International Education Strategy: global potential, global growth
Updated 16 February 2021
Foreword
Joint foreword from the Secretary of State for Education and the Secretary of State for International Trade
The UK has a world-class education offering, a global reputation and a strong presence in international markets. Our higher education institutions are amongst the most renowned and prestigious in the world. Our early years providers and schools provide international benchmarks for safeguarding and choice, and whilst it may have previously only been the names of top public schools that gathered recognition past our shores, we can now boast some of the best state schools in the world.
Our skills and training providers offer the flexibility and unique solutions required in a world where the nature of work and employment is changing at a pace unseen since the Industrial Revolution. Throughout the world, the UK brand is one that is earmarked by quality, excellence and pioneering thought leadership.
All of these bring many benefits to the UK. They make an important contribution to economic growth, helping to generate the investment and jobs the UK needs. There are also wider benefits that come from broadening the UK’s soft power. In strengthening our international collaboration, we can help to tackle global challenges like poverty, and, in turn, strengthen our national security.
The global education market is developing quickly. Whilst this changing market offers many opportunities to the UK, our ambitious competitors are also galvanised to action. It is becoming ever more globalised, specialised and competitive, rewarding providers with the experience, talent and reputation to meet its rapidly growing demand. We must rise to meet this challenge.
As we leave the European Union and reach out to meet the emerging possibilities of the wider world, we have the opportunity to build on these successes and embrace our ambitious objectives for the education sector.
The government, in partnership with industry, has been working hard to do just that: identifying where barriers to their exporting success exist, and finding the right tools to overcome them.
The government’s Export Strategy has set the scene for how government will support UK exporters following the UK’s departure from the European Union. This strategy builds on that ethos for the education sector.
UK education is punching above its weight, but below its potential. The sector tells us that they face a range of issues in increasing their international footprint. Some businesses may believe they are not suited to overseas sales, or lack the confidence or knowledge in how to pursue them. They may not have the information they need about how to tackle policy or regulatory barriers to access overseas markets, how to seek and get finance, or even where to go for help.
This strategy is about meeting these challenges. At its heart is an ambition to increase the value of our education exports to £35 billion per year, and to increase the number of international higher education students hosted in the UK to 600,000 per year, both by 2030.
In sharing knowledge, skills and innovation with international partners around the world, we can also generate opportunities to help raise education standards both at home and around the world.
To do this, this strategy sets out a cohesive approach to our global education sector, recognising where government can best help and where the sector should take the lead.
It sets out a whole-of-government approach, across government departments and devolved administrations, to put in place the practical, advisory and promotional support to further strengthen the UK’s position at the forefront of global education and as an international partner of choice for institutions and governments around the world.
But it also recognises that it is the sector – not government – that must be at the forefront of our ambition. That is why this strategy has been developed in cooperation with education providers across the education sector to understand their ambitions and address the practical barriers they face in expanding their exports and breaking into new markets.
With around 90% of global economic growth in the next 5 years expected to originate outside the European Union, forging a new role for the United Kingdom on the world stage starts with rising to the exporting challenge – of which this strategy and the education sector will form a key part. Working together, we can help UK education reach its full, global exporting potential.
The Rt Hon Damian Hinds MP, Secretary of State for Education
Dr Liam Fox MP, Secretary of State for International Trade and President of the Board of Trade
Executive summary
The UK has a global reputation for education, characterised by excellence and quality. Our global education offer encompasses the full range of the education spectrum, including early years, independent schools, further education and colleges, higher education, transnational education, education services, education technology and English language training.
We have 4 universities in the world’s top 10 and 18 in the world’s top 100, according to the QS[footnote 1] world rankings. We have some of the best known schools and universities in the world. This is underpinned by the quality of our globally recognised assessment system, from the early years foundation stage through to A levels. We are ranked first by international students for student experience across several measures[footnote 2]. With almost a quarter of Europe’s education technology companies based in the UK, we are the European leaders for education technology.
Our cultural credentials generate global connections and relationships. English is one of the most widely used languages in the world. Alumni of British education hold senior roles in many of the world’s governments. The Higher Education Policy Institute estimates that over 50 serving world leaders have benefited from a British education[footnote 3].
This position on the global stage delivers many benefits to the UK. Education related exports deliver an important economic contribution generating almost £20 billion in 2016. This includes over £1.8 billion generated by our transnational education (TNE) activities, an increase of 73% since 2010 in current prices. In 2014 to 2015, Universities UK estimates that UK universities and their international students and visitors supported over 940,000 jobs. We have seen students who come to the UK to study stay on as graduate innovators, setting up enterprises such as language training in London, catering services in Newcastle and business support technology in Glasgow.
Even as UK education exports continue to grow, an increasingly competitive global environment means that we need to take steps to preserve market share. To meet this challenge, we will provide the support to our education sector that only government can give.
We will seek to grow education exports and international partnerships through encouragement, information, and connections, mirroring the ethos of the 2018 Export Strategy, supporting and connecting businesses to grow on the world stage. We will seek to use the opportunities presented by our newly independent trade policy when the UK leaves the EU to boost our trading relationships and push for greater access for UK services and service providers.
Education exports also bring value in the collaboration and partnerships they foster, helping to forge soft power and global relationships. These underpin opportunities for the UK and our international partners to develop, trade and collaborate. Our approach to international engagement is based on partnership. We work with UK education sector providers, UK global industry, and governments around the globe to meet the multiple opportunities and challenges of the modern world by sharing knowledge, skills and innovation.
Our objective is to drive ambition across the UK education sector. We will champion the breadth and diversity of the UK’s international education offer, strengthening our position as the partner and provider of choice for countries and individuals around the world.
Working in tandem with the education sector, we will provide the practical solutions and tools it needs to harness its full international potential. We will focus on the role of government in supporting exports while recognising that government should do only those things which it alone can do. To make a real difference, the government’s action must be met by the ambition and activity of the sector.
Our ambition is to increase education exports to £35 billion by 2030. International education exports were worth almost £20 billion to the UK in 2016 and, based on current rates of growth, could be expected to reach an estimated £23 billion by 2020[footnote 4].
Achieving this ambition will require an average annual growth rate of 4% per year. In order to drive progress against this target, we intend to build our global market share in international students across the education sectors. We also intend to improve how we capture education exports data in order to monitor our progress against this ambition.
This ambition is not just economic: international collaboration brings with it a better understanding of the UK system by our overseas partners. When appropriate, we will offer government support to UK providers working to support other countries’ education reforms, by helping them to share knowledge and exchange policy, as set out in Section 4.
As part of this ambition we want to grow the numbers of international higher education students studying in the UK to 600,000 by 2030. More broadly, we will support our global partners in their education objectives and, by doing so, increase the UK’s global reach and influence.
The actions we set out in this strategy aim to make these ambitions achievable and support the education sector to drive progress towards them. We have engaged with the sector in developing our actions and will continue to do so as we work towards implementing this strategy. This document sets out the start of that journey and its actions should lay the foundations for continued growth to help boost the activity of sectors across the education spectrum. A list of the actions, including time frames and additional information, is provided in Annex A.
To support implementation of the strategy, we are committing to 5 key, cross cutting actions that will support the whole education sector:
1. Appoint an International Education Champion to spearhead overseas activity, open international opportunities, develop strong international partnerships in new and established markets and help tackle challenges and barriers
2. Ensure Education is GREAT promotes the breadth and diversity of the UK education offer more fully to international audiences, from early years through to higher education. We will encourage education bids to the GREAT Challenge Fund for 2019. This £5 million fund supports export activity for the sector across the globe
3. Continue to provide a welcoming environment for international students and develop an increasingly competitive offer. This includes extending the post-study leave period[footnote 5], considering where the visa process could be improved, supporting employment, and ensuring existing and prospective students continue to feel welcome
4. Establish a whole-of-government approach by implementing a framework for ministerial engagement with the sector and formalised structures for co-ordination between government departments both domestically and overseas. This will be managed through an officials’ steering group including other government departments and the devolved administrations feeding into the existing Education Sector Advisory Group, chaired by Department for International Trade (DIT) and Department for Education (DfE) ministers
5. Provide a clearer picture of exports activity by improving the accuracy and coverage of our annually published education exports data, developing an approach with a strengthened methodology and a better range of sources.
In addition to these headline actions, we will also implement a range of specific actions to support each part of the education sector to build its international presence and exporting activity. These actions are set out in Section 4, Equipping the sector to reach its global potential
We will publish annual updates to the strategy to reflect progress made against the overarching ambitions and actions. This ongoing review will create the flexibility to set out further plans and actions when needed, to respond to emerging opportunities and global trends and to reflect on the education sector’s experiences.
Education is a devolved policy area and the responsibility of the Scottish, Welsh and Northern Irish Governments. Officials from the devolved administrations have been engaged in the development of the International Education Strategy, however, this strategy represents UK government policy and not that of the devolved administrations.
