Manufacture and supply of medicated feedingstuffs
For manufacturers and distributors of intermediate and final feedingstuffs containing a medicinal premix or specified feed additives in Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
Medicated Feed Manufacture in Northern Ireland
Regulation (EU) 2019/4 applies in respect to medicated feed manufacture in Northern Ireland. The different types of medicated feed authorisation and associated fees can be found in Schedule 7 of The Veterinary Medicines Regulations 2013.
Medicated Feed Manufacture in Great Britain
This guidance should be read together with Schedule 5 of the Veterinary Medicines Regulations (VMR).
This relates to feedingstuffs containing a veterinary medicine authorised for incorporation into medicated feedingstuffs, known as a medicinal premix, and feedingstuffs containing specified feed additives (SFAs) regulated under Schedule 5 of the VMR.
There are a number of different authorisations for feed businesses and they are split into different categories depending on the activity carried out at the establishment (premises). These are:
| Category | Activity Description |
|---|---|
| S | Manufacturer of a specified feed additive (SFA) |
| I | Manufacturer of an intermediate feedingstuff, including balancers, containing a medicinal premix and/or an SFA |
| C | Manufacturer of a feedingstuff for sale containing: a medicinal premix and/or an SFA, and/or an intermediate feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix and/or an SFA |
| F | Manufacturer of a feedingstuff for feeding to their own animals only, containing: a medicinal premix and/or an SFA incorporated at a rate of at least 2kg/t, and/or an intermediate feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix and/or an SFA incorporated at a rate of at least 2kg/t |
| D | Distributor or trader of Schedule 5 products. A distributor of specified feed additives, or intermediate feedingstuffs containing a specified feed additive and/or a medicinal premix; or feedingstuffs containing a medicinal premix |
Authorisation requirements for manufacturers of Schedule 5 products
A Feed Business Operator (FeBO) that manufactures and supplies the following products must be authorised and comply with Schedule 5 of the VMR:
- specified feed additives (SFAs)
- intermediate feedingstuffs containing an SFA and/or a medicinal premix
- complementary feedingstuffs containing an SFA
These are collectively known as Schedule 5 products.
Authorised FeBOs are inspected regularly and must meet strict inspection criteria. Information on the requirements for authorisation can be found in the application form and the Hazard Analysis and Critical Controls Points (HACCP) guidance which are available on the Apply for animal feedingstuffs authorisation (medicated feed) page.
To check if a feedingstuffs manufacturer or distributor is authorised, check the Register of authorised premises.
The inspection frequency is risk based and depends on the nature of the products the FeBO manufactures and its compliance with the VMR.
FeBOs that manufacture Schedule 5 products for feeding to their own animals on their own holdings must also comply with these requirements. However, those that only manufacture complete feedingstuffs using complementary feedingstuffs that contain SFAs must be registered rather than authorised.
Designated Persons
You are required to name a person responsible for production: Designated Person for Feedingstuffs - Production (DPFP). You may also require a responsible person for Quality Control: Designated Person for Feedingstuffs Quality (DPFQ). These should be different people but in a small business where this is not practical it can be the same person. The DPFQ may be someone outside the business, for example your nutritional adviser.
Any person capable of competently performing the following duties can be a DPFP or DPFQ. Specific qualifications are not required.
Designated Person for Feedingstuffs Production
A DPFP is responsible for:
- the written procedures and instructions that define, check and monitor the critical points in the manufacturing process
- ensuring that measures are taken to avoid or minimise, any cross-contamination and errors
- ensuring appropriate control strategies are put in place to minimise risk
- ensuring that waste and materials not suitable as feed are isolated, identified and disposed of in the correct way so they are not used as feed
- following the quality control plan, referred to below
- ensuring adequate measures are taken to ensure effective tracing of the products
Designated Person for Feedingstuffs Quality
A DPFQ is responsible for ensuring that they use a laboratory with adequate staff and equipment as part of a quality control system. They must also write up and implement a quality control plan. This should include:
- checks on the critical points in the manufacturing process
- monitoring the presence of micro-organisms, prohibited feed, undesirable substances and other contaminants in relation to human or animal health
- a description of the tests that need to be carried out and their frequencies. As a minimum the tests should include:
- an annual mixer dispersion test
- routine tests on the amount of active substance of the SFA or medicinal premix in the finished product
- testing for carryover of active substances into non-target products and any root-cause analysis in response to that testing
- how analysed results are compared against product specifications - what action is taken for compliant and non-compliant samples
- the destination of feed materials or finished products in the event of non-compliance
Record keeping
The DPFQ must keep records to enable traceability of feed materials (ingredients) from intake through to the manufacture and supply of final products.
