Criminal court statistics quarterly: April to June 2023
Published 28 September 2023
Applies to England and Wales
We are seeking user feedback on the use of HTML for the publication of statistical bulletins. Please send any comments to: datausers@justice.gov.uk.
Main Points
| Magistrates’ court: outstanding caseload increased | Case receipts remained stable, while disposals fell on the previous quarter. Disposal volumes fell below receipts, resulting in outstanding cases increasing by 2% on the previous quarter to 345,285 in Q2 2023. |
| Crown Court: outstanding caseload increased | Receipts increased on the previous quarter, with disposals falling below receipts. As a result, the outstanding caseload increased 4% on the previous quarter to 64,709 in Q2 2023. |
| Crown Court: rise in outstanding cases open for a year or more | The volume of outstanding cases that had been open for a year or more rose to 17,649– this represents 28% of outstanding cases – down slightly on the series peak (29%). |
| Effective trial rates stable | The effective trial rate at the magistrates’ courts and Crown Court stabilised and remains in line with the previous quarter (42% and 41% respectively). |
| Offence to completion duration reduced on average for magistrates’ court cases | The median time from offence to completion at the magistrates’ court fell slightly on the previous quarter (from 187 to 183 days) but remains above pre-COVID levels (175 days in Q1 2020). |
| Offence to completion duration reduced on average for Crown Court cases | The median time from offence to completion at the Crown Court decreased slightly on the previous quarter (from 398 to 387 days) but remains above pre-COVID levels (254 days in Q1 2020). |
The technical guide to ‘Criminal court statistics’ and ‘Language interpreter and translation services in courts and tribunals’ can be found at the links below:
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/a-guide-to-criminal-court-statistics
Statistician’s comment
This report covers the period to the end of June 2023.
The volume of receipts in the Crown court in the latest quarter is the highest for over two years, and coupled with a reduction in disposals, has led to an increase in the outstanding caseload in the Crown Court. Outstanding cases in the magistrates’ court have also increased in the latest period, with more receipts than disposals recorded.
The effective trial rates at both magistrates’ and Crown Courts showed little change, after recovering in the previous two quarters, following the Criminal Bar Association action; and the average length of time between offence and completion (end-to-end timeliness) decreased at both magistrates’ and Crown Court.
1. Changes to note
Common Platform and reform to criminal court data[footnote 1]
‘Common Platform’ is a new digital case management system for the magistrates’ and Crown Courts. The system seeks to streamline data collection, data accessibility and improve the way criminal cases are processed across the Criminal Justice System. It will eventually replace the existing ‘legacy’ criminal court systems Libra (magistrates’) and XHIBIT (Crown), with a single, streamlined system.
Early adopter courts across England and Wales are testing the system before the subsequent rollout to all criminal courts concludes. Derbyshire magistrates’ and Crown Court began this process in September 2020 and the roll out has continued across England and Wales[footnote 2].
New cases entering courts from the point at which they adopt the Common Platform are held on the new system – cases that began at court prior to that court transitioning to Common Platform will remain on the ‘legacy’ system (e.g., LIBRA or XHIBIT).
All measures relating to magistrates’ courts and Crown Court cases include both ‘legacy’ and Common Platform estimates on a ‘best equivalent’ basis. This includes all key breakdowns in published quarterly tables and associated data tools.
Methodologies are as similar as possible however there are areas of known difference. The ‘legacy’ and ‘new’ data systems are fundamentally different, they do not record information in the same way and as such it is not possible to exactly replicate the existing published methodologies.
Areas of known difference that impact the statistics in this release include: the allocation of case type (such as triable-either-way, indictable only, committed for sentence and appeal), the inability to account for case transfers, main hearing allocation and changes to case ownership.
We will continue to develop data processes from the new system in collaboration with HMCTS and partner agencies as the Common Platform roll out continues. As we continue to develop these solutions, some series may be disrupted, with an increased likelihood of revisions to data in future.
We are committed to ensuring that published statistics remain accurate, robust and coherent for users during the operational transition of data systems at the criminal courts. For further information regarding the extent of the differences summarised above please see the Guide to criminal court statistics.
