Browser Security Guidance - Microsoft Internet Explorer
Published 28 November 2014
This ALPHA guidance builds on the End User Devices Platform Security Guidance and is applicable to devices running Microsoft Internet Explorer 11 on a supported and well configured version of Windows. This guidance was tested on 64-bit Windows 8.1 Enterprise edition running Internet Explorer 11.
Internet Explorer 11 on Windows 8.1 can be run in two modes: as a traditional window and tab management experience with ‘Internet Explorer 11 for the desktop’ or as a Windows 8 touch-first, immersive experience app with ‘Internet Explorer 11’. This guidance is applicable to both modes of use.
1. Usage scenario
Internet Explorer will be used to access a variety of web services including:
- accessing intranet services hosted on an enterprise-provided OFFICIAL network
- accessing enterprise cloud services sourced from the Digital Marketplace
- accessing other Internet services and web resources
To support these scenarios, the following architectural choices are recommended:
- all data should be routed through a secure enterprise Virtual Private Network (VPN) to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the traffic intended for the enterprise intranet
- all Internet data should be routed through an enterprise-hosted proxy to benefit from enterprise protective monitoring and logging solutions
- arbitrary third party extension installation by users is not permitted in the browser. A list of allowed trusted extensions can be configured in Group Policy
2. Summary of browser security
This browser has been assessed against each of the 12 security recommendations, and that assessment is shown in the table below. Explanatory text indicates that there is something related to that recommendation that the risk owners should be aware of. Rows marked [!] represent a more significant risk. See How the browser can best satisfy the security recommendations for more details about how each of the security recommendations is met.
| Recommendation | Risks |
|---|---|
| Protecting data-in-transit | Internet Explorer does not support HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) |
| Protecting data-at-rest | |
| Enabling authentication | Built-in authentication schemes cannot be disabled for cleartext channels |
| Protecting privacy | Not all third party cookies can be blocked |
| Plugin and renderer sandboxing | |
| Plugin and site whitelisting | |
| Malicious code detection and prevention | |
| Security policy enforcement | Restrictions on third party cookies can be disabled by the user |
| External peripheral and sensitive API protection | |
| Update policy | |
| Event collection for enterprise analysis | |
| Active scripting |
2.1 Significant risks
The following significant risks have been identified:
-
Internet Explorer does not support HTTP Strict Transport Security which means the end user is not fully protected against certain types of attack, such as SSL-Stripping man-in-the-middle attacks
-
Built-in authentication schemes such as basic and digest cannot be disabled for unencrypted requests. There is a risk that credentials sent using these methods could be stolen via a man-in-the-middle attack
3. How the browser can best satisfy the security recommendations
3.1 Protecting data-in-transit
Configure a gateway web proxy to ensure that all Internet traffic is routed through the enterprise for inspection and logging. Use the platform’s data-in-transit protection to securely route all intranet traffic back to the enterprise and provide access to the proxy.
Certificate Pinning is not natively supported, but can be added via Microsoft’s Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (EMET).
3.2 Protecting data-at-rest
The platform enforces user separation ensuring that temporary data and saved credentials can only be accessed by that user.
Use the platform’s data-at-rest protection to encrypt profile data and temporary files.
3.3 Enabling authentication
Deploy any required enterprise client authentication certificates to the user’s personal certificate store.
3.4 Protecting privacy
Turn off features that collect data such as browsing history, typed URLs, usage statistics and location data to submit to Microsoft.
Device Sync should be explicitly disabled as per the End User Device guidance as it can send saved passwords to Microsoft’s OneDrive cloud service.
SmartScreen can be disabled if the trade-off between privacy and security is not acceptable.
Procedural controls should be put in place to ensure that users do not override the Group Policy preference registry configuration for blocking third party cookies.
3.5 Plugin and renderer sandboxing
For Internet Explorer 11 this requirement is met by the browser without additional configuration. Built-in sandboxed features are preferred over third party plugins.
