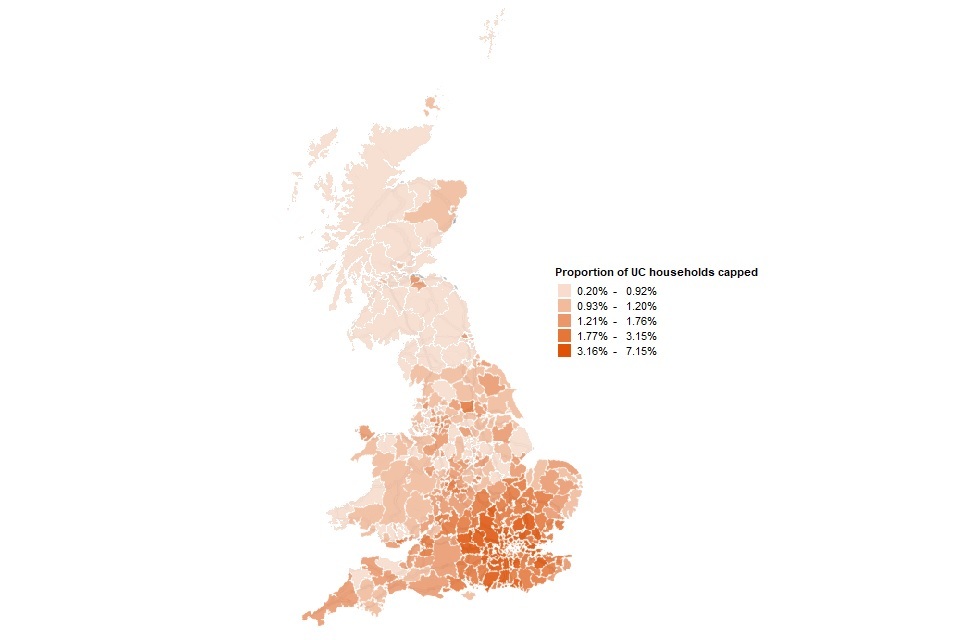
Source: DWP Universal Credit Quarterly Statistics and Benefit Cap UC point in time caseload statistics at November 2022, Stat-Xplore
Note: LAs which are shaded grey in the above maps could be due to several factors such as data being sparse and /or missing.
The proportion of households claiming UC that had their benefits capped at November 2022 was 2.1%, which is a decrease from 2.2% at the previous quarter (August 2022). The London region continues to have the highest proportion of UC households affected by the benefit cap, with 4.4% capped at November 2022, a decrease from 4.6% at August 2022.
Of the 10 Local Authorities (LAs) with the highest proportion of UC households having their benefits capped at November 2022, 6 of them are in the London region, and 4 are in the South East region. Of the 10 LAs with the highest proportion of UC households having their benefits capped, 9 were also in the top 10 LAs at August 2022, although the order is different.
At November 2022, Scotland remains the region with the lowest proportion of UC households capped at 0.8%, which is a decrease from 0.9% at August 2022.
See the number of households that had their benefits capped and Households on UC through Stat-Xplore for full data on the proportion of UC capped households using residential geographies.