2. Criminal cases in the magistrates’ courts
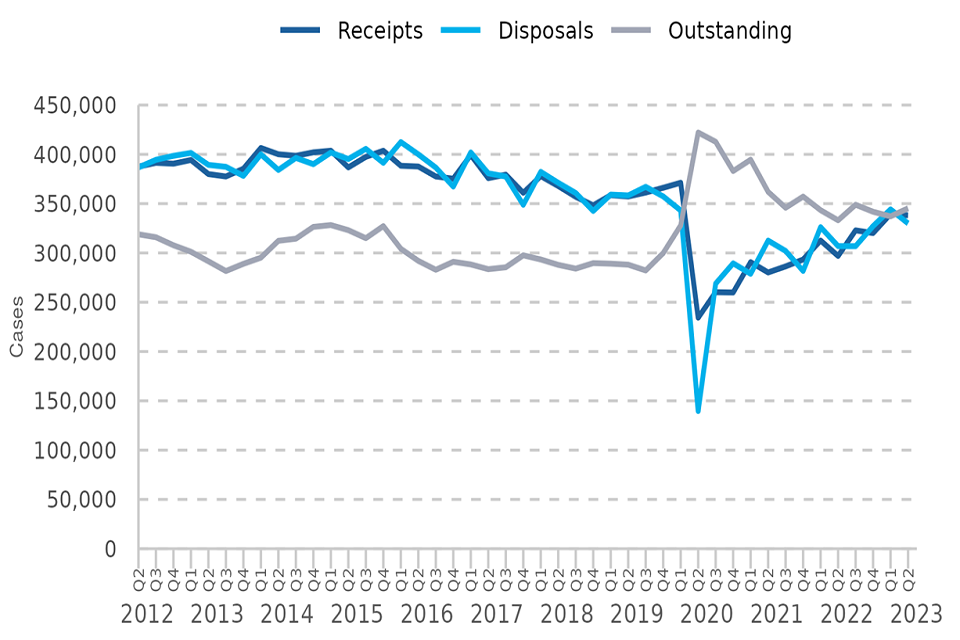
Outstanding caseload at the magistrates’ courts increased as disposals volumes fell below case receipts.
Receipts remained stable with the previous quarter while disposals fell. Disposals fell below receipts and as a result the outstanding caseload increased by 2% on the previous quarter.
Figure 1: Magistrates’ courts caseload, Q2 2012 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table M1)
Magistrates’ court caseload
Receipts and disposals have both tended to rise from series lows in Q2 2020 when the initial measures were put in place to manage the immediate risks of the COVID-19 pandemic in courts[footnote 3][footnote 4][footnote 5]. The levels remain a little below those seen prior to the pandemic.
-
Receipts into the magistrates’ courts increased by 14% compared to the previous year and remained similar to those seen in the previous quarter.
-
Disposals at the magistrates’ court increased by 7% on the previous year but fell back on the previous quarter (down 4%) – this was largely due to a 6% reduction in summary motoring disposals.
-
At the end of June 2023 there were 345,285 outstanding cases at the magistrates’ courts. This represents a 2% increase on the previous quarter (337,104) and a 18% decrease on the series peak seen in Q2 2020 (422,156).
The latest HMCTS management information provides monthly volumes of receipts, disposals and the open (‘outstanding’) caseload for all case types at the magistrates’ courts (e.g., including civil and enforcement) beyond the published period. The data to July 2023 shows that the open caseload increased – up 2% on the previous month and 5% on the previous year.