For Internet Explorer 11 for the desktop this requirement is met when Enhanced Protected Mode (EPM) has been enabled.
Disable EPM for Internet Explorer for the desktop if it stops line of business web applications functioning correctly.
Only internal enterprise websites should be explicitly added to the Intranet Zone to ensure their function is not reduced. External trusted websites that can be reached via SSL should be added to the Trusted Sites Zone if a richer web experience is required.
3.6 Plugin and site whitelisting
Deploy a site whitelist on the web proxy if required.
For Internet Explorer 11 for the desktop use Group Policy to configure a list of allowed plugins ActiveX Controls and Browser Help Objects(BHOs). These plugins should be inspected to ensure they do not opt out of the Internet Explorer sandbox.
Internet Explorer Accelerators allow data to be easily shared between services and applications. They can be disabled if the trade-off between privacy and security is not acceptable. If enabled, configure Internet Explorer to restrict the use of accelerators to those deployed through Group Policy.
3.7 Malicious code detection and prevention
Ensure that the platform’s anti-malware protection is enabled and kept updated. Internet Explorer can use Microsoft’s SmartScreen filter service to help protect against phishing websites and malicious downloads. If Microsoft reports that the content is unsafe, it will be blocked from being accessed, and a message displayed to the user informing them of the unsafe content. Configure this feature so that the user cannot choose to bypass its warnings once a decision has been made regarding sending potentially private URLs and file hashes to Microsoft.
3.8 Security policy enforcement
Settings applied through Group Policy cannot be removed by the user.
3.9 External peripheral and sensitive API protection
Access to geolocation information can be disabled.
3.10 Update policy
This requirement is met by the browser without additional configuration.
If Windows Update Services is in use, ensure that Internet Explorer updates are imported and distributed via this mechanism.
3.11 Event collection for enterprise analysis
Install the Windows Internet Explorer Compatibility Test Tool Kit and configure it to forward Internet Explorer events to the central enterprise logging server.
3.12 Active scripting
This requirement is met by the browser without additional configuration.
4. Network architecture
Deploy a DMZ web proxy in an architecture based on the Internet Gateway Architectural Pattern. The following network diagram describes the recommended architecture for this browser. The proxy/content filter includes user and machine request logging, anti-malware and content inspection components.
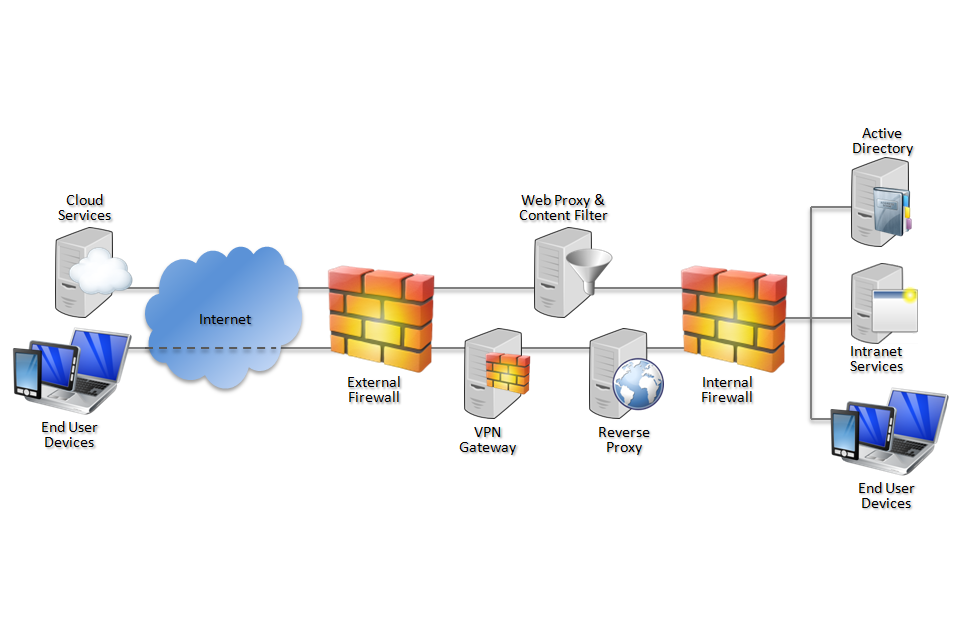
Recommended network architecture for deployments of Microsoft Internet Explorer on Windows
5. Deployment process
The following steps should be followed to prepare the enterprise infrastructure for hosting a deployment of the browser and provision it to end user devices.