1. Setting the foundations for global success
1.1 The story so far
In 2013, the government published the International Education Strategy: global growth and prosperity. This strategy set out an ambition for the government and education sector to work together to take advantage of global opportunities. Aiming to build on the UK’s strengths, it focussed on international students, TNE, education technology (EdTech) and, more broadly, strengthening the UK’s education brand overseas.
Since the launch of the 2013 strategy, the government has worked across the UK education sector with international stakeholders and the British Council to strengthen the promotion of the UK’s global education offer in established and emerging markets around the world. An education team has been established within DIT that focuses on 4 key geographical regions where we believe the work of government can best support the sector.
Figure 1 : UK revenue from education related exports and TNE activities
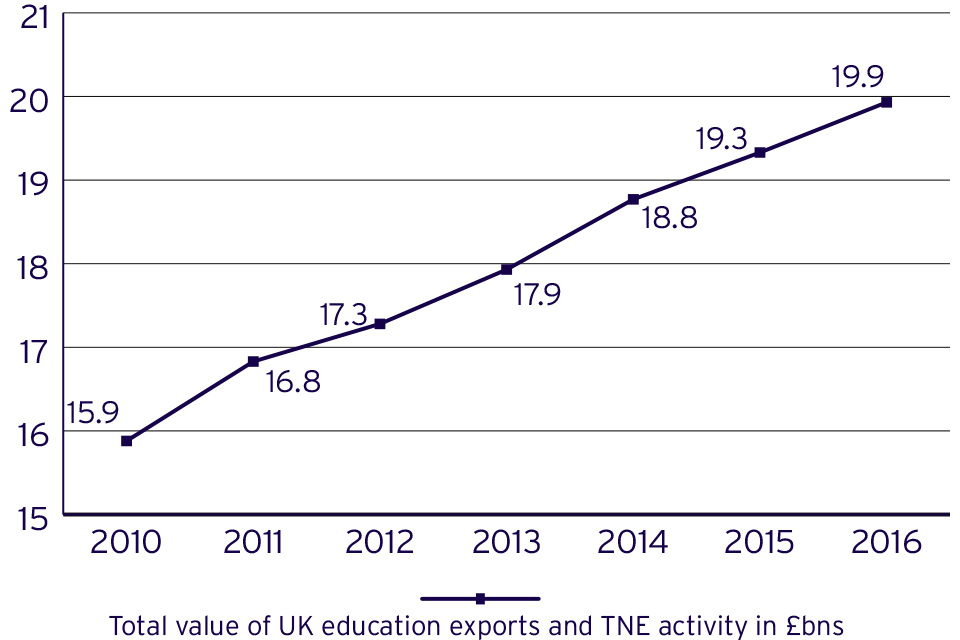
UK revenue from education related exports and TNE activities
Source: Department for Education (2019)
The GREAT campaign showcases the very best of what the UK has to offer, encouraging the world to visit, study and do business with us. The #EducationIsGreat banner has been used in over 36 countries over the past 2 years, covering Europe, Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Middle East. The GREAT campaign and the British Council’s efforts generated £309 million for the UK economy in 2017 to 2018.[footnote 6]
UK education has a well-established global reputation for excellence, built on the strength of individual institutions, located across our regions and nations, many of which have a long tradition behind them. The global reputation of these institutions feeds into the broader renown of the UK education ecosystem. This is underpinned by autonomous institutions and organisations having the ability to set priorities, take decisions and develop strategies.
Recent reforms, such as the Higher Education and Research Act 2017 have reinforced this tradition, increasing innovation, quality and choice by removing the distinctions between public and for-profit higher education providers and encouraging new providers and competition. Government has also strongly encouraged the growth of academies and free schools, again with a view to increasing diversity, choice and improving overall standards. Many of these schools, often serving children from deprived backgrounds, are amongst some of the most successful in the country.
The UK has maintained its highly competitive position in the global education market. We are the second most popular study destination in the world for international students, behind the US. For higher education alone, the UK hosted almost 460,000 international students in 2017 to 2018[footnote 7]. In 2016 to 2017, over 700,000 students were studying for UK degrees outside the UK, up 17% from 2012 to 2013[footnote 8].
The value of education exports has also grown steadily over time. In 2016, education exports and TNE activity was worth £19.9 billion to the UK economy, marking a 22% increase since 2010[footnote 9].
1.2 Challenges and opportunities
The global economy is changing fast. By 2017 total global exports were worth roughly twice what they were in 1997 in real terms[footnote 10]. Leaving the EU presents the UK with the opportunity to extend its international ambitions and role on the global stage and by utilising our newly independent trade policy to boost our existing trading relationships by securing new trade agreements.
This is why the government set its ambition to grow exports as a share of GDP from 30% to 35% in the 2018 Export Strategy. This International Education Strategy sets out how the education sector can help contribute towards this ambition. Since 2013 a rapidly growing global education market has created strong competition from other countries around the world.
One of the main challenges we face is that worldwide there are no clear estimates of the size of the global education market beyond international students.
The data currently published by DfE on the value of UK education exports are experimental statistics, based on multiple sources, some with varying quality or limited coverage. There is also a delay in the publication of the figures, which means there is a lag in the latest statistics. We will provide a clearer picture of the UK education sector’s exports activity by improving the accuracy and coverage of education exports data, as set out in Section 4.
The UK is a prominent player in global education and we are world leaders in higher education. Spectacular growth in exports from areas such as TNE student numbers demonstrate that the sector is capable of innovative new business models and forms of provision.
Growth is fuelled in part by a global drive to achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals around access to good quality education. Alongside this initiative, national vocational reform programmes across regions such as South East Asia and Latin America indicate growing opportunities for globally minded providers.
We cannot afford to rest on our laurels. As students face increasing choice, some of our competitors are outpacing global growth rates. That is why this strategy sets out proactive steps to help the UK maintain and increase market share, even as the global market grows more competitive.
1.3 Championing the UK’s world leading education offer
We want to continue to promote the UK’s education sector and its potential to address the world’s increasingly complex education needs. To open opportunities for the UK education sector we must be proactive in identifying and overcoming regulatory barriers, building our international presence and promoting our education interests in key markets.
The UK would benefit from being able to call on a globally recognised figure from the world of education to promote our international education interests to help break down barriers that can impede UK providers. This work needs a figurehead who understands the nuances and potential of the UK education offer, can develop long-term relationships with international governments, overseas stakeholders, and is respected by the UK sector.
Action 1
The UK government will appoint an International Education Champion in 2019. They will be tasked with opening up international opportunities for the UK sector, connecting the education sector to overseas opportunities, and helping to overcome any challenges and barriers to growth.
The role of the champion will involve targeting priority regions to build networks and making personal connections with influential figures in overseas governments and the education sector. They will represent the UK overseas and promote it as the international education partner of choice. The champion will lead delegations of UK education providers overseas, as well as receiving international delegations in the UK, complementing the roles already undertaken by UK ministers and trade envoys.
A strategic annual programme of activity designed around priority regions will steer the champion’s activity, using input from the Education Sector Advisory Group and the cross-government International Education Steering Group. Through the advisory group, the champion will also report back to the sector about exporting opportunities and progress in tackling barriers.
Case study : Kangaroo Pouch Day Nursery
In 2017, as part of the Exporting is GREAT campaign, the Department for International Trade ran an early years education trade mission to China and Hong Kong. The mission facilitated networking opportunities between potential partners, and resulted in Kangaroo Pouch Day Nursery, the largest nursery chain in the West Midlands, securing a contract in China.
With support from DIT and the Black Country Chamber of Commerce, Kangaroo Pouch Day Nursery signed a contract with Jiangsu Junyi Education Group to open British-style nurseries in Nanjing.
The first 2 nurseries will be opening in April 2019. The business is aiming to open 15 centres in Jiangsu Province over the next 3 years
1.4 Communicating the breadth of the UK education offer
Education is GREAT is both a trusted brand and an effective vehicle for promotion of UK education overseas. In 2015 the British Council and GREAT launched the ‘Study UK: Discover You’ campaign to better promote UK higher education. Visible in over 65 countries, this campaign is currently concentrated in China, Turkey, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia and India.
Moving forwards, the campaign needs to promote the full breadth of our UK education sector, including independent higher education providers, schools, English Language Teaching (ELT), skills and training providers, EdTech and TNE, in addition to our excellent universities. The GREAT Challenge Fund has already funded over £1 million of education-related activity over the past 2 years. Over the next year we will work across government to prioritise education bids, providing a springboard for promoting the UK education offer overseas.
Action 2
The UK government will ensure Education is GREAT promotes the breadth and diversity of the UK education offer more fully to international audiences, from early years through to higher education. We will encourage education bids to the GREAT Challenge Fund for 2019. This £5 million fund supports export activity for the sector across the globe.
Education is GREAT will continue to help amplify and signpost the full geographical range of the UK education offer, encompassing the rich diversity of the education offer across England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. This will complement promotion activity that also takes place across Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Programmes such as the ‘Scotland is Now’, ‘Study in Wales’, ‘Global Wales’ and ‘Invest Northern Ireland’, all provide additional platforms to drive international activity and promote the education strengths of Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland to international audiences.