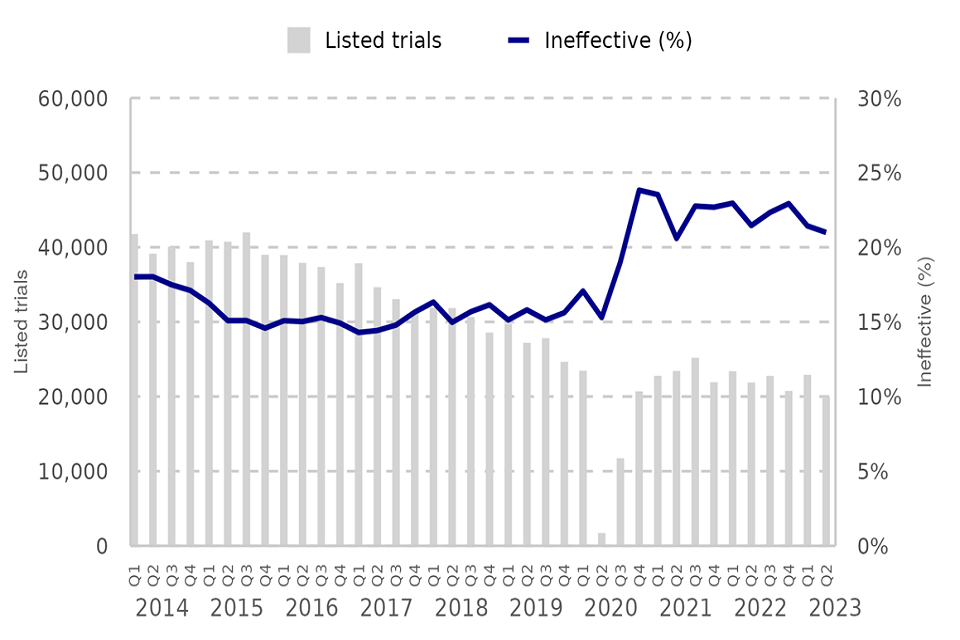
Trial efficiency at magistrates’ court
There were 20,011 trials listed for Q2 2023, this represents a 9% decrease on the previous year (21,885).
- Of trials listed for Q1 2023, the proportion that were effective was unchanged on the previous quarter, remaining at 42%. Similarly, the cracked rate (37%) and ineffective rate (21%) were unchanged – the ineffective rate remains above pre-COVID levels (~15-17%).
Figure 2: Magistrates’ courts listed trials and ineffective trial rate (%), Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table M2)
3. Criminal cases in the Crown Court
Increase in the outstanding caseload at the Crown Court
Receipts increased on the previous quarter while disposals reduced – although both remain above volumes seen a year ago. Disposals fell below receipts, so the outstanding caseload increased, up by 4% on the previous quarter.
Crown Court caseload
The increased throughput from the magistrates’ courts as part of the initial recovery from the pandemic response saw the volume of receipts at the Crown Court exceed pre-COVID levels in late 2020. Following a slight decline, receipts have since returned to levels comparable to those pre-COVID.
Figure 3: Crown Court caseload, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table C1)
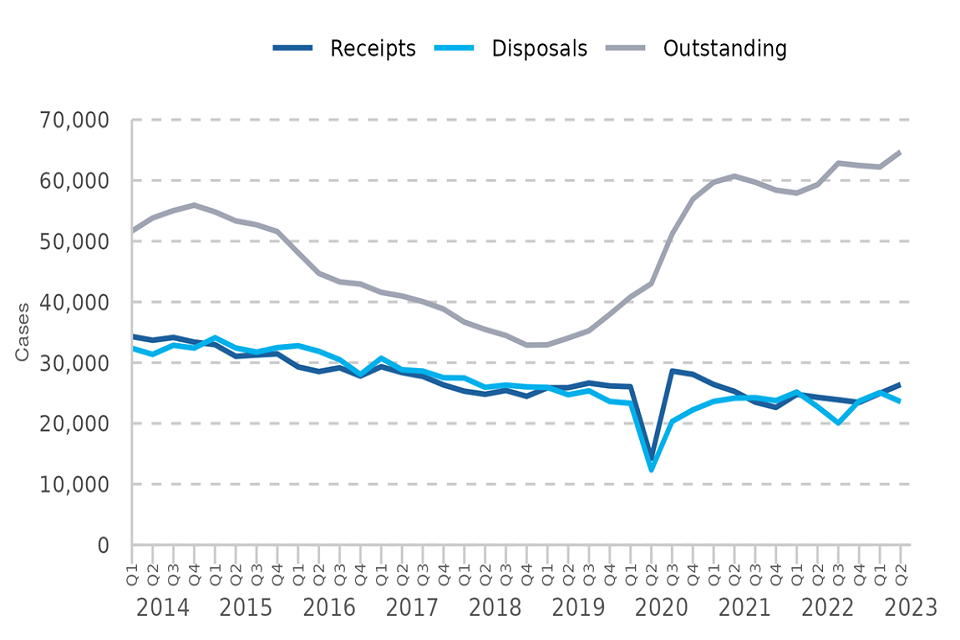
Following the initial phased reintroduction of jury trials[footnote 6] disposals have gradually increased from a series low in Q2 2020 and returned to pre-COVID levels in Q1 2022. The Criminal Bar Association industrial action starting in April 2022 contributed to disposals falling in Q2 and Q3 2022. The Criminal Bar Association industrial action was resolved in October 2022[footnote 7] following the extension of fee rises[footnote 8] and subsequently disposals increased.