-
Procure, deploy and configure network components, including a web proxy/content filter.
-
Provision Windows in line with the EUD Platform Security Guidance including EMET.
-
Install the Microsoft Internet Explorer 11 Security Baseline in the Group Policy management terminal.
-
Create Group Policies for users in accordance with the settings later in this section.
-
Deploy the Internet Explorer Compatibility Test Toolkit to each EUD to enable logging and auditing.
6. Recommended configuration
The following settings can be applied using Group Policy.
For easy configuration, the custom CESG GPO settings described below can be provided to Government organisations on request through CESG Enquiries.
6.1 User configuration
All settings are found in User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer.
Additional information regarding Internet Explorer’s Zones can be found below.
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Disable changing Automatic Configuration settings | Enabled |
| Prevent "Fix settings" functionality | Enabled |
| Prevent managing SmartScreen Filter | Enabled Select SmartScreen Filter Mode: On |
| Prevent participation in the Customer Experience Improvement Program | Enabled |
| Prevent running First Run wizard | Enabled Go directly to home page |
| Turn off suggestions for all user-installed providers | Enabled |
| Turn on compatibility logging | Enabled |
| Turn on Suggested Sites | Disabled |
| Accelerators > Restrict Accelerators to those deployed through Group Policy | Enabled |
| Accelerators > Turn off Accelerators | Configure as required |
| Application Compatibility > Clipboard Access > Bypass prompting for Clipboard access for scripts running in the Internet Explorer process | Disabled |
| Browser menus > Help menu: Remove ‘Send Feedback’ menu option | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Disable the Advanced Page | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Disable the Connections Page | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Disable the Privacy Page | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Disable the Security page | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Allow active content from CDs to run on user machines | Disabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Do not allow resetting Internet Explorer Settings | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Do not save encrypted pages to disk | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Empty Temporary Internet Files folder when browser is closed | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Turn off encryption support | Enabled Secure Protocol combinations: Use TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2 |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Turn off the flip ahead with page prediction feature | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Use HTTP 1.1 | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Advanced Page > Use HTTP 1.1 through proxy connections | Enabled |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > Site to Zone Assignment list | Enabled Configure as required |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Allow cut, copy, and paste operations from the clipboard via script | Enabled Allow paste operations via script: Disable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Allow font downloads | Enabled Allow font downloads: Disable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Allow video and animation on a webpage that uses an older media player | Enabled Allow video and animation on a Web page that uses a legacy medial player: Disable (Enable in trusted zones if required) |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Display mixed content | Enabled Display mixed content: Disable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Include Local path when user is uploading files to a server | Enabled Include local directory path when uploading files to a server: Disable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Java Permissions | Enabled Java permissions: Disable Java (High Safety in trusted zones if required) |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Render legacy filters | Enabled Render Legacy filters : Disabled (Enabled in trusted zones if required) |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Run .NET Framework-reliant components not signed with Authenticode | Enable Run .NET Framework-reliant components not signed with Authenticode: Disable (Enable in trusted zones if required) |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Run .NET Framework-reliant components signed with Authenticode | Enable Run .NET Framework-reliant components signed with Authenticode: Disable (Enable in trusted zones if required) |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Scripting of Java applets | Enabled Scripting of Java applets: Disable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Turn on Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Filter | Enabled Turn on Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Filter: Enable |