The proportion of HB claiming households that are capped is greatest in English LAs
Proportion of HB households capped at Local Authority level at November 2022
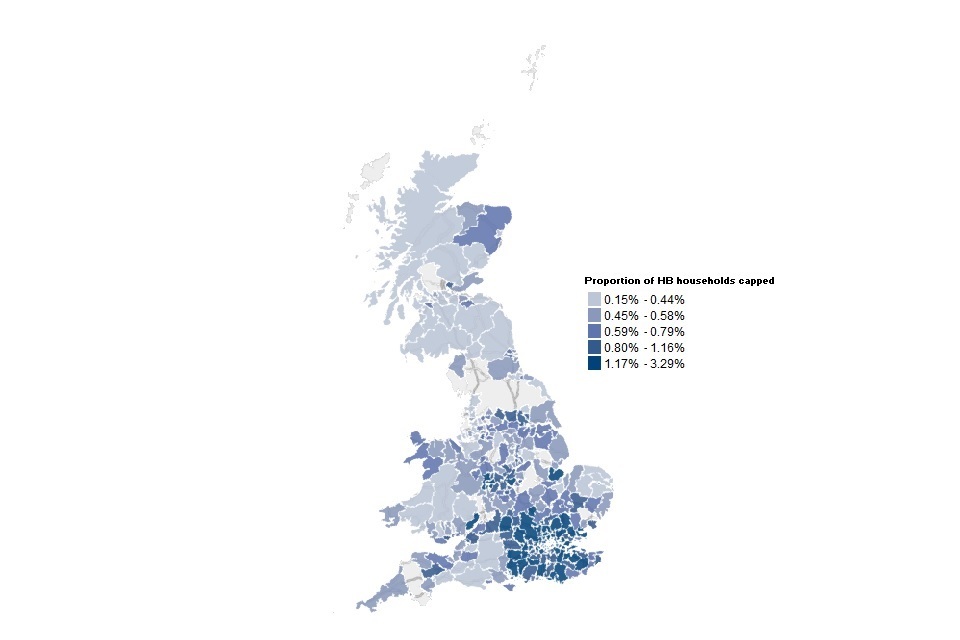
Source: DWP Housing Benefit Caseload Statistics and Benefit Cap HB point in time caseload statistics at November 2022, Stat-Xplore
Note: LAs which are shaded grey in the above maps could be due to several factors such as data being sparse and /or missing.
0.8% of households claiming HB had their benefits capped at November 2022, which is a decrease from 0.9% at last quarter (August 2022). The London and South East regions continue to have the highest proportion of HB households affected by the benefit cap, with both having 1.2% capped at November 2022, a decrease from both at 1.3% at August 2022. At November 2022, Scotland remains the region with the lowest proportion of HB households capped at 0.4%, the same proportion as at August 2022.
To see full data on the proportion of HB capped households, you can use Stat-Xplore using HB data from April 2018 and the number of households that had their benefits capped and select residential geographies and working age client type.
4. The financial impact of being capped
Households had their benefits capped by an average of £50 a week at November 2022.
The weekly average (mean) amount capped at November 2022 was £50 (when combining HB and UC) which is a decrease from last quarter when it was £51.
The average weekly amount capped for UC and HB are now at the same level at November 2022
Weekly capped amount for UC and HB households from February 2019 to November 2022
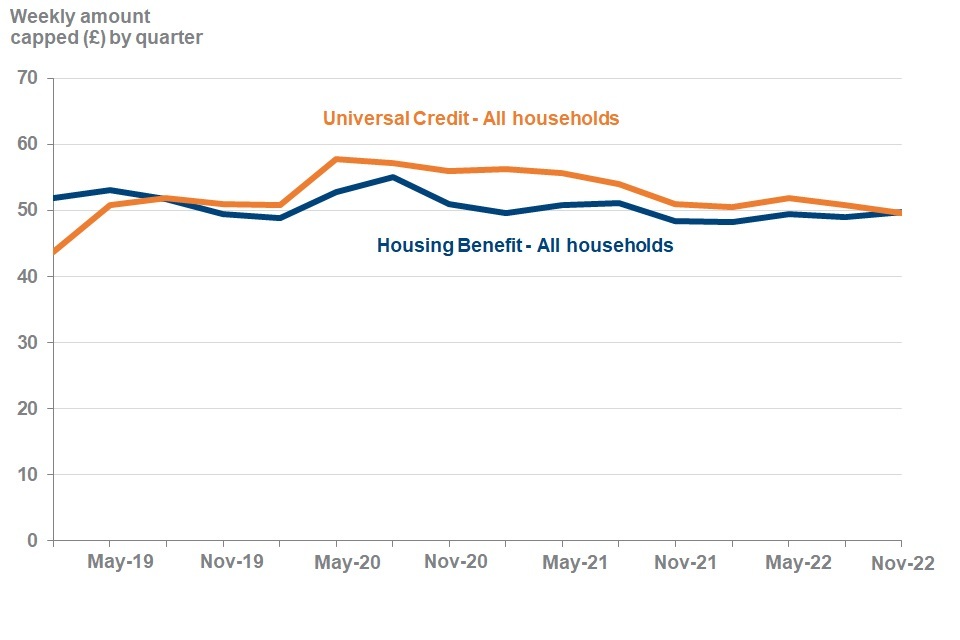
Source: DWP Universal Credit Quarterly Statistics and DWP Housing Benefit Caseload Statistics
The average monthly amount that UC households are capped by is £215 at November 2022. This is the equivalent of £50 per week. This is a decrease from £220 monthly, or £51 per week, at August 2022.