1.5 Attracting and welcoming international students
The UK hosts the second-largest group of international higher education students in the world. International students make an invaluable contribution to British society, bringing with them new knowledge, cross-cultural understanding and global friendships, enriching the education experience of domestic students.
International students play an important role in maintaining the viability of certain courses so that our domestic students can continue to access them. They also bring important revenue to the UK higher education sector and to the UK economy. International students have the potential to become some of the UK’s best advocates overseas.
As a longstanding policy, there has been no limit on the number of international students who can come to the UK – we have seen record highs in numbers of non-EU international students, with over 170,000 non-EU entrants to UK higher education institutions for the seventh year running in 2017 to 2018. This policy will continue into the future.
At the same time, the global market for international student recruitment is changing. The British Council suggests that, as international student numbers continue to grow, so too do the number of competitors. In the face of such challenges, we cannot afford to be complacent and we must do more to ensure that a high-quality student experience remains at the heart of our offer, and that international students continue to see a UK higher education as a valuable, long-term investment.
That is why this strategy sets out an ambition to increase the numbers of international higher education students studying in the UK to 600,000 by 2030.
Case study : Merchiston Castle School in China
Merchiston Castle School, a leading all-boys independent boarding school in Scotland, joined a DIT mission to mainland China in December 2016. Alongside meeting potential partners, Merchiston began negotiations on setting up schools in China and signed an agreement to do so in mid-2017 with the parent of a former pupil.
During this period a policy change was announced in China that impacted international schools. The Department for International Trade’s Education team worked with Merchiston and its Chinese partner to help them set up a foreign passport holder school to mitigate risks and to provide insight on choosing a site for their first school in Shenzhen.
The school officially opened in August 2018 and successfully enrolled its first cohort of students.
We know domestic and international students value the international classroom experience they get in UK institutions, the diversity of their cohorts and the global networks available to them after graduation. We also value this diversity and will look to ensure that the UK always has students coming from around the globe and recruitment follows sustainable patterns. We will continue to provide and will promote a competitive, welcoming offer for international students by seeking opportunities, both in the UK and overseas, to promote study in the UK and the UK’s strong enthusiasm to host international students.
The government’s 2018 immigration white paper, The UK’s Future Skills-Based Immigration System, sets out a number of positive changes to the visa offer for international students.
We will increase the post-study leave period to 6 months for all masters and undergraduate students at institutions with degree awarding powers, and to 12 months for all doctoral students. During the post-study leave period, students will have unrestricted access to work. We will also make it easier for international higher education students to move into skilled work in the UK should they wish to do so, by allowing them to apply for a skilled work visa 3 months before their course ends, or to switch into skilled work from their home country for 2 years after graduation.
Action 3
The UK government keeps its visa system under review to ensure it remains fit for purpose and that the UK’s visa system is world-class. Government will strengthen the UK’s visa offer for international higher education students by increasing the post-study leave period and making it easier for students to move into skilled work after graduation.
We also want to ensure that international students have a positive experience in applying to study in the UK. In 2018, 97% of students applying for a Tier 4 visa to study in the UK were successful[footnote 11], but we will consider ways in which we can improve the application process and encourage more students to study in the UK. We are clear that international students are welcomed and valued in the UK, but we must redouble our efforts to amplify this message. This will include the whole of government promoting our visa offer, highlighting that there is no limit on the number of international students that can study in the UK and that we are improving our post-study offer.
Action 4
The UK government will keep the visa application process for international students under review, with the aim of improving the customer journey both for students and their sponsoring institutions. This will include reviewing processes for conducting interviews to ensure that these are appropriately focussed and to minimise any inconvenience for applicants.
Action 5
The UK government will work with Universities UK International (UUKi) and the sector to identify and share good practice in how universities effectively support international students into employment and further study, both here in the UK and when they return to their home nation. We will also work with the sector to enhance the evidence base on international graduate outcomes and to monitor the UK’s comparative position with respect to international student recruitment and the international student experience.
1.6 The UK government’s global agenda
In the context of the UK’s departure from the EU, and as part of its global ambition, the government has launched a series of interconnected strategies and policy objectives which together set out the UK’s position and aspirations on the global stage. These are mutually reinforcing, and this document is the latest contribution to that broader picture.
The Export Strategy, published by DIT in August 2018, sets out the UK’s exporting ambition and how the government will help businesses make the most of opportunities presented by markets around the world. This strategy contributes to that exporting ambition and is modelled on the same roles for government partnering with the sector to encourage, inform and connect.
These roles are focused directly on breaking down the barriers to export and each is supported by a set of resources and initiatives, including great.gov.uk[footnote 12], the DIT’s UK-based sector teams and the UK government’s international network of Trade Commissioners, Ambassadors and High Commissioners. These initiatives and resources will also support the delivery of this strategy, as it fits within government’s wider ambitions for exporting.
The Export Strategy also recognises the role of government in ensuring that no viable UK export fails for lack of finance or insurance from the private sector. That is why UK Export Finance (UKEF), as part of DIT, can play a key role in supporting education exports by providing a range of flexible support, including guarantees to banks and the provision of insurance to both exporters and overseas investors.
As set out in the 2017 white paper Preparing for our future UK trade policy, when the UK leaves the EU, it will have its own independent trade policy for the first time in over 40 years. The UK will take this opportunity to expand on our existing trade relationships and push for greater access to other countries’ markets for UK services and services providers.
The UK’s Industrial Strategy, published by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) in November 2017, sets out how the UK will develop its emerging and established strengths to boost productivity and become a world leader. This document builds on this through the potential offered by education exports to support the growth of the sector more broadly, both at home and overseas. For example, we will be investing in support for additional PhDs in artificial intelligence and related disciplines and supporting universities to develop industry-funded masters programmes.
The UK Aid Strategy: ‘tackling global challenges in the national interest, published in November 2015, and Department for International Development’s (DFID) Education Policy : Get Children Learning, published in February 2018, both set out how overseas development activity helps UK education trade and investment opportunities overseas and strengthens UK influence.
The international engagement that is central to exports also serves the important development objectives of other countries. The solutions that UK education provides deepens the understanding and respect between the countries with whom we collaborate. This helps to shape our approach to identifying new and emerging global opportunities for UK providers.
The Foreign and Commonwealth Office’s (FCO) Global Britain policy sets out how the UK is reinvesting in our relationships around the world and demonstrating that we are open, outward looking and confident on the world stage. Education exports are an important contribution to this bigger picture.
Education exports contribute to the UK’s soft power, as well as generating economic value. The flow of international students, international collaboration between institutions and partnerships all help to generate goodwill towards the UK, on which we can build mutually beneficial relationships and interactions.
The white paper, The UK’s future skills-based immigration system set out plans for a new, global immigration system which will support an open, global economy in line with the Industrial Strategy. This aims for a highly skilled, innovative and highly productive workforce, and continues to place no limit on the number of international students that can come to study in the UK.
With education and research being devolved responsibilities, the respective strengths of the education systems across the devolved nations combine to enrich and strengthen the UK’s international offer as a whole.
Whilst it is important that the UK communicates a recognisable and cohesive brand overseas, it is also important that in identifying global opportunities and shaping global activity, we account for the unique nuances, needs and drivers throughout the UK. That is why the UK government will continue to work collaboratively with the devolved administrations to ensure education exports activity complements and reinforces their activities.
Case study : Bell in Saudi Arabia
Bell has grown from one prestigious English language school in Cambridge to an internationally recognised organisation with over 60 years’ experience. Bell experts ran a 4 year project at King Saud University to prepare around 20,000 students for undergraduate study at an English-speaking university.
In addition to a tailor-made curriculum and an intensive 20-hour week campus-based programme in Riyadh, students had access to online learning through a bespoke Bell self-study portal. Over 70 teachers were trained for internationally recognised teaching qualifications by Bell and over 350 members of staff were recruited. 100% of students achieved Key English Test level certification and more than 50% achieved Preliminary English Test level.
The students acquired the language knowledge and skills necessary to study an undergraduate degree course.
1.7 A whole-of-government approach
The government recognises that to be effective, the ambition and activity set out in this strategy need to be supported by clear leadership and a joint UK government agenda. We must speak with one voice on our international ambition, and seek opportunities to maximise resources, networks and expertise for shared objectives.
In countries around the world, the government works together both for and with the UK education sector to develop opportunities, build partnerships and tackle challenges. The FCO, DfE, DIT, the British Council, DFID and BEIS all play important front-line roles in facilitating market access, shaping international agendas and opening opportunities for UK trade, influence, relationships and partnerships. The devolved administrations also play an important role in championing the strengths and supporting the interests of providers in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Education is an important part of a larger whole and it is essential that this is brought together in a cohesive and meaningful way. Building on the principle of the Export Strategy, we will adopt a ‘whole-of-government’ approach to international education which will help to ensure that specific strands, such as education exports, international research and innovation, soft power and overseas development effectively support each other and form a collective contribution to the UK and international partners’ interests.