They must ensure records are available to the competent authorities for at least 5 years.
Samples
Samples of sufficient quantities of feed materials and of each batch of products manufactured and placed on the market must be taken and kept for an appropriate period. This is at least until the shelf life of the manufactured product has passed.
If the production is continuous then samples should be taken during each part of production using a pre-established procedure in order to ensure traceability.
Retained samples must be sealed and labelled for easy identification and stored appropriately to maintain the sample’s integrity. Only samples of the finished product need to be kept of feedingstuffs for non-food producing animals. Samples should be made available to an inspector on request.
Samples for cross-contamination
A feed business operator must take samples of feedingstuffs to analyse and determine whether cross-contamination into non-target feed has occurred.
If more than 1%, but less than 3%, of the authorised maximum content of an active ingredient is found in a non-target feed, the feed business operator must make a record of this cross-contamination.
If 3% or more of the authorised maximum content of an active ingredient is found in a non-target feed, the feed business operator must also conduct a root-cause analysis in order to discover the cause of the cross-contamination and make a record of any conclusions.
The feed business operator must keep these records for at least five years.
Exemption from authorisation
The following are exemptions from the requirement to be authorised under Schedule 5 of the VMR:
-
(1.) a person who incorporates a medicinal premix into feedingstuffs on domestic premises for feeding on those premises to:
- non-food producing animals
- food producing animals kept purely for domestic purposes, including consumption by the keeper of those animals.
The supply of animals or animal products to third parties, which includes farm gate sales of eggs, milk and meat, is not considered as domestic purposes and the exemption from authorisation does not apply.
- (2.) a person who incorporates a medicinal premix into feedingstuffs for ornamental fish not intended for human consumption, providing that person does not use more than a total of 1kg of VMP annually for that purpose.
In these instances a prescription is still required in order to obtain the medicinal premix. Under the exemption, the prescription can be either oral or in writing. However, if the prescription is not in writing, the medicinal premix may only be supplied by the person who prescribed it and appropriate advice on safe use must be given.
These exemptions allow a vet, pharmacist or appropriately registered Suitably Qualified Person (SQP) to supply an intermediate feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix, or a feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix to domestic keepers of animals. All other VMR requirements for advice and record keeping apply to the feedingstuff as if it was the veterinary medicine.
An SQP cannot use an exemption to supply any intermediate feedingstuffs or feedingstuffs containing Prescription Only Medicine – Veterinarian (POM-V) medicines.
Authorisation Inspection
An inspection of the proposed manufacturing premises will be arranged following receipt of a valid application.
The inspector will check:
- facilities and equipment are suitable for the proposed operation
- appropriate record keeping plans are in place, particularly relating to medicated feedingstuffs prescriptions (MFSps) and traceability, including batch numbers. Further information can be found on the Record keeping requirements for veterinary medicines page.
- hygiene standards
- secure storage arrangements for Schedule 5 products
- documentation relating to procedures and controls, including a Quality Control plan and a HACCP plan
The authorisation may be refused if the premises, equipment or procedures do not meet the required standards. In this case, the inspector will explain the reasons why and the measures that must be taken to obtain authorisation. A FeBO can appeal this decision, more information can be found on the Appeal against a regulatory decision made by the VMD page.
Registration
Requirement for manufacturers of complete feedingstuffs using complementary feedingstuffs containing SFAs for the exclusive requirements of their own holdings.
FeBOs that only want to manufacture complete feedingstuffs using complementary feedingstuffs containing SFAs for the exclusive requirements of their own holdings must be registered rather than authorised. These feed business operators must meet the applicable criteria set out in Annex II of Regulation EC/183/2005, with the exception of HACCP. These are not subject to an inspection prior to registration.
Commercial FeBOs manufacturing these products still need to be authorised.
What a Registration Inspection covers
Although these FeBOs are not subject to an inspection prior to registration, they will still be subject to regular inspections. The aim is to check that the premises, equipment and procedures are capable of producing Schedule 5 products to the required standard.
