How many people are detained or returned?
Published 28 February 2019
Back to ‘Immigration Statistics, year ending December 2018’ content page.
This is not the latest release. View latest release.
Data in this section relate to the year ending December 2018 and all comparisons are with the year ending December 2017, unless indicated otherwise.
This section contains data on:
- individuals held in immigration detention (solely under Immigration Act powers)
- returns of people, by the Home Office, who do not have any legal right to stay in the UK
The Home Office provides a more detailed commentary on an annual basis. The latest detailed annual commentary is included in ‘Immigration statistics, year ending June 2018’.
1. Immigration detention
At the end of December 2018, there were 1,784 people held in the detention estate, a fall of 30% compared with the same date 12 months earlier and the lowest level since comparable records began in 2009. The fall follows the introduction of the new Immigration Bail in Schedule 10 of the Immigration Bill 2016 (15 January 2018), and changes across the immigration system following Windrush (see the ‘about the statistics’ section for details on Windrush).
In 2018, 24,748 individuals entered the detention estate, 10% fewer than the previous year and the lowest level since comparable records began in 2009.
Over the same period, 25,487 left the detention estate (down 10%). Over two-thirds of these were detained for less than 29 days and 4% were detained for more than 6 months. The Home Office would usually only detain someone for more than 6 months if they are a foreign national offender (FNO), or if they have subsequently claimed asylum while in detention.
Of those leaving detention, 44% were returned from the UK to another country (compared with 47% in the previous year) and a further 40% received Secretary of State (SoS) bail. The remaining 16% will include people granted bail by an Immigration Judge, those granted leave to enter or remain, and those leaving for other reasons (such as deaths and absconders).
Data on deaths in detention and absconds from detention were published for the first time in November 2018. See ‘Immigration statistics, year ending September 2018’ for details.
Table 6: People entering, leaving and in detention, 2014 to 20181,2
| Year | Entering detention | Leaving detention | In detention3 | In detention (excl. HM Prisons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 30,364 | 29,674 | z | 3,462 |
| 2015 | 32,447 | 33,226 | z | 2,607 |
| 2016 | 28,903 | 28,677 | z | 2,738 |
| 2017 | 27,348 | 28,255 | 2,545 | 2,138 |
| 2018 | 24,748 | 25,487 | 1,784 | 1,418 |
| Change: latest year | -2,600 | -2,768 | -761 | -720 |
| Percentage change | -10% | -10% | -30% | -34% |
Sources:
Detention tables dt 01 q, dt 08 q and dt 13 q
Table notes:
- Data from July 2017 include those entering and leaving detention through HM Prisons, as well as those held in detention in HM Prisons. Data are not directly comparable with previous years. See the user guide for more details.
- Data on those in detention are as at the end of December each year.
- z = Not applicable
Table 7: Top 10 nationalities of people leaving detention by reason for leaving in 2018
| Nationality | Leaving detention | % Returned from the UK1 | % Bailed (SoS)2 | % Other reason3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | 2,666 | 63% | 23% | 14% |
| India | 1,946 | 21% | 57% | 22% |
| Pakistan | 1,927 | 23% | 53% | 24% |
| Romania | 1,414 | 93% | 3% | 4% |
| China | 1,177 | 32% | 58% | 11% |
| Bangladesh | 1,155 | 18% | 62% | 20% |
| Iraq | 1,140 | 8% | 84% | 9% |
| Poland | 958 | 74% | 8% | 18% |
| Nigeria | 955 | 29% | 35% | 36% |
| Brazil | 903 | 93% | 3% | 3% |
| Other nationalities | 11,246 | 43% | 41% | 16% |
| Total | 25,487 | 44% | 40% | 16% |
Source:
Table notes:
- ‘Returned from UK on leaving detention’ includes enforced returns, voluntary returns and those refused entry at port (in the UK) who were subsequently detained and then departed the UK.
- Detention closed reason: Bailed (SoS) replaced the existing powers of granted temporary admission/release from 15 January 2018, following the introduction of the new Immigration Bail in Schedule 10 of the Immigration Bill 2016.