The average weekly amount that HB households are capped by is £50 at November 2022 which is £1 higher than at August 2022.
Note: UC is assessed and paid monthly and the benefit cap is applied to the full UC award. For these statistics, a weekly cap equivalent has been calculated for UC households by dividing the amount a household has been capped by in an assessment period (which lasts one month) by 4.33.
See the Background Information and Methodology document for further details.
The difference in average cap amounts across the two benefits may be affected by the differences in their caseload compositions and the different entitlement conditions across the benefits. The UC cap caseload contains a larger proportion of single people and smaller families, affecting the average amount by which households are capped.
The benefit cap is applied to the full UC award not just to housing costs. Therefore, direct comparisons of cap amounts across HB and UC should not be made.
See Stat-Xplore for full data, including by region and LA.
Proportion of UC capped households at November 2022
At November 2022:
-
63% (64,000) of households that had their UC capped were capped by the equivalent of £50 or less per week
-
24% (25,000) were capped by the equivalent of £50.01 to £100 per week
-
8% (8,000) were capped by the equivalent of £100.01 to £150 per week
-
3% (3,100) were capped by the equivalent of £150.01 to £200 per week
-
2% (1,700) were capped by the equivalent of more than £200 a week, including 0.3% (280) capped by the equivalent of more than £300 per week
See Stat-Xplore for full data.
5. Definitions
Point-in-time caseload
The number of capped households at each month.
Point-in-time datasets contain one record per household, per month capped. It is possible to identify the capped caseload at each month from these datasets. The DWP UC Quarterly Statistics are subject to revision for the latest two years. The most recent quarter of UC published data are therefore marked provisional and will be subject to revision in subsequent releases up to a period of two years. Once data are two years old, they are not refreshed in subsequent releases. However, the UC data used within the Benefit Cap publication is refreshed for the full back series. It is expected that the latest quarter’s overall provisional figures (for capped UC figures) will be around 2% of their revised figure in future releases.
Off-flows
The number of previously capped households that are no longer capped on either benefit (HB or UC).
These are true off-flows i.e. no longer capped on either benefit. However, it is possible to talk about households that are off-flows from the HB cap or off-flows from the UC cap. Where this is the case it will clearly state HB off-flows or UC off-flows, and if it is not stated then it is assumed to be a true off-flow.
On-flows
The number of households that are capped on their respective benefit (HB or UC) for the first time.
It is possible to be capped on HB and when no longer capped on HB to immediately on-flow to UC and remain capped i.e., the household is capped on UC for the first time.
Newly capped
The number of households that have their benefits capped for the very first time.
Unlike on-flows, newly capped is the first time a household is capped irrespective of the benefit (HB or UC). This means that households that on-flow to the UC cap having immediately off-flowed from the HB cap are not newly capped because they have been capped previously.
Due to limitations of the current methodology, it is not possible to identify a household that off-flows the HB cap and later (however, not immediately) on-flows to the UC cap. They would currently be counted as newly capped because they did not immediately flow from the HB cap to the UC cap.
Household
One or two adults, living together as a couple, plus any children they are living with.
This definition applies to the benefit cap policy and hence this analysis. A household may also be referred to as a ‘benefit unit’. This definition differs from the Office for National Statistics (ONS) definition that defines a household as one person alone, or a group of people (not necessarily related) living at the same address who share cooking facilities and share a living room or sitting room or dining area. A household by the ONS definition may contain multiple benefit units.
There are a small number of cases where an individual or household has more than one HB claim, for these cases, only the most recent claim is reported on.
Reporting month
For HB data, LAs extract and return their data to DWP over a four-week rolling period based on an extraction schedule for each LA. For example, “February 2020” data was typically extracted between 28 January and 21 February 2020. Each LA may extract their data up to a week before the date it is scheduled to be returned to DWP. Consequently, the statistics do not directly relate to a particular date but rather show the position of capped cases over a monthly cycle.
