Direct Research Portfolio Annual Report 2018 to 2019
Published 6 January 2020

Airborne drone with R&D text superimposed over the images
Introduction
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) is responsible for cleaning up the legacy from the UK’s pioneering post-war nuclear programme.
From the late 1940s onwards, the country’s smartest scientists and engineers led the world with ground-breaking nuclear discoveries. The result was a diverse range of experimental facilities and early nuclear power stations, designed initially for the UK’s defences but later to provide electricity for its citizens.
Their work spanned 17 locations across the UK and included:
- Dozens of prototype reactors
- 11 nuclear power stations
- Scores of research labs
- Fuel-manufacturing and enrichment facilities
- Spent fuel reprocessing plants
Many of the designs were unique, producing radioactive wastes and spent fuel that no-one had ever dealt with before. Structures, pipework, container vessels and land became contaminated and were mostly left for a future generation to clean up.
Many years later, the NDA is dismantling this historical legacy, demolishing structures and preparing sites for future uses. The mission will stretch for another 100-plus years and cost more than £100 billion.
Dealing with such a range of complexities and uncertainties requires fundamental science, innovative thinking and novel engineering. Progress depends on clearly understanding the problems, finding solutions and ensuring the cost for taxpayers remains acceptable. Research & Development (R&D) is therefore an essential part of decommissioning programme. The aim is to solve the challenging technical problems more effectively, more efficiently, more safely and, where possible, for less cost.
A total of approximately £90 million was spent on R&D during 2018 to 2019 by the NDA group.
The bulk of this forms part of the budget allocated to our Site Licence Companies and subsidiary organisations, and is aimed at addressing specific on-site challenges identified during decommissioning activities. The work is carried out by SLCs, the subsidiaries and through contracts awarded to their supply chain.
Separately, the NDA also retains a strategic portfolio to commission projects directly, particularly in areas with potential to have an impact across a number of sites, or to develop our overall strategy. This kind of research may help shape and develop our strategy, encourage early innovation or maintain key technical skills.
About the DRP
The Direct Research Portfolio (DRP) is a key component of the NDA’sR&D programme. It accounts for approximately £4 million of our annual investment and represents an important area of overall support for R&D across the group’s 17 sites and subsidiary organisations.
The DRP is made up of projects that:
- Help shape and underpin the NDA’s overall strategy for the UK
- Deliver innovation across multiple sites
- Develop vital technical expertise for the future
DRP projects are aligned against the NDA’s 4 driving strategic themes:
- Integrated waste management
- Site decommissioning and remediation
- Spent fuel management
- Nuclear materials
DRP projects are commissioned through framework contracts that last up to 4 years. The current contracts, awarded in 2016, involve 3 framework contracts:
- Lot A: University interactions
- Lot B: Integrated waste management plus site decommissioning and remediation
- Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials
Overall, 10 consortia are involved in the DRP, comprising around 70 organisations ranging from UK universities and research bodies to global corporations and small businesses.
Topics for individual projects are identified either by the NDA’s internal technical experts or through members of the Nuclear Waste and Decommissioning Research Forum (NWDRF), a cross-industry forum which promotes collaboration across the UK on nuclear decommissioning R&D.
This report outlines a number of projects funded through the DRP during 2018 to 2019. Some are ongoing from earlier contracts, but all have potential for a significant impact across the group.
Total investment in the DRP over the financial year was £3.9 million.
Further information on NDA’s R&D programme can be found in our 5-year R&D plan.
DRP spend and key facts

Graphic showing overall £3.9 million spend
2018 to 2019 spending breakdown
| Lot | 2018 to 2019 spend |
|---|---|
| Lot A | £1.3 million |
| Lot B | £1.6 million |
| Lot C | £1.1 million |