- Other reason on leaving detention includes bailed (Immigration Judge), granted leave to enter/remain, deaths in detention, absconders and other categories.
2. Returns
There were 9,474 enforced returns from the UK in 2018, 21% fewer than the previous year. The fall coincides with changes across the immigration system following Windrush, and was largely accounted for by falls in:
- enforced returns of people who were in detention prior to their return, which fell by 17% to 8,578 compared with 10,362 in the previous year
- enforced returns for both EU nationals (down 1,117 to 3,797) and non-EU nationals (down 1,458 to 5,677). EU nationals accounted for 40% of enforced returns throughout the year and the majority (55%) of these were Romanian and Polish nationals
Of the enforced returns in the latest period, 23% (2,163) were enforced returns of people who had previously sought asylum (see the ‘About the Statistics’ section for the definition of asylum-related returns).
Figure 13: Returns by type, 2014 to 20181
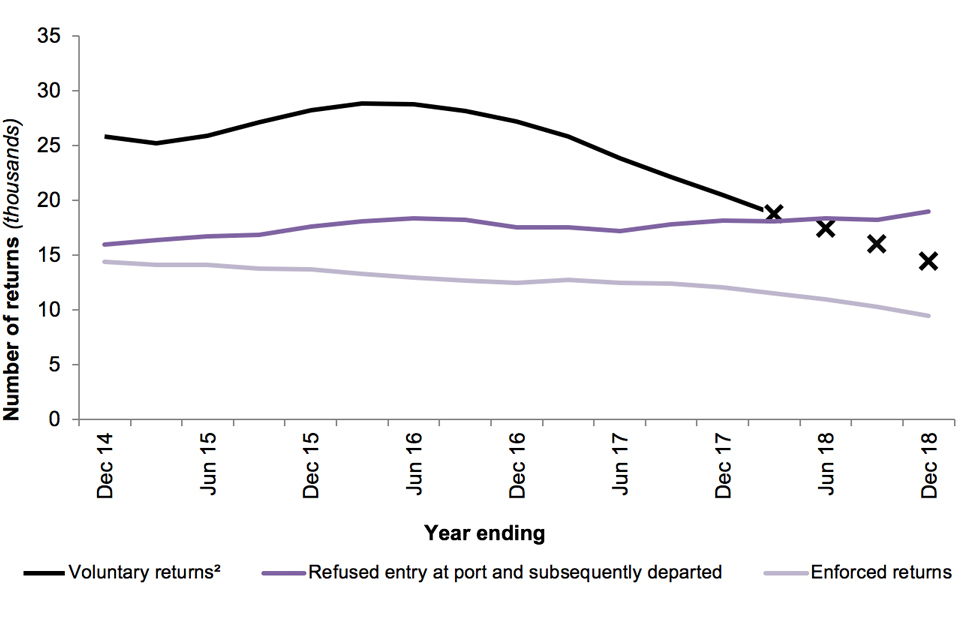
The chart shows the number of returns (by type of return) for the last 5 years.
Source:
Returns table rt 02 q(volume 1)
Chart notes:
- Data prior to 2014 are not directly comparable with data from 2014 onwards due to a change in the classification of returns. See the user guide for more details. Data prior to 2014 can be found in the returns table rt_02 (volume 1).
- ‘Voluntary returns’ are subject to significant upward revision (in particular for the last 12 months, shown as crosses in the chart) as matching checks are made on travellers after departure. They include a variety of departures, including assisted voluntary returns, controlled returns and other verified returns (for example, through data matching).
