Laboratory reports of Haemophilus influenzae by age group and serotype, England: annual 2024 (and 2023)
Updated 26 June 2025
Applies to England
During 2024 (January to December inclusive), there were 701 laboratory-confirmed cases of invasive Haemophilus influenzae (Hi) disease in England. This compared with 706 cases in 2023 (see table).
Restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic were associated with reductions in a number of infections including invasive Hi disease during 2020 (1), with cases remaining low during 2021 and then increasing from 2022.
In 2024, all invasive Hi isolates were serotyped, compared to 96.9% (684 of 706) during 2023. Of those serotyped, most isolates were non-encapsulated Hi (ncHi) (84.5%; 592 of 701) – this compares to 83.9% (574 of 684) in 2023.
In 2024, there were 22 cases of invasive H. influenzae type a (Hia) disease, accounting for 3.1% (22 of 701) of all invasive Hi cases, compared to 2.5% (18 of 706) in 2023. Of the 22 Hia cases, 14 were diagnosed in persons over the age of 15 years and 8 were in children under the age of 5 years.
There were 72 (10.2%) cases of invasive disease due to other Haemophilus influenzae types in 2024 including: 57 (8.1%) serotype f, 14 (2.0%) serotype e and one (0.1%) serotype c. In 2023, 59 (8.4%) were due to type f, 17 (2.4%) were due to type e, and there were no serotype c cases.
The incidence rate of invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease across all ages remains low at 1.22 per 100,000 population during 2024, of which most cases (87.0%; 610 of 701) were aged 15 years and over. Infants aged less than one year accounted for 4.9% (34 of 701) of cases in 2024 (see table).
There were 2 adult deaths attributed to invasive Hib disease in 2024. The most recent child death attributed to invasive Hib disease was in 2011. There were 2 other adult deaths attributed to invasive Hia disease in 2023 and one in 2024.
In conclusion, invasive Hib disease continued to be well controlled across all age groups in 2024.
Number of Haemophilus influenzae cases by serotype and age group, England, 2023 and 2024
(‘Not typed’ refers to samples that have not been received at the reference laboratory for typing, have failed to re-culture, or results were equivocal.)
| Type | Under 1 year 2023 | Under 1 year 2024 | 1 to 4 years 2023 | 1 to 4 years 2024 | 5 to 14 years 2023 | 5 to 14 years 2024 | 15+ years 2023 | 15+ years 2024 | Total 2023 | Total 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 12 | 14 | 18 | 22 |
| b | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 12 | 16 | 15 |
| c | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| e | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 12 | 17 | 14 |
| f | 3 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 53 | 51 | 59 | 57 |
| Non capsulated | 32 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 18 | 17 | 497 | 521 | 574 | 592 |
| Not typed | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
| Total | 41 | 34 | 34 | 38 | 21 | 19 | 610 | 610 | 706 | 701 |
Total cases of Haemophilus influenzae type b by year, 2006 to 2024
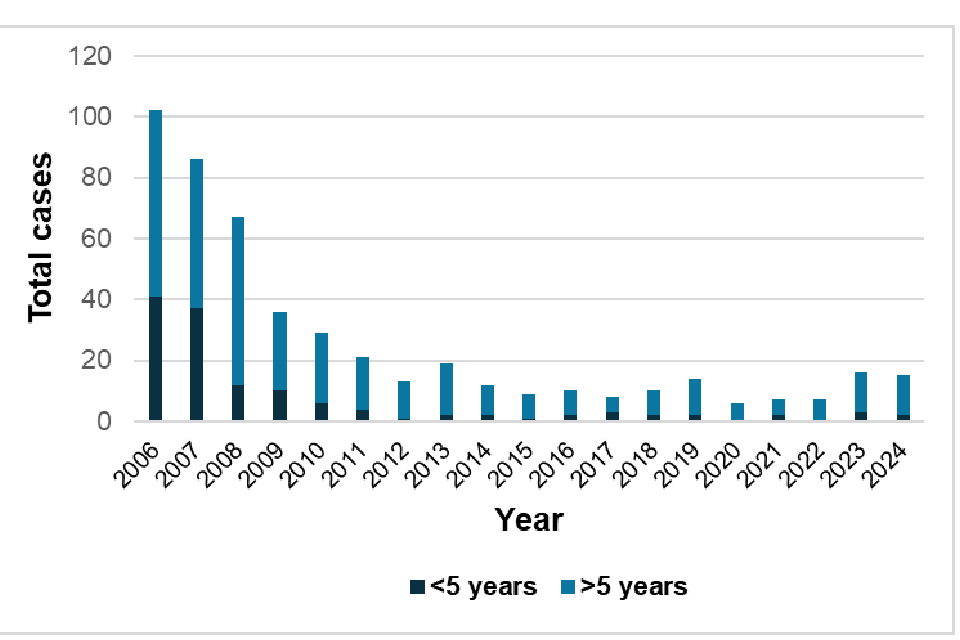
Reference
1. Brueggemann AB, Jansen van Rensburg MJ, Shaw D, McCarthy ND, Jolley KA, Maiden MCJ and others. ‘Changes in the incidence of invasive disease due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis during the COVID-19 pandemic in 26 countries and territories in the Invasive Respiratory Infection Surveillance Initiative: a prospective analysis of surveillance data’ The Lancet Digital Health 2021: volume 3, issue 6