-
There were 26,403 case receipts into the Crown Court in Q2 2023. This is up 6% on the previous quarter and 9% above levels seen in Q2 2022.
-
There were 23,581 case disposals at the Crown Court in Q2 2023. This is a 6% decrease on the previous quarter but 4% above levels seen in the previous year and 18% above levels at the height of the Criminal Bar Association action.
-
There were 64,709 outstanding cases at the end of June 2023. This is up 4% on the previous quarter (62,212 cases) and 9% above the previous year (59,299 cases).
The latest published HMCTS management information provides monthly volumes of receipts, disposals and the open (‘outstanding’) caseload for all case types at the Crown Court. The data to July 2023 shows that the open caseload has increased, up 1% on June 2023 and 8% on July 2022.
Analysis of the outstanding caseload at the Crown Court – experimental statistics
To address additional interest in the outstanding case estimates at the Crown Court we are continuing to publish ‘experimental statistics’ providing estimates of the average length of time (days) that a case has been outstanding.
The age of an outstanding case is calculated from receipt at Crown Court to the end of the reporting period.
Figure 4: Age of outstanding cases at the Crown Court, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table O1)
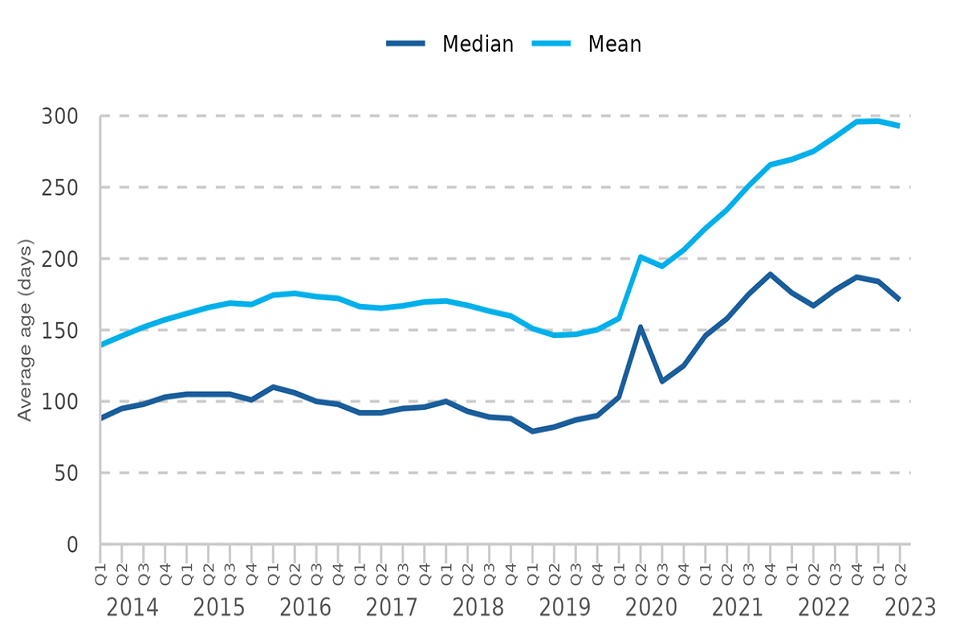
The average age of an outstanding case has increased markedly on pre-COVID levels. Both the median and mean averages fell on the previous quarter but remain close to series peaks. In Q2 2023 the median age of all outstanding cases decreased by 7% on the previous quarter, from 184 days to 171 days.