Requirements for authorised Distributors of Schedule 5 products
An authorised Distributor is a FeBO who is authorised to store, supply, wrap and/or package;
- SFAs
- intermediate feedingstuffs containing an SFAs and/or a medicinal premix
- complementary feedingstuffs containing an SFA
- feedingstuffs containing a medicinal premix
However, they may not retail supply veterinary medicines, including medicinal premixes.
There is no requirement for authorisation to store or supply complete feedingstuffs containing SFAs.
Distributors of Schedule 5 products must meet the criteria set out in the Distributor’s application form.
Distributors who do not take physical hold of the products on their premises must still be authorised.
They can choose to have either an on-site inspection or a remote inspection. The inspection will cover the same requirements no matter which option is chosen. This is to ensure that the distributor is complying with the applicable areas of the VMR.
Authorisation as a feedingstuffs’ manufacturer, other than category F manufacturers, permits the supply of that manufacturer’s own product, but not those manufactured by third parties. They would also need to be authorised as a distributor to do this. Where businesses with more than one authorisation are inspected at the same time, the highest inspection fee is payable plus 50% of all other inspection fees (Schedule 7, para 4 of the VMR).
A toll manufacturer is a manufacturer who provides a manufacturing service on behalf of another, to that manufacturer’s specific request to a specific specification and formulation. This is contract manufacturing. Only toll manufacturers are permitted to supply another manufacturer in this way without being authorised as an authorised distributor.
Apply for Authorisation or Registration
Details of how to apply can be found on the Apply for animal feedingstuffs authorisation (medicated feed) page.
Details of the fees involved can be found on the Fees relating to Feedingstuffs.
Labelling of Schedule 5 products
All Schedule 5 products placed on the market must be labelled in accordance with paragraphs 12-14 of the VMR.
For feedingstuffs containing a SFA the labelling requirements are detailed in article 15 and 17 of Regulation EC/767/2009.
Labels must be clear, legible and indelible and be written in English. They may also contain other languages but the information in each language must be the same.
Where more than one SFA or medicinal premix is incorporated into a feedingstuff the shortest in-feed shelf life must be shown on the label.
If there is no medicated feedingstuffs prescription at the time of labelling, the withdrawal period must be that specified in the medicinal premix’s summary of product characteristics (SPC). If there is more than one medicinal premix the longest withdrawal period must be used. The label must also state “If the prescription requires a longer withdrawal period that is the one that applies”.
The label must include the batch number.
Labelling requirements for SFAs, intermediate feedingstuffs containing SFAs and complementary feedingstuffs containing SFAs are detailed in article 16 of Regulation EC/1831/2003.
For a product manufactured by a toll manufacturer, the establishment authorised number of the toll manufacturer and the name and address of the receiving manufacturer must appear on the label.
The label must state in capital letters whether it is an “INTERMEDIATE FEEDINGSTUFF”, a “MEDICATED COMPLEMENTARY FEEDINGSTUFFS”, or a “MEDICATED COMPLETE FEED”.
Medicated Feedingstuffs prescriptions
Information on Medicated Feedingstuffs prescriptions (MFSps) can be found in paragraphs 19 and 20 of Schedule 5 of the VMR.
An MFSp must include:
- the name and address of the person prescribing the product
- the qualifications enabling the person to prescribe the product
- the name and address of the keeper of the animals to be treated
- the species of animal, identification and number of the animals
- the premises at which the animals are kept if this is different from the address of the keeper
- the diagnosed disease to be treated, or, if an immunological or antiparasitic without antimicrobial effect, prevented
- the date of the prescription
- the signature or other authentication of the person prescribing the product
- the name, the active substance, the amount of the product prescribed and the inclusion rate of the medicinal premix and resulting inclusion rate of the active substance
- the dosage and administration instructions
- any necessary warnings
- a statement that the prescription may not be re-used
- the withdrawal period
- the manufacturer or the distributor of the feedingstuffs; who must be authorised for the purpose, whichever is the supplier to the end user
- if the validity exceeds one month, a statement that not more than 31 days’ supply may be provided at any time
- the name, type and quantity of feedingstuffs to be used
- the overall amount of feedingstuff to be supplied under the prescription
- any special instructions
- the percentage of the prescribed feedingstuffs to be added to the daily ration
- if it is prescribed under the cascade, a statement to that effect
Medicated feedingstuff prescription
Only a vet may prescribe the manufacture of a feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix classified as POM-V, and the MFSp must be in writing.