Graphic showing key facts about spending

Graphic showing how many PhDs are being supported
New DRP projects in 2018 to 2019 by NDA R&D driver
| NDA R&D Driver | Number of new projects (2018 to 2019) |
|---|---|
| Delivering innovation | 3 |
| Inform strategy | 20 |
| Maintaining skills | 12 |
Note: Some DRP research projects have multiple drivers
Lot A: University interactions
New PhDs funded during 2018 to 2019
| PhD title | University | R&D Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-scale characterisation of residual stress in AGR fuel cladding | University of Bristol | Maintaining skills |
| Printed graphene-based sensors for real-time and wireless monitoring of nuclear waste storage containers | University of Manchester | Maintaining skills |
| Evaluation of uranium retention in geological minerals at the sub-micron level | University of Manchester | Maintaining skills |
| Bad laser cutting to get good laser fume | Loughborough University | Maintaining skills |
| An acoustic analysis tool for detecting hydrogen gas in sealed pressurised storage packages and containers | London South Bank University | Maintaining skills |
| Development of novel radiochemical methods for the analysis of challenging nuclides in nuclear decommissioning samples (part of TRANSCEND consortium) | University of Birmingham/University of Surrey/National Physical Laboratory | Maintaining skills |
Note: A number of other PhD projects were supported in the TRANSCEND consortium but did not start until Financial Year 2019 to 2020, so are not included in this annual report.
Lot B: Integrated waste management and site decommissioning and remediation
New projects started during 2018 to 2019
| Project title | Lead Organisation | R&D Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Managing on-site stockpiling and use of high volumes of concrete based demolition material | NSG | Inform strategy |
| Assessments to support the Near-Surface Disposal (NSD) project | Eden | Inform strategy |
| CL:AIRE membership year 2 of 3 | CL:AIRE Ltd | Inform strategy |
| Identification of synergies between AGR and Magnox reactor decommissioning | Wood | Inform strategy |
| Nuclear industry aqueous waste management good practice guide | Wood | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in nuclear decommissioning – current use and future opportunities | Wood | Delivering innovation |
Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials
New projects started during 2018 to 2019
| Project title | Lead Organisation | R&D Driver |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical work to further evaluate alternative techniques for online pond water monitoring | # Wood | Inform strategy |
| Preliminary desktop study to improve understanding of the availability and applicability of 3D imaging techniques for spent fuel examination | Wood | Inform strategy |
| Exploring Innovative means to manage and monitor pressure build-up in sealed spent fuel containers | NNL | Delivering innovation |
| Programme to pursue non-active experimental drying trials on intact and failed fuel pins | NNL | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| Desktop study on investigating on the influence of radiation induced microstructural changes on stainless steel susceptibility to InterGranular Attack (IGA) | Wood | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| Inactive Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) trials in support of CI-contaminated plutonium disposal | NNL | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| DoE-NDA HIP can filling system demonstrator collaboration | NNL | Inform strategy |
| Desktop study on investigating the influence of stress on stainless steel susceptibility to Intergranular Corrosion (IGC) | Wood | Inform strategy & delivering Innovation |
| Desktop study on choice of neutron poisons for Pu immobilisation | NNL | Inform strategy |
| Preliminary design and safety assessment of a technical solution to manage an increase in hydrogen concentration in gas feeds in the manufacture of MOx fuels in Central Laboratory | NNL | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| Desktop study on mill design for HIP process | NNL | Inform strategy |
| Desktop study on pre-heat treatment specification for plutonium | Wood | Inform strategy |
| Modelling the temperature and pressure of immobilised HIP product in cask storage | Wood | Inform strategy |
| Determining the mass balance of gaseous species in plutonium storage cans | NNL | Inform strategy |
| Literature review of radiation damage and leach rates for plutonium-bearing ceramic wasteforms | Wood | Inform strategy & maintaining skills |
| Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR) spent fuel technical forum meeting in March 2019 | NNL & Orano | Inform strategy |
Case studies
TRANSCEND consortium
Elanor Murray (left) and Hannah Parish discuss their academic research during a meeting of the TRANSCEND consortium
(Lot A: University interactions)
We need to maintain and develop sufficient high-level expertise to support decommissioning as the mission moves forward over the next 100-plus years. We therefore invest in a range of university research programmes targeted at decommissioning, and fundamental supporting topics, while supporting wider collaborative research programmes that align with industry requirements.
Read more: Academic research group builds skills for the future
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (drones)

A drone in flight at the Winfrith site in Dorset
(Lot B: Integrated waste management and site decommissioning and remediation)
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), popularly known as drones, have undergone rapid development over the last few years can now deploy a huge array of different equipment that allows them to analyse and interact with the world around them. Within nuclear decommissioning, such versatility offers enormous potential to save time and costs associated with inspecting the legacy facilities, while reducing risks for employees.
Read more: Decommissioning drones take to the sky
Concrete
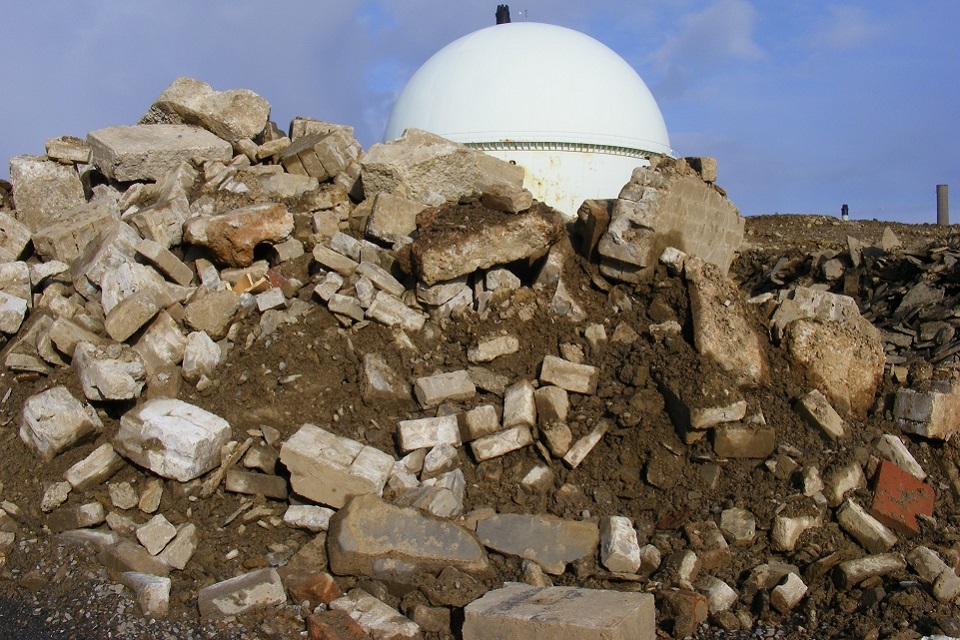