Figure 5: Proportion of outstanding cases at the Crown Court by grouped age, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table O3)
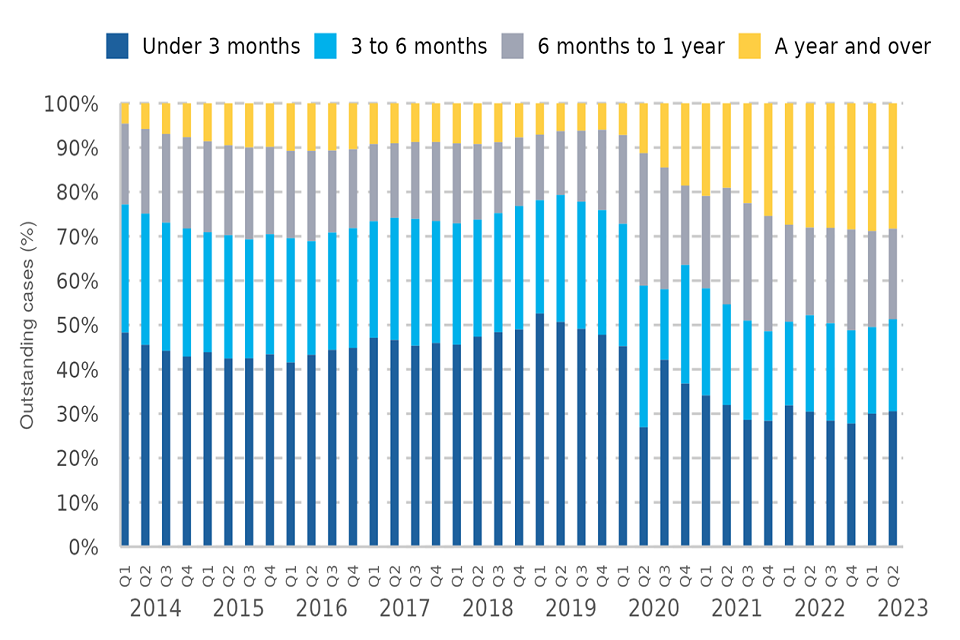
At the end of Q2 2023 there were 17,649 cases that had been outstanding for a year or more. This has tended to increase since Q4 2019 and accounted for 28% of the outstanding caseload in the latest quarter.
- Within the ‘year or more’ grouping there were 6,427 cases which had been outstanding for over two years – this accounts for 10% of the outstanding caseload.
Trial efficiency at Crown Court
There were 6,711 listed trials in Q2 2023 - the volume of trials listed fell back following a sharp increase in the previous quarter (7,560). The latest data is down 11% on the previous quarter but 17% above levels seen in the previous year.
The effective trial rate was similar to the previous quarter at 41%, this has tended to increase from a series low seen in Q3 2022 (25%). The cracked and ineffective trials rate remained unchanged on the previous quarter – the ineffective rate remains above pre-COVID levels (~13-19%).
Figure 6: Crown Court listed trials and ineffective trial rate (%), Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table C2)
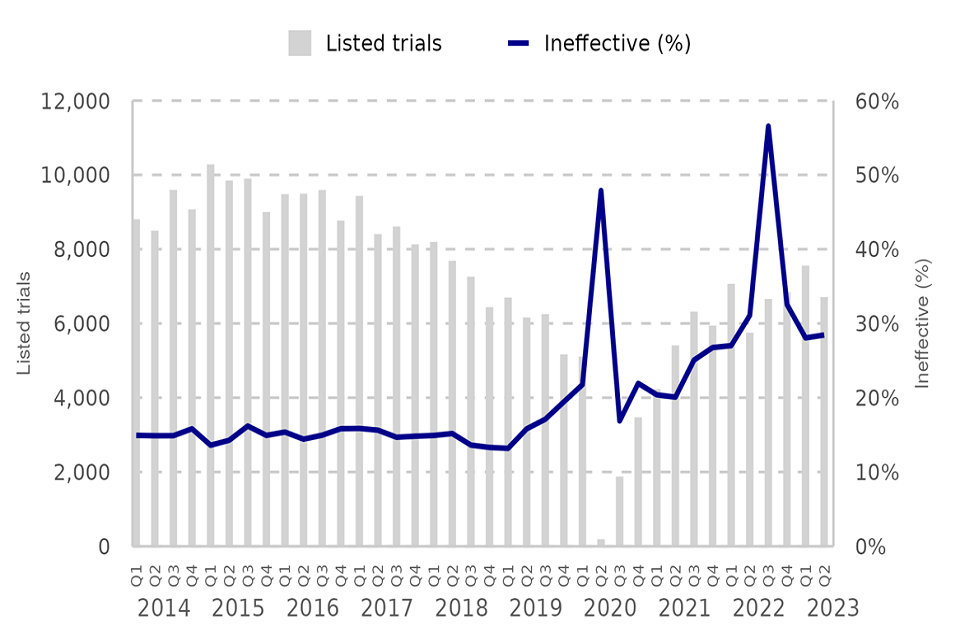
’Overlisting (insufficient cases drop out/floater/backer not reached)’ was the largest reason for ineffective trials, accounting for 20% (430 trials) in Q2 2023. This follows sharp falls in the volume of ineffective trials due to defence advocate availability following the conclusion of the Criminal Bar Association action in October 2022.