A vet providing an MFSp for a feed containing a POM-V premix must ensure that:
- a clinical assessment has been made of the animals that are to be treated, and the animals are under the vet’s care. The RCVS provides guidelines on what constitutes ‘under a vet’s care’.
- all the required details on the MFSp are filled out accurately
- the quantity of medication prescribed does not exceed that required for a single course of treatment
- careful consideration is taken regarding the appropriateness of prescribing antimicrobial medicines and reduce the unnecessary risk of resistance
The vet may discuss a MFSp with a feed mill but should only accept a request for a MFSp from a mill if they believe there is an actual need for an MFSp. Feed mills must not make unsolicited approaches to vets with a draft MFSp for their approval.
If an animal keeper approaches a FeBO without an MFSp when one is required they should be told that it cannot be supplied and they need to contact their vet.
In the case of an anthelmintic, wormer, classified as Prescription Only Medicine - Veterinarian, Pharmacist, Suitably Qualified Person (POM-VPS), the MFSp may be written by a vet, pharmacist or Suitably Qualified Person (SQP). The following paragraphs refer to the prescribing of medicated feedingstuffs by vets, but the same requirements apply to pharmacists and SQPs prescribing feedingstuffs containing a POM-VPS anthelmintic.
An MFSp must be written, in ink or other indelible format, or it may be produced and sent electronically or by fax.
An MFSp for a medicated feed used via a medicated intermediate feedingstuff requires extra details. The MFSp must include clear instructions regarding:
- the inclusion rate of the VMP into the intermediate feedingstuff
- the subsequent range of acceptable inclusion rate of the intermediate feedingstuff into the final feedingstuffs
- the range of acceptable levels of the active ingredients in the final feedingstuffs
The words “refer to the prescription for the exact inclusion rate” or equivalent wording should also appear.
The MFSp must be signed by the vet. A per pro signature is not acceptable. The vet must check that the MFSp has been completed correctly before authorising its issue.
A MFSp is valid from the date the vet signs it. An MFSp is valid for three months, or a shorter period if specified by the vet in the MFSp, except where the prescription is for a feed containing an antibiotic.
For an MFSp for a feed containing antibiotics, the time between a prescription being issued and the course of treatment starting must be no more than five working days. This means the medicated feedingstuffs prescription can be valid for up to three months, but the initial treatment must start within the five working days.
An MFSp for medicated feedingstuffs containing an antibiotic must not be written for prophylactic purposes, unless it complies with the requirements under Schedule 3, paragraph 7A.
Guidance on prescribing antibiotic veterinary medicines can be found under Retail of veterinary medicines.
In relation to food-producing animals a MFSp may not confer authority for more than one course of treatment.
The vet must only prescribe enough medicated feed for one course of treatment. The quantities must be within the maximum limits laid down in the SPC.
When two medicinal premixes are being incorporated into the same feedingstuff, the vet may write one MFSp, provided that:
- the medicinal premixes are being mixed into the same final feedingstuff
- the MFSp clearly states that when the two products are incorporated into the feedingstuff the longest withdrawal period applies
If a medicated feed also contains an SFA there is no legal requirement for the vet to include details of that SFA on the MFSp.
Supply relating to an MFSp
It is the responsibility of the feed manufacturer or distributor to comply strictly with the terms of the MFSp. Where treatment lasts more than three months the vet, or in the case of an anthelmintic, the vet, pharmacist or SQP, must issue a new MFSp at three months.
A vet may only supply a medicinal premix to a feedingstuffs manufacturer authorised to use it. Exemptions for animals on domestic premises under paragraph 30 of Schedule 5 to the VMR are covered in the exemption from approval section of this guidance.
Medicated feedingstuffs containing a POM-V medicinal premix can only be supplied to the keeper of animals on receipt of a written MFSp issued by a vet. However, they may be supplied to an authorised distributor without an MFSp.
If the MFSp validity lasts longer than one month, the keeper of animals may only be supplied with enough medicinal premix, or intermediate feedingstuffs containing a medicinal premix, to cover 31 days at a time, up to the maximum amount specified in the MFSp.
A list of authorised premises can be found on the Register of approved premises page.
Record keeping relating to MFSp
An MFSp, including one produced electronically, must be kept for five years from the date the prescribing vet signed it.