We will also work with the sector to continue to strengthen the UK market, in particular by ensuring that our world class higher education system remains highly attractive to international students. To do this we need strong partnerships across government, the devolved administrations, local partners and with private and third sectors.
This whole-of-government approach will enable us to deliver the strategy’s actions and provide a coordinated approach to supporting the education sector.
Action 6
The UK government will enhance the Education Sector Advisory Group, co-chaired between DIT and DfE, as a partnership between government and the sector to implement this strategy, identify new opportunities and work jointly to identify solutions to challenges.
This will be supported by a cross-government, senior official-level International Education Steering Group, jointly chaired by DfE and DIT and including representation from the Home Office, FCO, DFID and other government departments.
2. The UK’s global ambition
2.1 Our global opportunity
There are many opportunities for the UK education sector. The total number of students studying overseas in higher education has risen from 2 million in 1999 to an estimated 5 million in 2016[footnote 13]. Although the average annual global growth rate of outbound students is projected to slow over the next 10 years, this will remain a vital market for the UK education sector.
In many regions around the world, there is a drive towards knowledge-based economies bringing together academic and technical skills education. This presents a significant opportunity for our technical and skills education sectors to export their services and contribute to developing a highly skilled global workforce.
As the demand for technology in the classroom grows, the UK has the opportunity to deliver creative and innovative solutions to the global challenges of teaching and learning in the 21st century.
The UK is well placed to take advantage of this global picture. We have strong historical links with many countries around the world. Underpinning these benefits are positive cultural relationships and the widespread use of English as the global language of business. Many UK education providers are already exporting successfully.
Leaving the EU gives the UK the freedom to pursue an independent trade policy that reflects its unique strengths. The UK will pursue ambitious trade agreements with other countries, which seek to tackle barriers to trade, provide greater certainty and reduce costs for exporters, whilst ensuring continued protections and exemptions for public services. Education services will form part of our trade policy considerations to make sure the sector can exploit the opportunities presented by these future agreements.
2.2 Setting our regional priorities
All UK education providers can access extensive government support, both in the UK and overseas. In the UK this takes the form of the DIT’s education sector team, the British Council, and regional trade advisers. Overseas, providers can access trade specialists across 108 countries and the government’s broader international network including 270 diplomatic posts in 168 countries, supported by DIT and the FCO.
DIT’s education team comprises civil servants and education specialists working with the sector and our international network to understand the exporting capabilities of UK education, tailoring government services to the needs of education providers, co-ordinating government-to-government engagement, and representing exporters to improve the policy environment domestically and overseas. Day-to-day, they organise trade missions, host overseas visitors, promote the UK at global education exhibitions, and work to bring more inward investment to the UK.
The government also helps advise UK institutions on how safely and securely to get the most out of education exports. It is important that we prioritise this support to where it can deliver maximum value for our education providers. It must be aligned to the principle of doing only what government can do.
This prioritisation has been driven by 3 factors, based on the criteria set in the Export Strategy:
- international opportunities – we will focus on markets with the largest potential for UK education providers.
- UK capability and capacity – we will recognise the UK education sector’s strengths and ability to provide bespoke solutions to each country’s educational needs.
- the government’s wider strategic stability, prosperity and security objectives
We recognise that education is not like other exports. In almost every country in the world, education is a priority, but there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Different global regions have different educational needs. Every country has its own opportunities and its own barriers to overcome. This is why in setting our regional priorities we have put further emphasis on the feedback we receive from the sector, market intelligence, other countries’ strategic and development priorities, and the experiences of existing UK exporters.
This approach has led us to identify 4 ‘high-value’ campaign regions:
- China and Hong Kong
- the Middle East and North Africa
- Latin America
- the ASEAN group of nations
Prioritising this group of regions allows government resources to be deployed towards developing and fast-growing education markets, where market access barriers are highest and where government can have the most impact. These regions also have a high concentration of countries undergoing education reform, which presents UK providers with a range of export opportunities.
Case study : Pearson in Thailand
Pearson, the digital learning company, received an official endorsement from the Thai government which allows BTEC qualifications to be delivered in every vocational and higher institution in Thailand, both in the public and private sector.
The pilot implementation began in December 2018 with the view to expand BTECs across 800 vocational institutions in Thailand. A delegation from the Thai Ministry of Education visited Pearson in November 2018 supported by the Department for International Trade, to discuss current and future plans and to sign an agreement between Pearson, the Ministry for Education and trade bodies of Thailand to work together on BTEC implementation.
2.3 High-value regions
These regions present many opportunities for UK providers, but various barriers and complexities mean that accessing these education markets can be difficult without the support of government. The regions share common features that underpin their high value and potential, including:
- a drive from governments to prioritise investment in education and research
- demand for the best learning experiences from the expanding middle classes
- economies that are diversifying towards skills, knowledge and services
Action 7
DIT will prioritise resources to support educational opportunities in the key geographic regions of:
- China and Hong Kong
- the ASEAN region
- the Middle East and North Africa
- Latin America
We will review current activity and expand our reach in these geographic areas. We will seek to better understand areas of opportunity in countries where DIT’s presence is less developed.
The ASEAN region
Opportunities in the 10 ASEAN countries differ substantially across the region. There are also various barriers that face UK providers, particularly the recognition of international qualifications. Government can provide support, such as demonstrating how the UK can provide solutions to these different countries’ challenges.
For example, in 2018, the Union of Myanmar Federation of Chambers of Commerce and Industry, British Embassy in Yangon and DIT organised a Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) conference in Burma to identify and close the growing gap between graduate skills and market needs. TVET is a priority in the country’s National Education Strategic Plan 2016 to 2021. Progress is being made, but UK providers will require further government support to unlock regulatory obstacles.
China and Hong Kong
China and Hong Kong is a very important market for UK education exports. UK providers from early years through to schools, skills, EdTech, ELT and higher education have all achieved significant traction in the region and we continue to see strong numbers of students from China and Hong Kong choosing the UK as their study destination. However, a change of approach may be needed in response to changing Chinese law, most recently impacting early years and schools. It is only through government-to-government engagement that we will be able to deliver the best operating environment for UK providers in China and Hong Kong.
The Middle East
There is a real appetite across the Middle East to strengthen education relationships with the UK. Stabilisation in the region is a key government objective, and the UK is well placed to offer that through education partnership. We remain alert to emerging opportunities across the region but given its many complexities it is vital that government supports the UK education sector. For example, supporting UK providers to identify opportunities resulting from the Saudi Arabian Government’s Vision 2030 programme and engaging with potential Saudi partners.
Latin America
Latin America offers a significant range of opportunities for the UK education sector. Building on the successes we have already had in several countries within the region, we will continue to support the sector by addressing legal and regulatory barriers.
An example of a successful model for broaching barriers in this region is our annual Brazil Education Working Group, which focusses at federal government level on key education topics, provides a platform for exchanging information and addressing potential challenges. We will learn from this method of engagement and look to apply it in other countries, where appropriate.
2.4 Potential growth regions
The UK education sector is active in almost every country in the world, but the scale of opportunity, and the type of activity being undertaken, has not previously justified a strategic approach supported by the UK government. However, more regions are demonstrating potential for an increased level of engagement. As our involvement with these other regions develops we will seek feedback from the sector through the Education Sector Advisory Group, and market intelligence, to gauge whether they should become priority regions.
There is growing interest in the education sector to understand more about opportunities in Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa where there is already some level of engagement by higher education institutions and schools. As with our more established partners, the demand for skills across Africa is significant and we must ensure that UK providers are in the best position to play a competitive role in meeting that demand for developing local capacity.
There is a long and important history of Indian students coming to study in UK universities and we intend to drive further growth through a number of the action set out in this strategy. This is alongside growing opportunities for more university partnerships. We will also look to grow the EdTech and supplies sectors whilst also being alert to growing opportunities in Central Asia for the ELT sector.
The UK’s departure from the European Union offers a series of opportunities for the education sector to engage afresh with the continent. We will build links through new and emerging markets, such as TNE, ELT, TVET, independent schools and early years provision, while cementing our position as the European leader for EdTech. As our future relationship with the EU matures, we will help providers to understand any new regulatory requirement for operating in Europe.
We will look to strengthen relationships with the United States of America, Australia and Canada by exploring opportunities to expand a more tailored UK offer that meets demand, for example, through lifelong learning providers and our chartered professional bodies. Both the US and Australia have well developed EdTech industries, but they are also hungry for new and innovative technology. The sector has told us that government can support them in these markets by helping to facilitate access to potential buyers and partners.
The UK has completed public consultations on potential trade agreement negotiations with the United States of America, Australia and New Zealand, and on potentially joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), a trade agreement amongst 11 countries across the Asia-Pacific.
Action 8
The Department for International Trade’s Education Team will work with UK government colleagues overseas to identify new opportunities for the sector and support UK providers in meeting those needs.