| Internet Control Panel > Security Page > [All Zones] > Turn on Protected Mode | Enabled Protected Mode: Enable |
| Internet Settings > Advanced Settings > Browsing > Turn on script debugging | Disabled |
| Internet Settings > Advanced Settings > Internet Connection Wizard Settings > Start the Internet Connection Wizard automatically | Disabled |
| Internet Settings > AutoComplete > Turn on inline AutoComplete | Disabled |
| Internet Settings > AutoComplete > Turn off Windows Search AutoComplete | Enabled |
| Privacy > Establish Tracking Protection Threshold | Enabled Threshold: 3 |
| Security Features > Turn off Data URI support | Enabled |
| Security Features > Add-on Management > Add-on List | Enabled See “Add-On Management” below |
| Security Features > Add-on Management > Deny all add-ons unless specifically allowed in the Add-on List | Enabled |
| Security Features > Add-on Management > Remove “Run this time” button for outdated ActiveX controls in Internet Explorer | Enabled |
| Security Features > Mime Sniffing Safety Feature > Internet Explorer Process | Enabled |
| Security Features > MK Protocol Security Restriction > Internet Explorer Processes | Enabled |
| Security Features > Protection from Zone Elevation > Internet Explorer Processes | Enabled |
| Security Features > Scripted Window Security Restrictions > Internet Explorer Processes | Enabled |
Add-On management
Internet Explorer can be extended via the installation of ActiveX Controls, Toolbars, and Browser Helper Objects (BHOs). Commonly required controls are listed below for ease of deployment and can be configured via the Group Policy setting User Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer’ > Security Features > Add-on Management > Add-on List.
| Value Name | Value | Plugin Name |
|---|---|---|
| {D27CDB6E-AE6D-11CF-96B8-444553540000} | 1 | Adobe Flash |
| {CA8A9780-280D-11CF-A24D-444553540000} | 1 | Adobe PDF Reader |
Additional Microsoft ActiveX controls for MSXML 6.0 and 3.0 need to be allowed to maintain compatibility with older websites which make use of their functionality. These have been added into the Group Policy files for ease of deployment.
Cookie control
Create a new Group Policy preference setting within User Configuration > Preferences > Windows Settings > Registry and add the following keys.
| PrivacyAdvanced | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Update |
| Hive | HKEY_CURRENT_USER |
| Key Path | Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings |
| Value Name | PrivacyAdvanced |
| Value Type | REG_DWORD |
| Value Data | 1 |
| {AEBA21FA-782A-4A90-978D-B72164C80120} | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Update |
| Hive | HKEY_CURRENT_USER |
| Key Path | Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\3 |
| Value Name | {AEBA21FA-782A-4A90-978D-B72164C80120} |
| Value Type | REG_BINARY |
| Value Data | 1a3761592352350c7a5f20172f1e1a190e2b017313371312141a152a |
| {A8A88C49-5EB2-4990-A1A2-0876022C854F} | Value |
|---|---|
| Action | Update |
| Hive | HKEY_CURRENT_USER |
| Key Path | Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\3 |
| Value Name | {A8A88C49-5EB2-4990-A1A2-0876022C854F} |
| Value Type | REG_BINARY |
| Value Data | 1a3761592352350c7a5f20172f1e1a190e2b017313371312141a1539 |
Proxy settings
These settings will be applied to all Windows applications, and will be inherited by Internet Explorer.
Create a new Group Policy preference setting within User Configuration > Preferences > Control Panel Settings > Internet Settings > Internet Explorer 10. These settings also apply to Internet Explorer 11.
| Group Policy Preference Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Internet Explorer 10 > Connections Tab > LAN settings > Use a proxy server for your LAN (These settings will not apply to a dial-up or VPN connections) | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer 10 > Connections Tab > LAN settings > Address | Configure as required |
| Internet Explorer 10 > Connections Tab > LAN settings > Port | Configure as required |
| Internet Explorer 10 > Connections Tab > LAN settings > Bypass proxy server for local addresses | Enabled |
6.2 Computer configuration
The following Group Policy configuration needs to be applied to the Computer configuration so that Site to Zone mappings configured above will be enabled correctly.