An MFSp must be available immediately on request by an authorised inspector.
It’s the responsibility of the FeBO supplying a medicated feedingstuff to a farmer to keep the original MFSp. If the feedingstuffs manufacturer supplies the medicated feedingstuff to an authorised distributor, there’s no legal requirement for the manufacturer to keep a copy of the MFSp. However, it is advisable for the manufacturer to ask for the feed order in writing or for a photocopy/fax of the MFSp to ensure that the correct feed is manufactured and supplied.
Manufacture of Medicated Feed subject to an MFSp
The MFSp must be strictly followed. If the quantity of medicated feed ordered exceeds the quantity prescribed, the feed supplier should advise the customer to discuss this with their vet. If the vet decides to increase the amount of feed prescribed they should instruct the feed manufacturer to amend their copy of the MFSp. This should be clearly recorded by the feed manufacturer. If the MFSp is not changed the manufacturer must not supply more than the amount stated.
It is an offence under the VMR to alter an MFSp without authorisation from the prescribing vet.
A feedingstuff containing a medicinal premix may be prepared in anticipation of an MFSp. However, it cannot be supplied until the manufacturer receives a valid MFSp authorising the supply of that product to the specified person.
A medicinal premix which is authorised for incorporation into feedingstuff must be thoroughly mixed into the feedingstuff. Top dressing is only permitted where the product specifies this form of administration. In the absence of a suitable authorised product, a vet may wish to prescribe the product for off-label use under the cascade. It is the vet’s responsibility to ensure the correct dose is delivered and withdrawal period applied.
Withdrawal periods for medicinal premixes prescribed under the Cascade
Information on the withdrawal periods for a medicinal premix prescribed under the cascade can be found in Schedule 4, paragraph 2 of the VMR.
Where more than one medicinal premix is prescribed and all are used according to their SPCs then the longest withdrawal period applies.
Where more than one medicinal premix is prescribed and one or more are used outside the terms and conditions of the SPC, then the statutory withdrawal periods set out in the VMR apply.
Importation of Feedingstuffs
For information on the importation of feedingstuffs containing a medicinal premix refer to Schedule 5 paragraphs 28 and 29 of the VMR.
You cannot bring a feedingstuff containing a veterinary medicine from another country into the GB unless it only contains a veterinary medicine that has the same quantitative and qualitative composition as a medicinal premix authorised in GB.
A manufacturer of intermediate feedingstuffs or feedingstuffs can import a veterinary medicine authorised in another country for the purposes of incorporating it into intermediate feedingstuffs or feedingstuffs for export.
They cannot place that intermediate feedingstuff or feedingstuff on the market in GB once the veterinary medicine has been incorporated into it.
For information on the importation of feed additives and feedingstuffs containing them refer to The Food Standards Agency.
Export of unauthorised substances or feed containing them
FeBOs must notify us if they are exporting or re-exporting unauthorised medicinal substances intended for feed, unauthorised SFAs, or feed containing them to another country, either directly or indirectly. This also applies to re-export of imported substances and when the unauthorised substance is incorporated into an intermediate feedingstuffs for export.
This notification must include all the details of the substances being exported and details of the final destination. FeBOs must have the express consent from the final destination country prior to the export. If an alternative proof of authorisation of the substance is available then this will be acceptable. This should be retained for inspection by our inspectors.
Possession
It is an offence to possess a medicinal premix, or any product regulated under Schedule 5 except in accordance with the VMR.
Inspectors appointed under the VMR may seize any medicinal premix, or Schedule 5 product if:
- it has not been lawfully manufactured, incorporated or supplied in accordance with the Regulations
- it has been stored in a way that affects its safety, quality or efficacy
- it is sold or offered for sale by a person not permitted to supply it under these Regulations
For more details on the seizure of products and appeals please refer to the Enforcement policy for animal medicines.
Requirements for animal keepers
An animal keeper must ensure that feedingstuffs supplied under Schedule 5 of the VMR are stored appropriately, in accordance with the requirements under the medicinal premix SPC.
They must ensure that:
- no cross-contamination occurs between feedingstuffs
- feedingstuffs or feed material is not contaminated by other products
- no product escapes into the environment
- feedingstuffs are fed only to the animals to which they have been prescribed
- they comply with any withdrawal periods required under the product SPC or the MFSp
It is an offence to feed a medicated feedingstuffs which has passed its expiry date to an animal.
