Factsheet 6: 5G
Published 24 November 2020
What is 5G?
5G is the 5th generation of mobile technology, following on from 4G (i.e. the 4th generation). In the same way that mobile phone technology develops with each new handset that is introduced, the same is true for the technology and equipment that forms the telecoms network. Once fully incorporated, 5G networks will provide speeds up to 20 times faster than 4G, will be more reliable and will be able to deliver new technical capabilities.
| Date | Generation | Speed | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990s | 2G | 0.006 Mb/s (64 Kb/s) | Voice communication and text capability |
| 2000s | 3G | 2 Mb/s | Voice communication, text, internet and location services |
| 2010s | 4G | 100 Mb/s | Higher speed internet, HD quality video, cloud technology and truly mobile broadband |
| 2020s | 5G | > 1000 Mb/s (1 Gb/s) | Faster data, ultra HD and 3D video, Smart Home, low-latency responsiveness and the ‘Internet of Things’ |
The UK is one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world, and 5G is the natural next step in progressing our society’s digital journey. The increased connectivity and capacity offered by 5G is opening up the potential for new, innovative services for individuals and industry. Already through 5G trials, we can see its potential value to manufacturing, farming, transport networks and healthcare.
Why do we need 5G?
The UK is committed to developing its 5G capabilities and shaping the future of its development. This is part of delivering leading digital infrastructure for the UK, enabling all regions to take advantage of the many opportunities of the digital economy. Now more than ever, digital connectivity is vital to enable people to stay connected and businesses to grow.
5G has the potential to support innovative new services like autonomous vehicles and smart cities, and increase efficiency through smart agriculture, factory robotics and healthcare applications such as remote surgery. It will bring down latency levels reducing delays on video calls. And it will underpin other advances in cutting-edge technologies such as Virtual and Augmented Reality, which will provide an economic benefit through the entertainment sector.
The following diagram features a selection of key uses of 5G technology arranged in a triangular diagram and arranged into three groups. Enhanced Mobile Broadband is classified as non-critical at the peak of the triangle, while Massive Internet of Things and Ultra-reliable, Low Latency Communications are considered critical and are arranged at the bottom of the diagram.
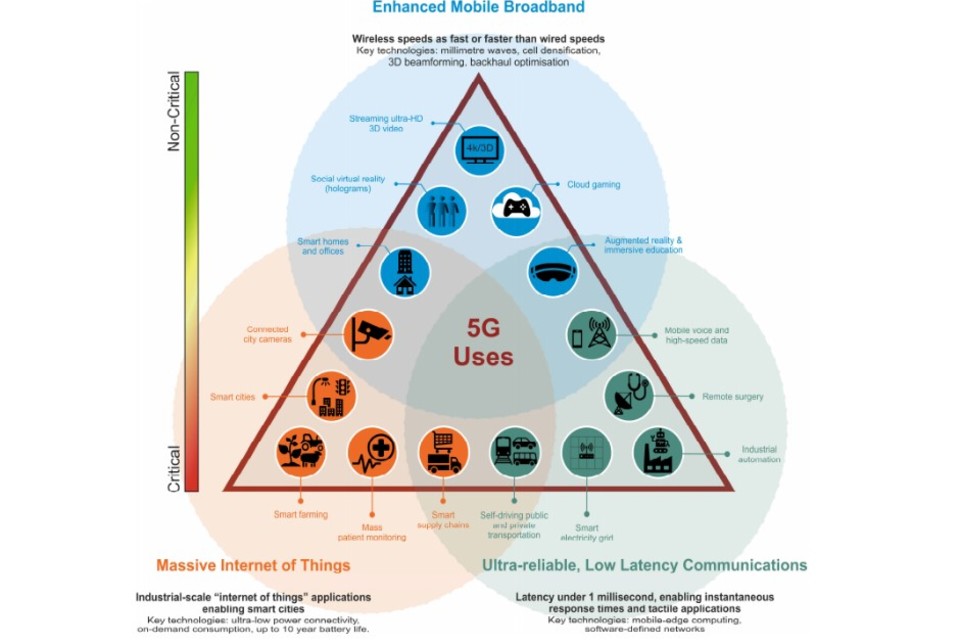
Diagram featuring a selection of key uses of 5G technology arranged in a triangular diagram and arranged into three groups: Massive Internet of Things, Ultra-reliable, Low Latency Communications and Enhanced Mobile Broadband.
The UK will continue its rollout of 5G to ensure everyone benefits from the opportunities of tomorrow’s technology, with the aim for the majority of the population to have access to a 5G signal by 2027. Currently, all four mobile network operators have launched 5G services, and 5G is available in over 100 towns and cities across the UK.
5G and health
The government has, in collaboration with Ofcom, produced materials explaining the facts about 5G to help you to combat the disinformation that is spreading online. Further information can be found in 5G mobile technology: a guide.