Large quantities of concrete rubble will arise from decommissioning facilities
(Lot B: Integrated waste management and site decommissioning and remediation)
Huge quantities of concrete rubble will arise all across the NDA’s 17 sites as nuclear facilities are demolished following decommissioning and clean-up. The vast bulk will be conventional demolition material that could be re-used, for example as landscaping, however, recycled concrete-based materials, or RCM, also generate highly alkaline and metal leachate which could undermine the environmental and cost savings, so investigations are under way into the risks in greater detail and possible treatment methods.
Read more: Concrete example of dealing with decommissioning rubble
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
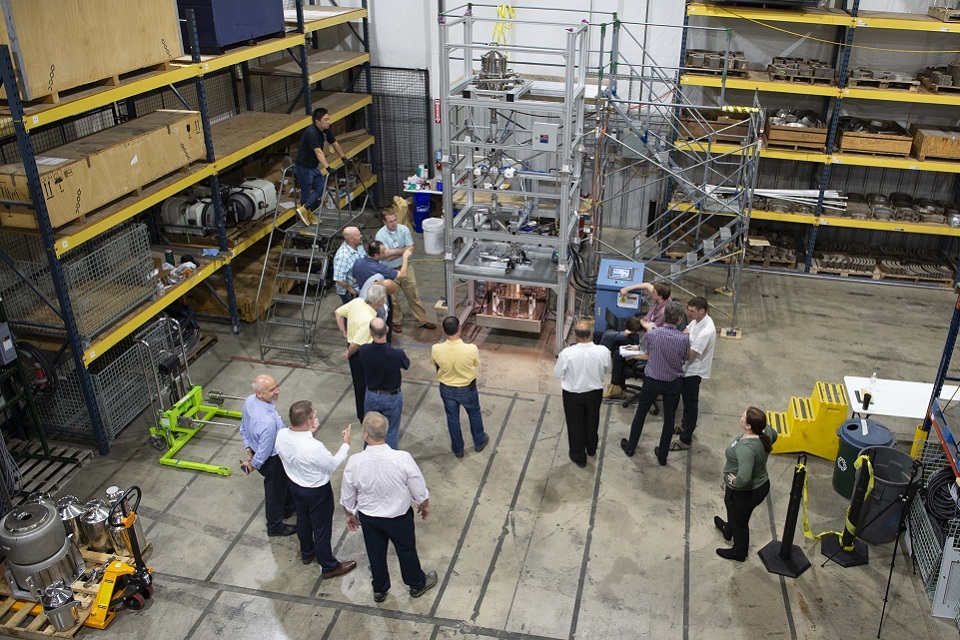