Non-compliance
Where an inspector identifies a non-compliance, that is a deficiency, with the VMR in the FeBO’s operations, they will deal with the deficiency in accordance with the VMD’s Enforcement Policy.
A FeBO served an Improvement Notice must take the appropriate remedial action within the specified timescale. Failure to comply is an offence that could lead to formal action being taken, including suspension or revocation of the FeBO authorisation and prosecution.
If an Improvement Notice is served, we will charge the person on whom the Notice was served, the full economic cost of any subsequent inspection necessary to check that it has been complied with.
Disposal of feed products
The Environment Agency is responsible for the legislation relating to disposal of feed products for England, Natural Resources Wales for Wales, and the Scottish Environmental Protection Agency is responsible in Scotland. Guidance is available on the Environment agency, Natural Resources Wales and Scottish Environment Protection Agency websites.
Additionally, local Waste Regulation Authorities can advise on the safe disposal of any unused product and empty containers. It is essential that any disposal be dealt with in accordance with the environmental legislation.
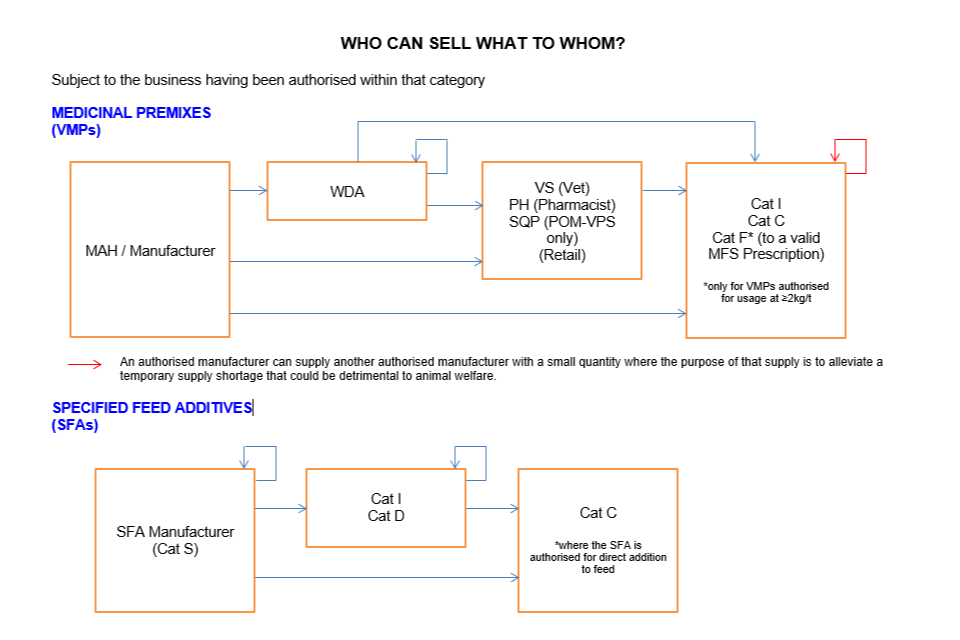
Who can sell what to whom
Subject to the business having been authorised within that category:
In feed medicinal premix
MAH/manufacturer can sell to:
- WDA holder
- VS (Vet) (Retail)
- PH (Pharmacist) or SQP (POM-VPS only) (Retail)
- Cat I
- Cat C
- Cat F* (to a valid MFSp)
*only for VMPs medicinal premixes authorised for usage at ≥2kg/t
WDA holder can sell to:
- Another WDA holder
- VS (Vet) (Retail)
- PH (Pharmacist) or SQP (POM-VPS only) (Retail)
- Cat I
- Cat C
- Cat C*
- Cat F* (to a valid MFSp)
*only for medicinal premixes authorised for usage at ≥2kg/t
VS (Vet), PH (Pharmacist), SQP (POM-VPS only) (Retail) can sell to:
- Cat I
- Cat C
- Cat F* (to a valid MFSp)
*only for medicinal premixes authorised for usage at ≥2kg/t
The only exemption to the above is that an authorised manufacturer can supply a small quantity to another authorised manufacturer where the purpose of that supply is to alleviate a temporary supply shortage that could be detrimental to animal welfare.