3.Global reach
3.1 Global partnerships and soft power
Whilst this strategy aims to facilitate growth in education exports and in the UK’s share of the global education market, our approach to international engagement is also based on a desire to help our partners build their education systems and deliver some of the expertise and resources that can support their aspirations. We work with UK education sector providers, the British Council, UK and global industries, and governments around the world to deliver the expertise and resources that can help other countries meet their aspirations.
This strategy is supported by a network of initiatives, such as the Skills for Prosperity programme and the #LeaveNoGirlBehind joint girls’ education campaign between DFID, the FCO and DfE, which will accelerate global action to ensure 12 years of quality education and learning for all girls by 2030.
The campaign aims to build international political commitment and global investment in education, harness UK expertise to ensure countries deliver quality education, and successfully deliver DFID’s Girls’ Education Challenge programme and a range of bilateral education programmes.
Education exports are just one tool that help to generate this broader global reach, creating opportunities to build international engagement and soft power. In particular, they help forge the relationships where other countries are able to draw on learning and best practice in the UK to respond to their own development needs, from quality assurance and accreditation, through to curriculum and teaching.
Major education transformation initiatives in developing countries are often funded with the support of international donor organisations, including multilateral development banks. Taking part in these programmes can deliver real benefits for improving education outcomes and supporting poverty reduction. Several UK providers have already delivered donor funded programmes successfully and we will continue to encourage bids. DIT will trial a new initiative in 2019 to assess how best to engage with donor organisations and will share lessons with the UK sector.
However, we cannot focus solely on promoting UK education abroad. We have a tremendous amount to learn from other countries and their education systems.
Through our international relationships we observe other nations’ best practice and innovative approaches to education which then help to inform how we deliver reform and improvements in the UK. For example, we have drawn on elements of German and the Dutch vocational training systems and introduced them into the English system.
In England, we are bringing in a new approach to teaching mathematics based on best practice from Shanghai and Singapore. This principle of mutual learning and partnership will continue to underpin our international engagement as we continue to look for new opportunities and great examples of global best practice.
3.2 Global mobility and exchange
Mobility and exchange are key components in forging international partnerships. Enabling this flow of people, both into and out of the UK, helps to strengthen the connectivity and export opportunities for our education sector.
Cultural exchange builds important academic, business, political and diplomatic bridges around the world. Supporting students to study abroad helps create a new generation of globally mobile, culturally agile citizens who can succeed in an increasingly globalised world. Equally, outwardly mobile young people can function as ambassadors for UK education, raising the profile and reputation of individual institutions and UK education internationally. Their experiences and presence abroad are further evidence that the UK is outward looking and internationally minded.
In short, mobility and exchange must be a part of any broader internationalisation agenda. That is why we have endorsed, and continue to support, Universities UK International’s (UUKi’s) ‘Go International: Stand Out’ campaign to double the percentage of UK-domiciled students experiencing outward mobility as part of their degree by 2020.
The UK has played an important part in developing and shaping the Erasmus+ programme and its predecessors, which have benefited millions of Europeans over the last 30 years, including over a quarter of a million from the UK. Between 2014 and 2016 there were over 100,000 outward (mobile) placements from across the UK education and youth sectors, involving both staff and learners. In the period between 2014 and 2015 there were nearly 130,000 inward mobile placements[footnote 14] .
As stated in the white paper on the future relationship between the UK and the EU, we are open to exploring participation in the successor scheme to the current Erasmus+ programme.
We continue to support the Chevening, Commonwealth and Marshall Scholarship Programmes alongside other initiatives specific to the devolved administrations, such as Scotland’s Saltire Scholarship Programme. The FCO has also increased the number of international places offered on its prestigious International Defence Training courses, from 1,221 places in 2015 to 2016 to 2,240 in 2016 to 2017.
At the same time, we are also supporting UK students to broaden their horizons through experiences of working and studying abroad. In December 2017, and again in September 2018, we announced expansions of the British Council’s Generation UK-China scheme, giving even more young people from disadvantaged backgrounds the opportunity to take up internships in China each year. We also fund the Study China Programme: a 3-week taster of Chinese language and culture for undergraduate students in England.
In September 2018, we announced an additional £400,000 per annum for the US-UK Fulbright programme. This will provide increased opportunities for talented postgraduates and professionals to study at world class British and American universities.
Case study : US-UK Fulbright Commission
Founded in 1948, the globally renowned Fulbright Commission provides valuable opportunities for outward mobility, awarding grants to masters students and post-doctoral academics and professionals, allowing them to pursue research on either side of the Atlantic.
In 2017 to 2018, 36 US masters students and 42 US post-doctoral scholars were funded to come to the UK for 3 to 12 months and 19 UK masters students and 23 UK post-doctoral scholars were funded to go to the US.
Fulbright also run programmes such as the highly successful social mobility programme for UK undergraduates to study in the US, funded by the Sutton Trust, and study abroad summer institutes for US undergraduates to come to the UK. The global Fulbright Programme has many notable alumni, including 33 heads of state or government and 57 Nobel prize winners.
4. Equipping the sector to reach its global potential
4.1 The role for government
We recognise that ambition and ownership from the sector will be the key factors in driving growth in exports. This section sets out how the government will connect, inform and encourage providers, to support their international efforts. DIT’s Education team will lead much of the direct work with the sector.
Figure 2: Share by revenue stream of education related exports and repatriated income from TNE activities, 2016 (£billions in current prices)
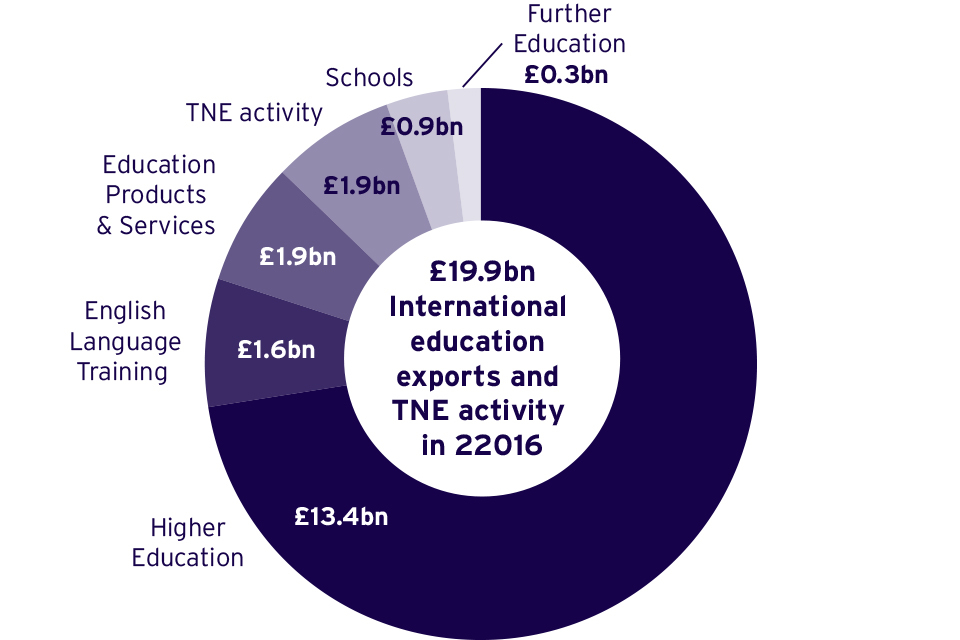
Share by revenue stream of education related exports and repatriated income from TNE activities, 2016 (£ billions in current prices)
Source: DfE (2019)
According to the latest statistics, international education exports brought an estimated £19.9 billion to the UK in 2016. Around 67% of that was from the higher education sector. Although higher education is evidently the dominant sector, this strategy sets out to promote a more holistic UK education international offer. It sets out to boost growth across all parts of the education sector.
Some sectors have experienced growth in the value of education exports, on which we can build. The value of TNE for example, rose by £779 million between 2010 to 2016, from £1.07 billion to £1.85 billion. Revenue from independent schools also rose by 48% in the same timeframe from £630 million to £930 million[footnote 15].
The following actions have been developed in response to the aspirations of the education sectors, and the challenges and opportunities providers have identified. These present a starting point for boosting activity and ambition across all the education sectors and bringing together a more complete UK education offer.
The actions will be monitored through the Education Sector Advisory Group and official’s steering group. They will be updated in the annual strategy review. This will provide an opportunity to add further actions in response to emerging sector developments, challenges and opportunities. DIT will continue to review the support needed by individual education sectors, and throughout the devolved administrations, and will adapt their activity to that need.
Case study : BESA in China
The British Educational Suppliers Association (BESA) identified strong demand from China for quality British educational products and services. This market is worth $500 billion, with $677 million spent on EdTech each year. Working closely with DIT and DfE, BESA ran a dedicated ministerial trade mission for EdTech companies to Beijing and Shanghai in 2016.
BESA has taken companies back over 10 times. A highlight in 2018 was a ‘Great British Classroom’ showcasing the best of British digital resources to Prime Minister Theresa May and Chinese hosts during her visit. BESA has since signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the Chinese Educational Equipment Industry Association and the China Modern Educational Equipment organisation opening doors to future collaboration.