An overhead view of the HIP rig in America, with various observers standing around
(Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials)
As part of ongoing research into technologies for immobilising plutonium, the NDA has embarked on a collaborative project with the US to examine the feasibility of a can-filling treatment in preparation for Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). HIP is a heat-plus-pressure treatment which has been used in industrial processes for a number of decades, including the nuclear industry, and can convert various materials into a glass-ceramic or ceramic form. HIP technology offers a potential solution if it can be successfully adapted and deployed on a large-scale basis.
Read more: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for plutonium
3D Imaging
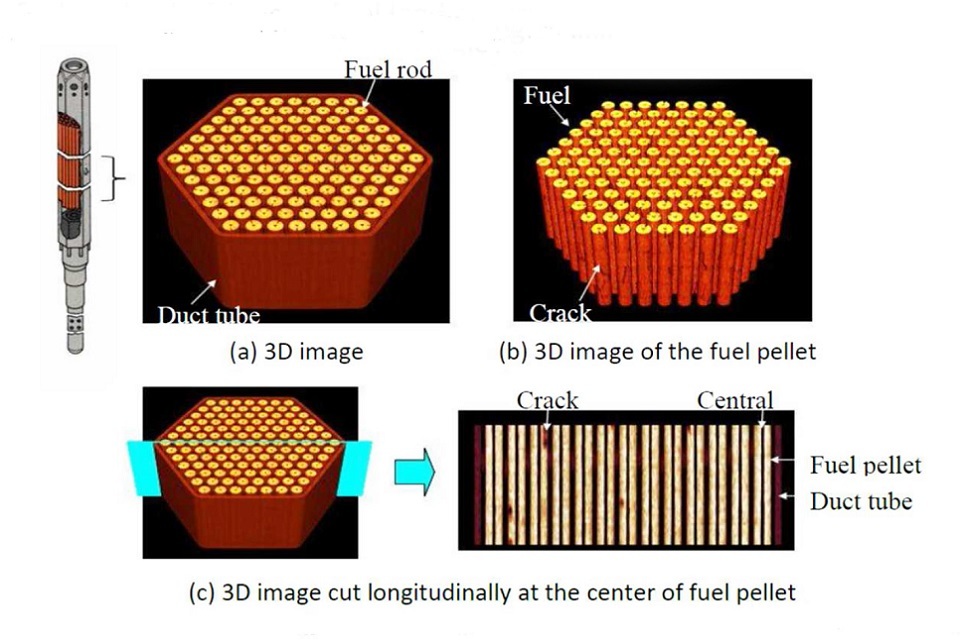
Image of AGR fuel assembly as seen by X-ray computed tomography
(Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials)
Research is under way into a range of 3D imaging techniques that could help predict the long-term behaviour of spent AGR fuel during storage in Sellafeld ponds. The NDA is contractually committed to receive and manage the spent fuel from the 7 EDF Energy (EDFE) AGR power stations. After finishing reprocessing the contracted amount of spent AGR fuel, the NDA plans to store the remaining AGR and other spent oxide fuels, pending a future decision on whether to declare them as waste for disposal in a GDF.
Read more: Role of 3D imaging in managing spent fuel stored under water
DRP framework contractors
Lot A: University interactions
| Lead Organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| National Nuclear Laboratory | Frazer-Nash Consulting |
Lot B: Integrated waste management and site decommissioning and remediation
| Lead Organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| Wood | Brenk Systemplanung, Jülich Research Centre, Andra, Cogentus Consulting, DAS, Imperial College London, Longenecker & Associates, MMI Engineering, NuVision, OC Robotics, Fortum, University of Birmingham, University of Bristol, University of Cambridge, University of Manchester |
| Arcadis | AdvanSci, Applied Photonics, Areva RMC, Aurora, ESI, MDecon, Pöyry, ProNu-Dec, Tradebe Inutec, TWI, University of Liverpool, Dalton Nuclear Institute, University of Surrey |
| Arup | Costain, Pöyry, Studsvik, James Fisher Nuclear, SN3, AdvanSci, MCM, Bilfinger GVA, Pinsent Masons, CL:AIRE, r3 Environmental Technology, Dalton Nuclear Institute |
| Eden Nuclear and Environment | Cavendish Nuclear, DBE TECHNOLOGY GmbH, Golder Associates, Tradebe Inutec, Project Time and Cost International |
| Galson Sciences | National Nuclear Laboratory, Frazer-Nash Consulting, Advansci, Amphos 21, Cogentus Consulting, Integrated Decision Management, Jacobs, Kurion, Rodgers Leask, VTT, University of Bristol, Lancaster University, University of Leeds, University of Manchester, University of Sheffield |
| NSG Environmental | AECOM, ARC, Oxford Technologies, NPL, ESG, Quintessa, React Engineering, KDC, Tradebe Inutec, Synergy Health, Nuclear AMRC, Loughborough University, University of Manchester, University of Surrey |
Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials
| Lead Organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| Wood | Andra, Brenk Systemplanung, Jülich Research Centre, Imperial College, DAS Ltd, Fortum, MMI Engineering, NPL, NRG, OC Robotics, Studsvik, University of Birmingham, University of Manchester, University of Bristol, University of Cambridge, Loughborough University |
| Orano | NSG Consultancy, MDecon, Quintessa, University of Liverpool, University of Sheffield |
| National Nuclear Laboratory | Frazer-Nash Consulting, Galson Sciences, ALD France, Aquila Nuclear Engineering, DBD, DAS, IDM, Jacobs, Kurion, Rodgers-Leask, University of Bristol, Lancaster University, University of Leeds, University of Manchester, University of Sheffield, Imperial College |