For UC data, a household must have an assessment period spanning the ‘count date’ for a particular month. An assessment period is the period of a month for which a UC payment is made. The count date is the second Thursday of the month. Entitlement to UC must also have been calculated.
Administrative geographies
In this release, HB data are presented using two sets of geographies:
-
administrative
-
residential
Administrative geographies represent the administrative body responsible for administering the HB and are therefore only meaningful at LA level. There are cases where the administrative LA is responsible for administering HB outside the geographical boundaries of the LA, and the responsibility for particular dwellings can also change with time.
Residential geographies
In this release, HB data are presented using two sets of geographies:
-
administrative
-
residential
Residential geographies represent the geographic boundaries of the LA area and are determined by the location of the dwelling that the HB relates to. Residential geographies can be presented using a wide range of geographies based on the postcode level of the dwelling itself, usually ranging from the output areas (OAs), which comprise a few postcodes only, up to country level. Residential geographies may change if there is a change in the geographical boundaries, and affect all the households affected by the boundary change.
6. About these statistics
Disruption to Housing Benefit data
An interruption in the supply of data from Gloucester City Council has affected Housing Benefit statistics from December 2021. Data problems are unlikely to be fixed until late into 2022 and until then HB statistics that cover Gloucester will be derived from earlier data. This means estimates for South West and Gloucester on Stat-Xplore will deteriorate in their quality and accuracy.
Housing benefit data covering the periods November 2020 to July 2021 were impacted by an interruption in the supply of data from Hackney Borough council. Hackney Borough Council have now resumed the supply of Housing Benefit data to DWP. Data from August 2021 is based on their most recent return. However, it should be noted that recovery work in Hackney is still ongoing, and therefore the statistics for the latest periods are presented as best available estimates.
Please note caveats and warnings in the accompanying ODS tables and Stat-Xplore where they appear.
More about the benefit cap
The benefit cap is applied to the combined income from benefits including:
-
UC
-
Income-based JSA
-
IS
-
Income-related ESA (except when the Support Component is in payment)
-
HB
-
CHB and CTC
-
other benefits, such as Incapacity Benefit and Bereavement Allowance
Read more about when benefits are affected by the cap and when benefits are not affected by the cap.
Release schedule
The statistics are published quarterly in March, June, September, and December and are sourced from data originally collected via administrative systems. Since November 2020 (data to August 2020), data for households capped under HB are taken from DWP HB Caseload Statistics, and data for households capped under UC are taken from DWP UC Quarterly Statistics.
Next release: 20 June 2023 (number of households capped to February 2023).
Status of these statistics
National, Official and Experimental Statistics are produced in accordance with the Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007 and the Code of Practice for Statistics (the Code).
This release contains Official and Experimental Statistics on the number of households that have had their benefits capped since the cap was introduced (in April 2013) to November 2022:
-
the HB statistics and data in this release are Official Statistics
-
the UC statistics and data in this release are Official Statistics that are Experimental. This is due to the ongoing development of the data systems that are used to support Universal Credit
The statistics are compiled following the standards of trustworthiness, quality, and public value set out within the Code.
Rounding
Volumes and amounts have been rounded as detailed below. Percentages are calculated using numbers prior to rounding and rounded to the nearest whole percentage point.
| Range | Rounded to the nearest |
|---|---|
| 0 to 1,000 | 10 |
| 1,001 to 10,000 | 100 |
| 10,001 to 100,000 | 1,000 |
| 100,001 to 1,000,000 | 10,000 |
| 1,000,001 to 10,000,000 | 100,000 |
| 10,000,001 to 100,000,000 | 1,000,000 |
Data sources
Data used to create the statistics comes from administrative databases. For these, accuracy is determined by how well the information is recorded and transmitted.
HB Data
HB capped household data are sourced from the DWP HB Caseload Statistics. Read more about HB Caseload Statistics (including their methodology).
The HB Caseload Statistics data source is the DWP 100% Single Housing Benefit Extract (SHBE). SHBE is a monthly electronic scan of claimant level data direct from LA computer systems. SHBE includes a field that contains the weekly amount that the HB of a household has been capped by. This marker is central to the production of the statistics on households that have had their HB capped.