Guilty plea rate
The guilty plea rate[footnote 9] increased sharply following the immediate COVID-19 response and the suspension of jury trials at the Crown Court. More recently it has fallen back to pre-COVID levels as the volume of ‘not guilty plea’ cases being disposed of has increased.
-
In Q2 2023 the guilty plea rate was 66%, unchanged on the previous quarter.
-
There were 3,120 defendants dealt with in Q2 2023 who entered a not guilty plea (e.g., went to trial) – this is a decrease of 5% on the previous quarter but follows a sharp increase since Q3 2022 reflecting the return to levels prior to the Criminal Bar Association industrial action and COVID.
Average waiting time at the Crown Court
The waiting time estimates are a ‘lagged measure’ and defendants are counted at the point of their case being disposed of. As such the waiting time estimates provide a ‘backwards’ look at the durations spent between receipt and main hearing at the Crown Court.
The median waiting time[footnote 10] for defendants dealt with at the Crown Court was 9.1 weeks in Q2 2023. This represents an 11% decrease on the previous quarter (10.3 weeks), a 7% increase on the previous year (8.6 weeks) and remains well above pre-COVID levels (5.3 weeks in Q1 2020).
- The median waiting time for defendants dealt with in ‘for trial’ cases where a not guilty plea was entered increased, up 8% compared to the previous quarter - from 38 weeks in Q1 2023 to 41 weeks in Q2 2023. This remains well above pre-COVID levels (25.4 weeks in Q1 2020).
Average hearing time at the Crown Court
The hearing time estimates are a ‘lagged measure’ and cases are counted at the point of disposal. As such the hearing time estimates provide a ‘backwards’ look at the duration of hearings at the Crown Court.
The median hearing time[footnote 11] of ‘for trial’ cases where a not guilty plea was entered remained stable at 12.4 hours (in line with levels seen in the previous quarter and previous year), in contrast to around 1.2 hours for ’for trial’ cases where a guilty plea was entered.
4. Timeliness
Timeliness increased at both the magistrates’ court and Crown Court
The median time from offence to completion for cases completing at the magistrates’ and Crown Court both decreased on the previous quarter, down 2% and 3% respectively.
The timeliness measures are based on defendants whose cases have been completed and as such are ‘backwards’ looking measures of timeliness between offence and completion at the relevant criminal court jurisdiction.
Experimental statistics using a new data linking methodology have been developed using the Ministry of Justices open-source statistical ‘Splink’ package to provide updated end-to-end timeliness estimates.
Alongside the gradual development of the experimental end-to-end series we will continue to best meet user demands via more granular data on separate (‘unlinked’) timeliness estimates for magistrates’ courts and Crown Court.
-
Magistrates’ court timeliness estimates (T1 – T3) – providing estimates of the time from offence to completion for defendants dealt with at the magistrates’ courts.
-
End-to-end timeliness estimates (T4) – providing estimates of the time from offence to completion for defendants dealt with at Crown Court.
-
Crown Court timeliness estimates (E1 – E2) – providing estimates of the time from case receipt at the Crown Court to completion.
Magistrates’ courts timeliness
Timeliness at the magistrates’ courts measures the time from an offence being committed through key stages of the criminal justice system including charge, first listing and subsequent completion of a defendant’s case at the magistrates’ court.