Table 8: Returns from the UK for EU/non-EU nationals by type of return, 2014 to 2018
| Year | Enforced returns1 | Voluntary returns2 | Refused entry at port who subsequently departed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 14,395 | 25,784 | 15,993 |
| EU | 3,158 | 433 | 1,409 |
| Non-EU | 11,237 | 25,351 | 14,584 |
| 2015 | 13,690 | 28,189 | 17,636 |
| EU | 3,848 | 669 | 1,918 |
| Non-EU | 9,842 | 27,520 | 15,718 |
| 2016 | 12,469 | 27,157 | 17,567 |
| EU | 4,905 | 775 | 2,272 |
| Non-EU | 7,564 | 26,382 | 15,295 |
| 2017 | 12,049 | 20,502 | 18,179 |
| EU | 4,914 | 724 | 3,751 |
| Non-EU | 7,135 | 19,778 | 14,428 |
| 2018 | 9,474 | 14,415 | 18,966 |
| EU | 3,797 | 208 | 3,071 |
| Non-EU | 5,677 | 14,207 | 15,895 |
| Change: latest 12 months3 | -2,575 | - | +787 |
| Percentage change3 | -21% | - | +4% |
Source:
Returns table rt 02 (volume 1)
Table notes:
- ‘Enforced returns’ cover enforced removals from detention, non-detained enforced removals and other returns from detention where the Home Office will have been required to facilitate or monitor the return.
- ‘Voluntary returns’ are subject to significant upward revision as matching checks are made on travellers after departure.
- ‘Voluntary returns’ include a variety of departures, including assisted voluntary returns, controlled returns and other verified returns (for example, through data matching). Comparisons with the previous 12 months for voluntary returns have not been included as data are not comparable over time.
Table 9: Enforced returns1 from the UK by nationality (top 5), 2018 compared with 2017
| Ranking (compared with 2017) | Nationality | 2017 | 2018 | Change | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (2) | Albania | 1,558 | 1,634 | +76 | +5% |
| 2 (1) | Romania | 1,675 | 1,271 | -404 | -24% |
| 3 (3) | Poland | 1,210 | 827 | -383 | -32% |
| 4 (15) | Ukraine | 165 | 504 | +339 | +205% |
| 5 (6) | Lithuania | 647 | 489 | -158 | -24% |
| - | Other nationalities | 6,794 | 4,749 | -2,045 | -30% |
| - | Total | 12,049 | 9,474 | -2,575 | -21% |
Source:
Returns table rt 02 (volume 1)
Table note:
- ‘Enforced returns’ cover enforced removals from detention, non-detained enforced removals and other returns from detention where the Home Office will have been required to facilitate or monitor the return.
There were 5,209 Foreign National Offenders (FNOs) returned in 2018, 15% fewer than the previous year. Of these:
- two-thirds (67%) were EU nationals (3,516)
- one-third (33%) were non-EU nationals (1,693)
- 9% were also known to have an overseas criminal record
3. About the statistics
Immigration detention
The statistics in this section show the number of entries into, and departures from, detention for those held solely under immigration powers. One individual may enter or leave detention multiple times in a given period and will therefore be counted multiple times in the statistics. Statistics on foreign nationals held in prison for criminal offences are published by the Ministry of Justice in its ‘Offender Management Statistics Quarterly’.
Data on those entering detention, by place of detention, relate to the place of initial detention. An individual who moves from one part of the detention estate to another will not be counted as entering any subsequent place of detention. The data therefore, do not show the total number of people entering each part of the detention estate.
Data on those in detention relate to those in detention on the last day of the quarter.
Data on those leaving detention, by place of detention, relate to the place of detention immediately prior to being released. An individual who moves from one part of the detention estate to another will not be counted as leaving each part of the detention estate. The data therefore, do not show the total number of people leaving each part of the detention estate.
From July 2017, data on detention of immigration detainees in prisons are included in the immigration detention figures. Previously, individuals who were detained in prison would have been recorded in the data upon entering the detention estate through an immigration removal centre (IRC), short-term holding facility (STHF) or pre-departure accommodation (PDA); now they are recorded upon entering immigration detention within prison. As a result, the length of detention of those entering prison prior to July 2017 will be recorded from the point at which they entered an IRC, STHF or PDA. Time spent in prison under immigration powers prior to entering an IRC, STHF or PDA will not be included in the length of detention figures.
For those entering detention from July 2017, the length of detention will include time spent in prison under immigration powers prior to entering an IRC, STHF or PDA. Data from Q3 2017 onwards are therefore not directly comparable with earlier data. Further details of these changes can be found in the user guide.