HB Caseload Statistics are merged with 100% DWP benefit scans to give data on the types of benefits claimed by capped households, and with His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs (HMRC) CHB data, to give information on the number of children and the age of the youngest child dependant in a capped household. HB caseload statistics are merged with Working Tax Credit data and 100% DWP benefit scans to provide information on the outcomes of households that have off-flowed from the benefit cap.
Data on those households that have ever had their HB capped that are no longer capped is linked to HMRC and DWP benefits data to determine why households are no longer capped.
UC Data
UC capped household data are sourced from the UC Quarterly Statistics. Read more about UC Quarterly Statistics (including their methodology).
The UC Quarterly Statistics data source is the DWP UC Official Statistics database, which is compiled using data from systems within local offices and records of UC benefit payments made by the DWP. This database includes a field that contains the amount of UC that a household has been capped by for an assessment period, which is used in the production of these statistics.
Data are merged with the DWP Customer Information System address file so that the number of households that have had their UC capped can be broken down by region and LA.
Data on households that have had their UC capped are matched with the full DWP UC Official Statistics database to obtain information on earnings, which is used to determine which households moved off the cap under UC after becoming exempt due to their earnings.
UC data are returned on a particular count date each month. Statistics on households capped under UC do not include figures for those capped at the start of the UC roll out. The initial, largely clerical payment system, UC Live Service (UCLS), was gradually replaced by the current digital system, UC Full Service (UCFS). Since March 2019 UCLS ceased to be operational and all UC awards have been delivered via the current service. Due to data quality and reporting it is not possible to produce robust experimental statistics on the number of households that were capped under UCLS.
Note: UC statistics throughout this release refer to UCFS only. This is especially important to remember when looking at time series data.
Figures relating to households with their UC capped are subject to retrospection. All figures in these statistics have been updated as at November 2022. For more information, see the Background Information and Methodology document. The timeseries detailing weekly cap amount does not include retrospection.
User engagement and consultation
As set out in the UC statistics release strategy, the statistics in this publication include:
-
the number of households that are currently capped, or have ever been capped, as well as those newly capped
-
the proportion of HB and UC claimants that have their benefit capped at the Local Authority (LA) level
-
the benefit make-up of HB capped households
-
average amount of benefits that households are capped by (in £)
-
the number of households that are no longer capped (off-flows), as well as a range of outcomes at off-flow for HB capped households – including those that move from HB to UC and remain capped, and the proportion of off-flows from the UC cap that are due to earnings
There are also plans to further develop the set of UC statistics, in particular outcomes at off-flow.
Following user engagement, information on the households capped due to the current lower, tiered cap levels are no longer included in these statistics. If users have any queries or feedback, contact the statistics team.
From the September 2021 release (data to May 2021) of these statistics, data that was previously provided to users in both Stat-Xplore and the accompanying ODS tables were only available on Stat-Xplore.
The DWP have provided new measures in the UC Quarterly Statistics, which is the source data for UC capped households. The new measures are:
-
number of children in UC households
-
age of the youngest child in UC households
Statistics on both of these measures are presented in this release and were previously obtained by merging with HMRC CHB scans. Now, the source data for UC capped households will provide these measures, for UC only. This means that the methodology of merging two administrative data sources can be replaced by a single data source, giving improved coherence throughout the Benefit Cap Statistics. The methodology of obtaining these measures for HB remain unchanged.
Where to find out more
Use Stat-Xplore to create your own tables and further breakdowns of these statistics.
View national and regional figures in an interactive visualisation.
Read older releases of these statistics.
Read Background Information about these statistics.
Read statistics for households who have their benefits capped in Northern Ireland.
Read statistics on HB caseload.
Read statistics on UC.
Read statistics on Local Authorities’ use of Discretionary Housing Payment funds.
Read more information on the benefit cap.
7. User Engagement
Contact us for statistical enquiries and publication feedback only please.
Producer: Michael Hatton
Lead Statistician: James Gray
DWP Press Office: 0115 965 8781
ISBN: 978-1-78659-500-3