Figure 7: Average number of days from offence to completion for defendants dealt with at the magistrates’ courts by stage, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table T3)
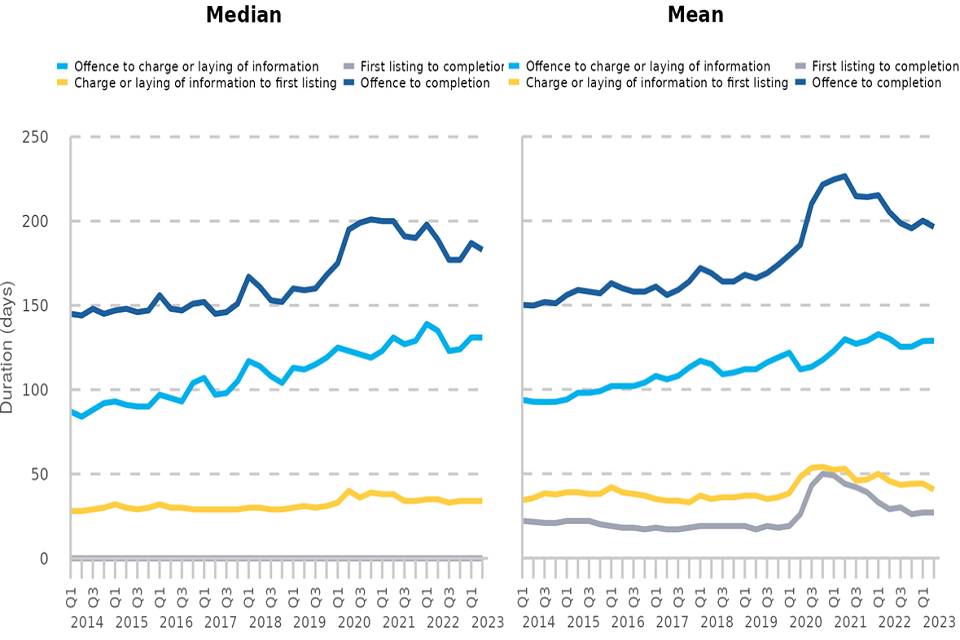
The median duration from offence to completion at the magistrates’ courts has tended to fall back from series highs of around 200 days seen in late 2020 and early 2021. The latest quarterly estimates decreased slightly on the previous quarter, from 187 days in Q1 2023 to 183 days in Q2 2023.
-
‘Pre-court’: the median time from ‘offence to charge’ and ‘charge to first listing’ both remained unchanged on the previous quarter (131 days and 34 days respectively).
-
‘At court’: the median estimate remained stable at 0 days, where the first listing and completion occur on the same day. The mean duration remained stable at 27 days – this follows sharp increases seen over the COVID period and a peak of 50 days in Q4 2020. Despite the fall since, the latest estimate remains above pre-COVID levels (e.g., 19 days in Q1 2020).
Crown Court timeliness - experimental statistics
‘Unlinked’ timeliness estimates at the Crown Court are measured from the point of a case entering a Crown Court, reaching a main hearing and then completing at court. This data series remains in development and is considered “experimental statistics”. Data presented here is not produced on the same basis as linked end-to-end timeliness data.
The median duration from case receipt to completion at the Crown Court for all cases was 142 days. This represents a 13% decrease on the previous quarter (164 days).