Following the introduction of the new Immigration Bail in Schedule 10 of the Immigration Bill 2016, the detention closed reasons ‘Bailed (SoS)’ replaced the existing powers of ‘granted temporary admission/release’ from 15/01/2018, and ‘Bailed (Immigration Judge)’ replaced ‘Bailed’ to differentiate from ‘Bailed (SoS)’. See the user guide for more details of this change.
Data on the number of children entering detention is subject to change. This will be a result of further evidence of an individual’s age coming to light, such as an age assessment.
Returns
The statistics in this section show the number of returns from the UK. One individual may be returned more than once in a given period, and if that were the case would be counted more than once in the statistics.
The Home Office seeks to return people who do not have a legal right to stay in the UK. This includes people who:
- enter, or attempt to enter, the UK illegally (including people entering clandestinely and by means of deception on entry)
- are subject to deportation action; for example, due to a serious criminal conviction
- overstay their period of legal right to remain in the UK
- breach their conditions of leave
- have been refused asylum
Deportations are a subset of enforced returns. They may occur either following a criminal conviction, or when it is judged that a person’s removal from the UK is conducive to the public good. Information on those deported is not separately available. The published statistics refer to enforced returns, which include deportations, as well as cases where a person has breached UK immigration laws, and those removed under other administrative and illegal entry powers who have declined to leave voluntarily. Most illegal immigrants are removed from the UK under administrative or illegal entry powers and not deported.
Data on voluntary returns are subject to significant upward revision, so comparisons over time should be made with caution. In some cases, individuals who have been told to leave the UK will not notify the Home Office of their departure from the UK. In such cases, it can take some time for the Home Office to become aware of such a departure and update the system. As a result, data for more recent periods will initially undercount the total number of returns. ‘Other verified returns’ are particularly affected by this.
Asylum-related returns relate to cases where there has been an asylum claim at some stage prior to the return. This will include asylum seekers whose asylum claims have been refused and who have exhausted any rights of appeal, those returned under third-country provisions, as well as those granted asylum/protection, but removed for other reasons (such as criminality).
Data on returns, and requests for transfer out of the UK under the Dublin Regulation, by article and country of transfer, are available from the Asylum data tables Asylum table as_23_q (volume 5). Further details on the Dublin Regulation are set out in the User Guide.
EU nationals may be returned for not exercising, or abusing, Treaty rights or deported on public policy grounds (such as criminality).
Eurostat publishes a range of enforcement data from EU member states. These data can be used to make international comparisons.
The Windrush Scheme
The Windrush generation refers to people from Caribbean countries who were invited by the British government between 1948 and 1971 to migrate to the UK as it faced a labour shortage due to the destruction caused by World War II. Not all of these migrants have documentation confirming their immigration status and therefore some may have been dealt with under immigration powers.
On 16 April 2018, the Home Secretary established a taskforce to ensure that members of the Windrush generation could evidence their right to be in the UK. The taskforce provide an update to the Home Affairs Select Committee on the work of the Home Office in relation to Windrush, including official figures, on a monthly basis. The updates are published on GOV.UK.
4. Data tables
Data referred to here can be found in the following tables:
- Detentions tables
- Returns tables volume 1
- Returns tables volume 2
- Returns tables volume 3
- Returns tables volume 4
- Returns tables volume 5
5. Review of immigration enforcement data
The Home Office is proposing to review the enforcement data that it publishes in order to ensure it provides a comprehensive overview of the detention and returns system. This will involve a consultation in 2019, where it will invite public views on its proposals. However, if you have any comments on the statistics currently published in this section and the associated data tables, including information that you find particularly helpful and information that you would like to see published in the future, please send these to MigrationStatsEnquiries@homeoffice.gov.uk.
We welcome your feedback
If you have any comments, or suggestions for the development of this report, please provide feedback by emailing MigrationStatsEnquiries@homeoffice.gov.uk. Please include the words ‘PUBLICATION FEEDBACK’ in the subject of your email.
See section 7 of the ‘About this release’ section for more details.