Specified Feed Additives (SFAs)
SFA Manufacturer (Cat S) can sell to:
- Cat I
- Cat D
- Cat C*
*where the SFA is authorised for direct addition to feed
Cat I and Cat D can sell to:
- Cat C*
*where the SFA is authorised for direct addition to feed
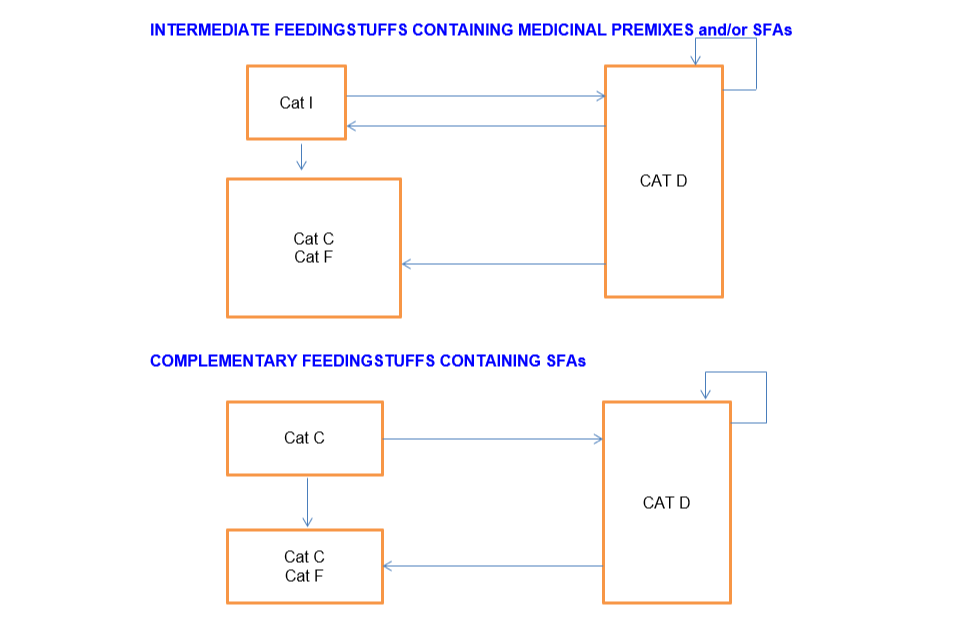
Intermediate feedingstuffs containing medicinal premix and/or SFAs
Cat I can sell to:
- Cat C
- Cat F
- Cat D
Distributor (Cat D) can sell to:
- Cat I
- Cat C
- Cat F
- Another Cat D
Complementary feeding stuffs containing SFAs
Cat C can sell to:
- Another Cat C
- Cat F
- Cat D
Cat D can sell to:
- Another Cat D
- Cat C
- Cat F
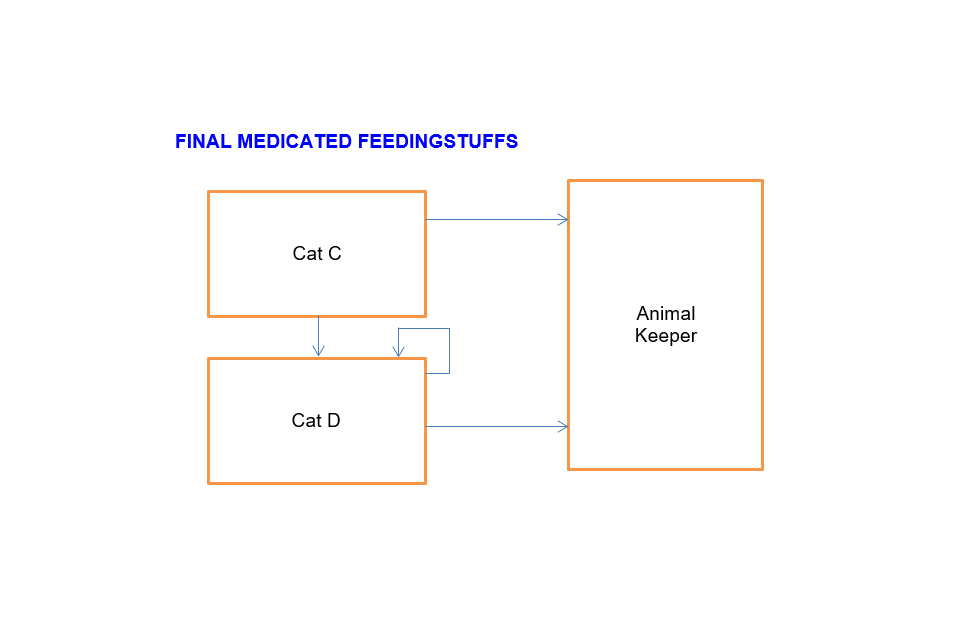
Final medicated feeding stuffs
Cat C can sell to:
- Animal keeper
- Cat D
Cat D can sell to:
- Another Cat D
- Animal keeper
Inspection of Feed Business Operators
We inspect authorised FeBOs to ensure they comply with the VMR.