4.2 Improving education exports data
UK government publishes annual estimates of the value of education exports. This information allows stakeholders to determine how the sector is performing overall and map where the opportunities for growth may lie.
The statistics currently produced are experimental and still need to be fully developed and rigorously tested to ensure they meet required standards for national statistics. They are published so that users and stakeholders can be involved in the assessment of their suitability and quality at an early stage.
Across the education sector, the data used to compile our estimates come from multiple sources, some with varying quality or partial coverage. This limits our ability to provide a clear view of growth and trends. We would like to move to a position where we can produce a more robust overall estimate of the value of education exports.
Action 9
UK government will provide a clearer picture of exports activity by improving the accuracy and coverage of education exports data. DfE, in partnership with DIT, the sector and other key bodies such as the Office for National Statistics (ONS), will work in between each annual data publication to strengthen the methodology, identify a better range of sources, and look for ways to deliver more accurate, up-to-date reporting.
Throughout, government will continue to look for ways to develop our picture of the global education market and regional trends, where the data allows, better to inform government and sector priorities.
There will be ongoing work across government and with sector bodies to improve the accuracy of the education exports data. We will use these discussions to gather feedback from stakeholders on the following aspects:
- coverage: bringing in sectors currently excluded due to data quality concerns or lack of data
- accuracy: refining the assumptions used to improve our overall estimates
- timeliness: making use of the most recent data where possible
- explanation: better communication of the limitations of the data sources used
- consistency: aligning with other statistics on exports and imports
- presentation: publishing the data in the right format to meet the needs of users and making it more accessible
We remain committed to annual publication of the education exports data so that we can continue to update and strengthen the picture of education exports performance and utilise that information to put in place appropriate metrics to set and measure market share.
4.3 Early years
There has been a significant increase in the global supply and demand for early years education. UNESCO reports that between 1999 and 2012 there was an increase of nearly two-thirds in the numbers of children enrolled in pre-primary education worldwide[footnote 16]. With a growing number of countries introducing compulsory pre-primary education, the need for quality early years provision will continue to grow.
Most of the UK early years sector is at an early stage in its exporting journey. Currently, few providers are equipped to take advantage of emerging global opportunities. There are some great examples of internationalisation, but UK early years providers are not yet exporting at scale. By modelling best practice identified in preparing the schools sector for exporting and overseas delivery, the following actions set out how we will support the early years sector to do the same.
Action 10
DIT will work with relevant sector bodies such as the Early Years Alliance and other industry bodies to inform providers about exporting opportunities. We will deliver a new programme of targeted training and information sessions to existing and interested providers.
Accurate and robust data should drive all our export decisions. The UK early years sector has real potential for growth on the international scale, but to achieve this it needs reliable information on where the best opportunities are for different types of providers.
Action 11
DIT will encourage the growth of the early years market by sharing more intelligence with the sector about the scale and scope of international opportunities.
In implementing these actions, we will consider the nuances and regional differences of the early years offer across the UK and ensure devolved administrations are included.
4.4 Independent schools
In 2017, there were more than 8,000 international schools teaching over 4.5 million students around the world. In the next 10 years, this is projected to increase to nearly 9 million students studying at more than 16,000 international schools[footnote 17]. China has been a driving force as parents seek to give their children the very best in international education, while we are also seeing growing demand for UK schools in the European market.
The UK’s independent schools are riding this global wave, with more believed to have opened overseas in 2018 than over the past 20 years. An estimated 46% of the 8,000 English-medium[footnote 18] international schools around the world adopt elements of the UK curricula (including Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland)[footnote 19]. We want to support this ambitious sector in its aspirations for continued international growth, including in the European market where we are seeing growing demand for UK schools.
Action 12
DIT will encourage independent schools to access international opportunities, using improved education exports data to identify the top countries where there is the most opportunity for UK schools. We will connect providers with investors and work with key sector bodies to produce information guides for schools interested in developing an international presence.
International pupils now make up roughly 5% of the independent school pupil population in the UK[footnote 20]. They bring with them and international outlook and rich cultural diversity. Schools in the UK have a global reputation for the safeguarding and wellbeing of all students, and this regulation, embedded in UK law, provides an excellent reason for parents to choose the UK.
Action 13
DfE, working with DIT, will coordinate efforts across government and key sector bodies to promote the quality and safety of our schools, both in the UK and overseas, by advocating the British Schools Overseas Inspection Scheme. We will encourage independent schools to have a better understanding of guardian arrangements, learning from those schools that do this well and the important role of accreditation bodies.
4.5 English language training
English is the dominant global language. It is spoken by around a quarter of the world’s population as the primary language for international business, science and academia. It is predicted to continue growing in importance, proliferated via film, TV and social media. Estimates suggest that over half of the Internet’s information is stored in English[footnote 21].
Emerging and developed economies recognise the important role that the English language plays in national development, with it contributing to employability, economic development and global connectivity[footnote 22]. Europe, Latin America, Asia and the Middle East in particular are English Language Training (ELT) growth markets.
From summer schools to pre-sessional academic English courses, the UK ELT sector helps prepare students for enrolment in UK schools, colleges and universities. Unlike some other education sectors nearly all ELT providers export, through overseas provision and provision to international students within the UK.
The UK has traditionally been the leading destination for ELT students. However, we face increasing competition from countries like Australia and Ireland. In 2017, over half a million people came to the UK to study English, generating an estimated £1.4 billion in exports earnings[footnote 23]. To continue this growth we need to increase the UK’s capacity to meet the growing demand for ELT and better promote the sector’s strengths.
Action 14
DIT will work closely with the ELT sector, providing information to increase their involvement in exporting services and expertise. We will organise workshops to encourage ELT providers to take advantage of export opportunities. We will also provide training on bidding for project work and establishing overseas centres, and logistical planning to support them to do so.
We recognise the important contribution of ELT to the UK’s broader international education offer. We must do more to foster partnerships between the ELT sector and other internationally focussed sectors. For example, English language training can feature more prominently in export campaigns for industries where English is the primary language, such as oil and gas, finance, hospitality and healthcare. We can also do more to promote the UK as a study destination for ELT students, through a more proactively positive and welcoming message in the UK.
Action 15
DIT will inform the UK ELT sector of global opportunities linked to other industries. We will ensure that ELT providers have the opportunity to take part in a broader range of DIT-led activity where ELT could play a more prominent role.
Action 16
DIT will utilise our exports pipeline database to exploit opportunities overseas for promoting the English language and the UK ELT sector, as valuable contributors to individual and national prosperity.
4.6 Technical and vocational education and training, skills and colleges
There is limited international data about the global demand for TVET, but we know there is strong demand for TVET overseas as countries look to increase their national skills competencies to meet global labour market demands[footnote 24]. DIT is regularly approached by countries in the ASEAN, China, the Middle East and North Africa and Latin America regions hoping to access UK expertise in the skills and training sector.
This is particularly true of countries who want to develop their manufacturing industries and there is a real, fast growing demand for skills across the industrial spectrum. The World Economic Forum estimates that as the Fourth Industrial Revolution unfolds no less than 54% of all employees worldwide will require significant re- and upskilling, by 2022[footnote 25]. The opportunity to work whilst studying for vocational qualifications is an increasingly attractive offer and people are embracing learning as adults. In 2016, 45.1% of adults aged 25 to 64 across the EU participated in education and training[footnote 26], compounding the demand for TVET providers.
The Further Education and TVET sectors encompass a broad range of education and skills provision, and many different types of providers. It is important that providers with the willingness and capacity to support internationalisation are able to do so, alongside sustaining essential domestic provision.
Significant reforms and changes to the domestic environment have limited the sector’s international growth. We hear regularly that the UK international skills offer is one of the UK’s lesser-known strengths that has the potential to be significantly more successful than it is currently, so we want to take advantage of this demand where there is capacity to do so. UK providers have a positive track record of developing bespoke skills solutions.
Amongst UK colleges, 28% have specific ‘consultancy’ offers that they deliver overseas[footnote 27], with UK providers successfully developing tailored skills solutions that are coherent and sympathetic to existing systems. The UK Skills Partnership, created in 2017, includes a broad range of UK providers across the UK skills sector and plays a significant role in promoting the UK skills offer internationally.
The UK has extensive experience of employer involvement in skills development through training bodies, continuing professional development initiatives and apprenticeship schemes. According to the CPD Certification Service, we have over 1,000 career professional development organisations and professional bodies across the UK, a number that is forecast to increase[footnote 28].
Action 17
DIT will encourage a greater proportion of UK skills organisations to consider taking their offer internationally, where there is capacity to do so. We will provide training, support and access to UKEF. From 2019, we will develop formal networks across government to highlight the capabilities of the UK TVET offer and its relevance to skills development across all industrial sectors. We will create and deliver a focused programme of support to the TVET supplier network, promoting the offer available from UKEF.
Action 18
DIT and DfE will continue to utilise government-to-government and government-to-industry links overseas to promote the UK skills offer. DIT will build on the UK Skills Partnership that brings together the best of the UK skills offer to provide coherent, structured and bespoke solutions to overseas partners.