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Internet Explorer > Security Zones: Use only machine settings | Disabled |
7. Enterprise considerations
7.1 SmartScreen
Microsoft SmartScreen is a security feature that aims to protect against phishing websites and malicious downloads. It works by sending URLs of visited websites and hashes of files downloaded to Microsoft. If Microsoft reports that the content is unsafe, it will be blocked from being accessed, and a message displayed to the user informing them of the unsafe content.
Microsoft SmartScreen should be enabled for all zones but can be disabled for the intranet zone if the trade-off between privacy and security is not acceptable.
7.2 Computer and user configuration settings
The Microsoft Security Baseline configuration available from within Security Compliance Manager applies a significant amount of configuration to the Computer account. In an environment where users share end user devices this approach may not provide the required flexibility between different users using the same computer. In this instance it is recommended, where possible, that settings in the Computer account be transitioned in to the User account.
7.3 Enhanced Protected Mode
Both versions of Internet Explorer 11 support Enhanced Protected Mode(EPM). EPM is enabled by default within Internet Explorer 11 but should also be enabled for Internet Explorer 11 for desktop. By default EPM only protects sites loaded in the Internet Zone.
Configure EPM so that it also protects both the Intranet and Trusted Sites zones as long as it does not cause issues with enterprise web applications.
7.4 Internet Explorer zones
Internet Explorer allows web content to be grouped with regards to respective level of trusts into what Microsoft call Zones.
These Zones allow an enterprise to distinguish between web content with differing levels of trust.
By default web content is rendered in the Internet zone which should apply the most restrictive security controls to give the user the best level or protection available against potentially malicious web content. For instance, ActiveX scripting should be controlled in this zone.
Web content which is rendered incorrectly due to the restrictive nature of the Internet zone can be added to the Trusted Sites zone where there is a business requirement to view the content and the website supports SSL. This zone can have slightly more permissive security controls as the sites added here should be more trusted eg News and Social Media websites.
Internal content, which does not function correctly due to the restrictive nature of the Internet Zone should be added to the Local Intranet zone. This zone can be configured to have the most permissive security controls applied to it as the media being added is internally trusted.
7.5 Internet Explorer Enterprise mode
Enterprise Mode provides a compatibility mode for web applications that were designed for older versions of Internet Explorer. Some organisations could not upgrade to the most recent version of IE as their websites were not compatible with more modern browsers. Organisations can put those sites in a list so that Enterprise mode can help them to run properly in IE11. The Enterprise Site Discovery Toolkit helps build a list of web applications on an organisation’s intranet. It also identifies those that would benefit from being put on the Enterprise Mode list and those that should be a priority for compatibility testing.
7.6 Plugin sandboxing and security
Internet Explorer allows plugins such as Java to opt out of the Internet Explorer sandbox. A malicious website that successfully exploits such a plugin or browser extension can gain full user privilege including access to their data and web content.
Internet Explorer applies its sandbox to most plugins, including Flash and the Adobe Reader. These plugins have therefore been enabled in the configuration above. If unsandboxed plugins are required, Internet Explorer should be configured to only allow them for a whitelisted set of trusted sites.
Some ActiveX controls and add-ons are not compatible with Enhanced Protected Mode (EPM) and will not load. If such plugins are required, Internet Explorer should be configured to only disable the EPM sandbox for a whitelisted set of trusted sites.
Internet Explorer 11 blocks the use of certain unpatched ActiveX controls. While it is not recommended, it is possible to override this control for specific web sites if required for line of business applications.
The immersive version of Internet Explorer 11 provides an add-on–free experience. Browser plugins will not load and dependent content will not be displayed. This does not apply to Internet Explorer for the desktop. For more information, see Browsing Without Plug-ins.