Inspections are carried out on a risk basis; the higher the risk the more frequent the inspections. FeBOs are inspected at least every four years. We will generally give a FeBO reasonable notice that they intend carrying out a routine inspection.
The Inspection Criteria is available from our Inspections Administration Team inspections@vmd.gov.uk and will be sent to a FeBO when it’s notified of an inspection.
Inspectors are authorised under the VMR to:
- inspect the premises, organisational arrangements and procedures used in the storage and distribution of Schedule 5 products
- interview key personnel named on the authorisation
- take samples
- examine any documentation or records relating to the manufacture, assembly, storage and distribution of Schedule 5 products
Following an inspection, the inspector will give the FeBO a report detailing any deficiencies, also referred to as non-compliances. For major and critical deficiencies, the inspector will request details of the measures that have been, or will be taken to correct them.
We categorises deficiencies as critical, major and other (minor).
Minor (Other) Deficiencies:
- minor and poses no potential risk to human or animal health, or the environment
- does not indicate a significant deviation from the requirements of the VMR or Guidance
- cannot be classified as either critical or major because there is insufficient information to classify it as such
Major Deficiencies:
- non-critical but has produced, or has the potential to produce, a possible risk to human or animal health or the environment
- a major deviation from the requirements of the VMR
- a failure to carry out satisfactory procedures to ensure that products are manufactured, stored or distributed in accordance with their specific requirements
- a combination of more than six other (minor) deficiencies, none of which on their own may be major, but which may together represent a major deficiency and should be explained and reported as such
- other (minor) deficiencies that have been brought to the attention of the business on previous occasions but have not been resolved
Critical Deficiencies:
- deficiencies that have produced, or have the potential to produce, a significant risk to human or animal health, or the environment
- a significant deviation from the requirements of the VMR through serious negligence or intent
Inspections are scheduled at intervals based on the number and type of deficiencies noted during an inspection, as follows:
| Inspection findings | Compliance category | Inspection Points* | Max inspection interval (months) S, I | Max inspection interval (months) C | Max inspection interval (months) F, D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 deficiencies; recommendations only | 5 | 0 | 24 | 24 | 48 |
| 1-6 minor (other) | 4 | 1-6 | 24 | 24 | 48 |
| More than 6 minors and / or 1-3 Majors | 3 | 7-21 | 18 | 18 | 36 |
| 3 Majors plus 1 or more minors up to and including 5 Majors | 2 | 22-35 | 12 | 12 | 24 |
| More than 5 Majors and / or any Critical | 1 | 36 and over | Follow up inspection as specified on Improvement Notice, then next inspection in 9 to 12 months | Follow up inspection as specified on Improvement Notice, then next inspection in 9 to 12 months | Follow up inspection as specified on Improvement Notice, then next inspection in 9 to 12 months |
*A minor deficiency = 1 point, a Major deficiency = 7 points and a Critical deficiency = 36 points
Enforcement
For the most serious deficiencies or failure to comply with the VMR, we may take formal action in accordance with our Enforcement Policy.
If we decide to suspend or revoke an authorisation, retailers have the right to appeal against that decision.
Contact
Enquiries should be sent to postmaster@vmd.gov.uk, in the title quote “medicated feedingstuffs”.
Updates to this page
-
Guidance updated to allow all those with an interest in the supply of veterinary medicines in Northern Ireland to prepare for the requirements under EU veterinary medicine regulations that will come into effect in Northern Ireland on 1 January 2026.
-
Updated to reflect changes to the VMR.
-
Reviewed and amended; minor changes include term 'Qualified Person' to 'Designated Person'
-
Guidence reviewed and updated with changes to deficiencies rankings
-
Details added regarding the inspection of Feed Business Operators
-
First published.