Case study : Grŵp Llandrillo Menai (GLLM) in Malaysia
Following early successes delivering short-term TVET projects in Malaysia, a Partnership Agreement between GLLM and A and E College Pvt Ltd Malaysia focussed on implementing a quality assurance service to support capacity building in several Malaysian colleges. GLLM staff shared their expertise to examine and study the Malaysian Colleges’ curriculums, benchmarking all course content, delivery and student work to a highly accurate standard.
This collaboration also enabled GLLM’s learning, to develop and improve their own provision. This transnational partnership provided students with increased opportunities to study in the UK, increased GLLM’s student numbers from Malaysia, increased revenue and helped to develop a foothold in the Malaysian market.
4.7 Higher education
Higher education is a valuable export alongside its important role in developing international relationships, facilitating the exchange of people, knowledge and ideas, and helping to build soft power. The latest data for 2016 estimates its export value including TNE activity at over £14 billion[footnote 29].
The UK continues to be the second most popular global destination for international higher education students. International higher education student numbers in the UK have increased since 2011 and are now at record highs and there continues to be no limit on the number of students who can come to study here. In the same period, the global market for international students has expanded by over 30%[footnote 30]. The USA, Australia, Canada and New Zealand have all taken advantage of this growth and, like the UK, successfully and significantly increased their international student numbers.
That is why we have set out an action to promote a more competitive, welcoming offer for international students. This offer includes increasing the leave period for work experience after graduation to 6 months for all masters students and undergraduate students attending institutions with degree awarding powers, and 12 months for PhD students. This complements our efforts to identify where we can improve the visa process, tackle myths and misconceptions around the student offer and make existing and prospective students feel more welcome.
Higher Education Statistics Agency (HESA) data shows that nearly 710,000 students were enrolled on the UK’s higher education TNE programmes outside the UK in 2016 to 2017[footnote 31]. These student numbers have grown by over 20% in the last 5 years. That is why we are also looking to support TNE as a key growth area.
TNE offers UK universities and their partners a range of benefits and positive outcomes. However, we recognise that there are considerable challenges to working overseas, both in established and new markets, and will focus on supporting providers which are able and willing to do so.
Action 19
DfE and DIT will work with the higher education sector and the British Council to identify more accurately the overall value of TNE to the UK economy. We will seek to provide better insight into potential markets for both new and existing providers, and to improve the overall evidence base around best practice and impact.
Action 20
DIT will encourage the sector to grow TNE by engaging in dialogue with countries with recognised export potential. We will work to resolve regulatory barriers through international agreements and the work of the International Education Champion. We will work to ensure these agreements include the recognition of UK degrees, including online and blended learning programmes.
Action 21
DIT will work with Universities UK international and the British Council to inform the UK sector of global opportunities for TNE through exhibitions, webinars and engagement sessions. We will support TNE activity by producing country-specific guides that support targeted partnership development and by actively facilitating partner matching between UK providers and potential international collaborators. These guides, which will be produced for 2020, will focus on countries of particular interest and opportunity for the sector.
These actions will directly support higher education providers’ activity in both existing and new markets and help to increase the number of students registered on UK higher education TNE programmes.
Case study: The University of Liverpool and the Philippines
Bicol University (BU) and Central Luzon State University (CSLU), the Philippines and the University of Liverpool (UoL) UK, established a new partnership in 2017 under the UK-PH Now TNE links programme.
It addresses research and training in the discipline of sustainable food systems, a strategic common interest to Bicol, CSLU and Liverpool. The importance of food security in providing affordable nutrition through sustainable agricultural practices and resilient supply chains is an urgent global challenge.
This partnership provides new innovative education and research activities, focused on sustainable food systems. Underpinned by a comprehensive postgraduate training programme, it supports the development of high calibre researchers in the Philippines, and fosters international collaboration in interdisciplinary research on food security.
There are 2 programmes: the masters degree in sustainable food systems is offered as a dual award from BU and UoL for Philippine students. The first year of the Programme is taught at Bicol University, students then transfer to Liverpool for their second year. A common research project links the 2 years of study. Liverpool and CSLU offer a dual PhD award. Student supervision is provided by supervisory teams from both universities with research investigations conducted in both the Philippines and the UK.
4.8 Education technology suppliers
The global education technology market is growing, driven by increasing penetration of SMART devices and greater and better access to the Internet. An increasing understanding of the potential benefits of using technology in education is also driving growth. The total export value of the UK EdTech sector is estimated to be around £170 million[footnote 32] and the Digital Strategy (published by the government in February 2017) highlighted education technology as one of the fastest growing UK sectors, accounting for 4% of all digital companies[footnote 33].
UK providers are at the forefront of developing and bringing to market innovative and world leading education technology supporting, for example education administration, reduction of teacher workload, student and community engagement, excellent teaching and student attainment. The forthcoming Education Technology Strategy due to be published in Spring 2019, will outline the government’s plans to encourage the good use of technology across England through working with Industry, the education sector and academia.
We also know that the EdTech sector values practical support from government to facilitate international engagement. It mainly comprises small companies where margins, at least initially, are likely to be low. UK EdTech companies tell us that the ability to demonstrate their products to prospective buyers is extremely valuable. Even in the age of digital connectivity, a physical presence at international EdTech trade fairs and conferences can be vitally important in supporting companies’ international objectives. It is this physical presence that the UK government can help facilitate.
Action 22
DIT will encourage the EdTech and educational supplies sector to engage with buyers both in the UK and overseas. We will provide government leadership where necessary and appropriate. We will run information webinars and face-to-face events and provide information briefings on the EdTech landscape in our key markets, highlighting opportunities for providers.
Action 23
DIT will work with the sector to continue to showcase the UK EdTech offer and help to build a stronger UK EdTech brand, using initiatives such as the GREAT British Classroom. Working with the sector, we will also utilise innovative multimedia platforms to help providers demonstrate their products to a global audience.
Case study : Whizz Education
With DIT’s advice and guidance, Whizz Education secured major contracts as a partner for the Ministry of Education Michoacán, Mexico, opening up further opportunities in that market. DIT’s support included market access advice and Trade Access Programme funding for Whizz to attend BETT (British Educational Training & Technology show) Latin America, in Mexico.
Whizz Education now delivers services in Mexico, including Education programme design for raising standards in maths, and teacher training on deploying innovative ICT to deliver learning outcomes. In Michoacán alone, over 15,000 pupils (and growing) have benefited from individualized learning support and are achieving remarkable learning outcomes.
Annex A: actions summary
Action 1
The UK government will appoint an International Education Champion in 2019. They will be tasked with opening up international opportunities for the UK sector, connecting the education sector to overseas opportunities, and helping to overcome any challenges and barriers to growth.
Completion Summer 2019
Action 2
The UK government will ensure Education is GREAT promotes the breadth and diversity of the UK education offer more fully to international audiences, from early years through to higher education. We will encourage education bids to the GREAT Challenge Fund for 2019. This £5 million fund supports export activity for the sector across the globe.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 3
The UK government keeps the visa system under review to ensure it remains fit for purpose and that the UK’s visa system is world-class. Government will strengthen the UK’s visa offer for international higher education students by increasing the post-study leave period and making it easier for students to move into skilled work after graduation
Ongoing
Action 4
The UK government will keep the visa application process for international students under review, with the aim of improving the customer journey both for students and their sponsoring institutions. This will include reviewing processes for conducting interviews to ensure that these are appropriately focussed and to minimise any inconvenience for applicants.
Ongoing
Action 5
The UK government will work UUKi and the sector to identify and share good practice in how universities effectively support international students into employment and further study, both here in the UK and when they return to their home nation. We will also work with the sector to enhance the evidence base on international graduate outcomes and to monitor the UK’s comparative position with respect to international student recruitment and the international student experience.
Ongoing: review annually
Action 6
The UK government will enhance the Education Sector Advisory Group, co-chaired between the Department for International Trade and the Department for Education (DfE), as a partnership between government and the sector to implement this strategy, identify new opportunities and work jointly to identify solutions to challenges.
This will be supported by a cross-government, senior official-level International Education Steering Group, jointly chaired by the DfE and DIT and including representation from the devolved administrations, Home Office, FCO, DIFD and other government departments.
Completion Summer 2019
Action 7
DIT will prioritise resources to support educational opportunities in the key geographic regions of China / Hong Kong, the ASEAN region, the Middle East and North Africa, and Latin America. We will review current activity and expand our reach in these geographic areas. We will seek to understand better areas of opportunity in countries where DIT’s presence is less developed.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 8
The Department for International Trade’s Education Team will work with UK government colleagues overseas to identify new opportunities for the sector and support UK providers in meeting those needs.
Completion Summer 2019
Action 9
The UK government will provide a clearer picture of exports activity by improving the accuracy and coverage of education exports data. DfE, in partnership with DIT, the sector and other key bodies such as ONS, will work in between each annual data publication to strengthen the methodology, identify a better range of sources, and look for ways to deliver more accurate, up-to-date reporting.
Throughout, government will continue to look for ways to develop our picture of the global education market and regional trends, where the data allows, to better inform government and sector priorities.
Ongoing: review annually
Action 10
DIT will work with relevant sector bodies such as the Early Years Alliance and other industry bodies to deliver a new programme of targeted training and information sessions on international opportunities to existing and interested providers.
The sessions will be delivered in multiple formats, such as webinars and presentations at industry conferences. Starting from 2020 there will be at least one webinar every quarter and presentations at a minimum of 3 conferences each year. Webinars will be hosted on a regional basis given the differences in demand from different parts of the world.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 11
DIT will encourage the growth of the early years market by sharing more intelligence with the sector about the scale and scope of international opportunities.
This will cover opportunities for setting up overseas sites, teacher training and curriculum design for UK providers. We will identify those providers that want to expand their offer to find the best export opportunities for them.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 12
DIT will encourage independent schools to access international opportunities, using improved education exports data to identify the top countries where there is the most opportunity for UK schools. We connect providers with investors and work with key sector bodies to produce guides for schools interested in developing an international presence.
This will be supported by face-to-face training events across the UK that promote the benefits of having an international dimension to independent schools.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 13
DfE, working with DIT, will coordinate efforts across government and key sector bodies to promote the quality and safety of our schools, both in the UK and overseas, by advocating the British Schools Overseas Inspection Scheme. We will encourage independent schools to have a better understanding of guardian arrangements, learning from those schools that do this well and the important role of accreditation bodies.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 14
DIT will work closely with the ELT sector, providing information to increase their involvement in exporting services and expertise. We will organise workshops to encourage ELT providers to take advantage of export opportunities. We will also provide training on bidding for project work and establishing overseas centres, and logistical planning to support them to do so.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 15
DIT will inform the UK ELT sector of global opportunities linked to other industries. We will ensure that ELT providers have the opportunity to take part in a broader range of DIT-led activity where ELT could play a more prominent role.
From 2019, we will hold webinars and workshops in the UK to share sector best practice and identify large-scale international projects run by other UK exporters that require skills and training, which can be supported by language training.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 16
DIT will utilise our exports pipeline database and exploit opportunities overseas to promote the English Language and the UK ELT sector, as valuable contributors to individual and national prosperity.
From 2019, DIT will host joint webinars with the British Council to raise awareness of the ELT offer for the benefit of the UK education sector.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 17
DIT will encourage a greater proportion of UK skills organisations to consider taking their offer internationally, where there is capacity to do so. We will provide training, support and access to UKEF. From 2019, we will develop formal networks across government to highlight the capabilities of the UK TVET offer and its relevance to skills development across all industrial sectors. We will create and deliver a focused programme of support to the TVET supplier network, promoting the offer available from UKEF.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 18
DIT and DfE will continue to utilise government-to-government and government-to-industry links overseas to promote the UK skills offer. DIT will build on the UK Skills Partnership that brings together the best of the UK skills offer to provide coherent, structured and bespoke solutions to overseas partners.
From 2019, DIT will deliver knowledge-sharing events for clients and stakeholders, including webinars and briefing documents, to enhance their knowledge and view of the UK TVET sector as a worldwide, world-class operator.
From 2020, DIT will deliver a series of face-to-face information sessions and materials to increase the number of TVET providers who are registered on donor procurement portals and their level of success.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 19
DfE and DIT will work with the higher education sector and the British Council to identify more accurately the overall value of TNE to the UK economy. We will seek to provide insight into potential markets for both new and existing providers, and to improve the overall evidence base around best practice and impact.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 20
DIT will support the sector to grow TNE by engaging in dialogue with countries with recognised export potential. We will work to resolve regulatory barriers through international agreements and the work of the Education Champion. We will work to ensure these agreements include the recognition of UK degrees, including online and blended learning programmes.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 21
DIT will work with Universities UK international and the British Council to inform the UK sector of global opportunities for TNE through exhibitionss, webinars and engagement sessions. We will support TNE activity by producing country-specific guides that support targeted partnership development and by actively facilitating partner matching between UK providers and potential international collaborators. These guides, which will be produced for 2020, will focus on countries of particular interest and opportunity for the sector.
Completion Spring 2020
Action 22
DIT will encourage the EdTech and educational supplies sector to engage with buyers both in UK and overseas. We will provide government leadership where necessary and appropriate. We will run information webinars and face-to-face events and provide information briefings on the EdTech landscape in our key markets, highlighting opportunities for providers.
Ongoing: review Spring 2020
Action 23
DIT will work with the sector to continue to showcase the UK EdTech offer and help to build a stronger UK EdTech brand, using initiatives such as the GREAT British Classroom. Working with the sector, we will also utilise innovative multimedia platforms to help providers demonstrate their products to a global audience.
Completion Spring 2020
Annex B: Organisations engaged in the development of the strategy
- ACCENT London Study Centre
- Advance HE
- Alpha Plus Group
- Association of Colleges
- Bell
- Boarding Schools’ Association
- British Study Centres
- British Council
- British Educational Suppliers Association (BESA)
- British Universities’ International Liaison Association
- Busy Bees
- Cardiff and Vale College, representing Colegau Cymru
- Childbase
- City and Guilds
- Council of British International Schools (COBIS)
- Coventry University
- Early Years Alliance
- Educate
- English in Chester
- English UK
- Federation of Awarding Bodies
- Grŵp Llandrillo Menai
- Hatching Dragons
- Independent HE
- Invest Northern Ireland
- Just2Easy
- Kangaroo Pouch Day Nursery
- Kaplan International Pathways
- King’s Ely
- KLC School of Design
- Learning Ladders
- London College of International Business Studies
- Manchester Metropolitan University
- Manga High
- Merchiston Castle School
- National Union of Students
- Nile ELT
- Northern Ireland Executive
- Ohbot
- Oxford Business College
- Pearson
- People 1st International
- Scottish Government
- Stamford Endowed Schools
- Study Group
- The London Institute of Banking & Finance
- The Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (QAA)
- Trinity College
- UK Council for International Student Affairs
- UK Skills Federation
- UK Skills Partnership
- Universities UK International (UUKi)
- University Campus of Football Business
- University of Greenwich
- University of Liverpool
- University of Portsmouth
- University of Westminster
- US-UK Fulbright Commission
- Welsh Government
- Whizz Education
- Wimbledon School of English
-
The UK’s Competitive Advantage, 2017 update, Universities UK International present findings from the International Student Barometer ↩
-
The 2020 figure is calculated by assuming the average growth rate seen between 2010 and 2016 continues. ↩
-
As set out in the The UK’s future skills-based immigration system, published on 19 December 2018. ↩
-
British Council, 2018, ‘GREAT Programme Board October 2018’ ↩
-
Higher Education Statistics Agency, 2019, HE Student Enrolments by HE provider 2014/15 to 2017/18 ↩
-
Higher Education Statistics Agency, 2018, Aggregate Offshore record 2017/18 ↩
-
Department for Education, 2019, UK revenue from education related exports and TNE activity 2016 ↩
-
United Nations Conference on Trade Development. ↩
-
Home Office Immigration Statistics, Dec 2018 ↩
-
great.gov.uk brings together international trade and investment information and services from across government. It is maintained by the Department for International Trade.. ↩
-
UNESCO Institute for Statistics. ↩
-
Eramus+ Annual Report 2017, Statistical Annex ↩
-
Department for Education, 2019, UK revenue from education related exports and TNE activity 2016 ↩
-
UNESCO, 2015, Education for All 2000-2015: Achievements and Challenges ↩
-
ISC Research, 2017. ↩
-
ISC Research defines an English-medium international school as such if (a) the school delivers a curriculum wholly or partly in English outside an English-speaking country, or (b) it is in a country where English is one of the official languages and the school offers an English-medium curriculum other than the country’s national curriculum and the school is international in its orientation. ↩
-
ISC Research, 2018. ↩
-
Independent Schools Council, 2018. ↩
-
w3techs, 2019, ‘Historical yearly trends in the usage of content languages for websites ↩
-
World Economic Forum, 2017, ‘The link between English and economics’. ↩
-
English UK, 2019, English language teaching – what’s it worth? ↩
-
OECD, 2014, Skills Beyond School; Synthesis Report ↩
-
World Economic Forum, 2018, The Future of Jobs ↩
-
Association of Colleges, 2018, ‘International Activity report 2017/2018’ ↩
-
CPD, 2019, CPD explained ↩
-
Department for Education, 2019, UK revenue from education related exports and TNE activity 2016 ↩
-
OECD, 2018, Education at a Glance 2018 ↩
-
Higher Education Statistics Agency, 2018, Aggregate Offshore record 2017/18 ↩
-
British Educational Suppliers Association, 2018, ‘Member Reported Turnover 2017 and 2018; BESA EdTech Market Map’. ↩
-
Department for Digital, Culture, Media & Sport, 2017, UK Digital Strategy ↩