Figure 8: Median duration from receipt to completion in ‘for trial’ cases by plea at the Crown Court, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: E2)
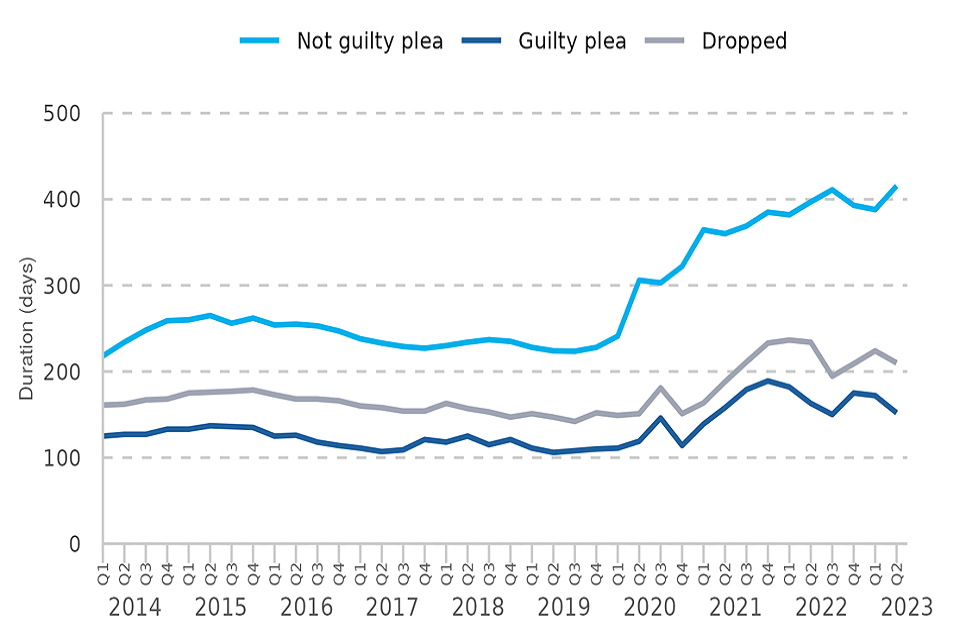
In ‘for trial’ cases where a not guilty plea was entered, the median duration from receipt to completion increased, up 7% on the previous quarter (from 388 to 416 days). For guilty pleas, the median duration fell (by 12%), from 172 to 152 days.
End-to-end timeliness
The median duration from offence to completion for defendants dealt with at the Crown Court fell slightly (down 3%), down from 398 days in Q1 2023 to 387 days in Q2 2023.
This fall follows two successive quarterly increases, and the latest median estimate of 387 days remains well above pre-COVID levels (254 days in Q1 2020).
Figure 9: Average number of days from offence to completion for defendants dealt with at the Crown Court, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: T4)
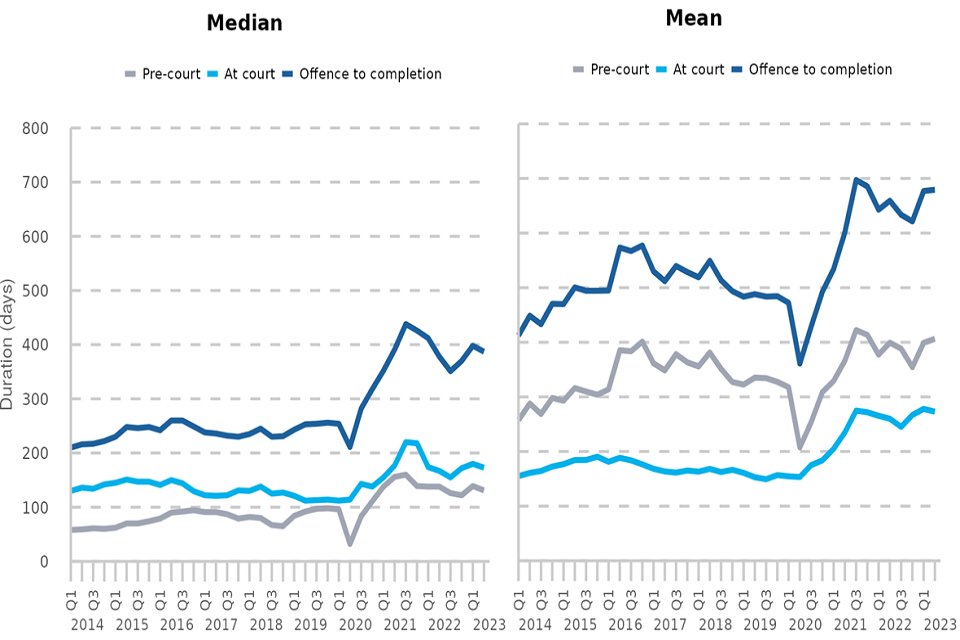
-
‘Pre-court’: the median time from ‘offence to first listing’ decreased by 6% from 139 days in Q1 2023 to 131 days in Q2 2023.
-
‘At court’: the median time from first listing at the magistrates’ courts to completion at the Crown Court decreased by 4%, from 180 days in Q1 2023 to 173 days in Q2 2023. The latest estimate is well below the series peak seen in Q3 2021 (220 days) but remains well above levels seen pre-COVID (112 days in Q1 2020).
5. Enforcement of financial impositions
Total financial impositions fell
The total value of financial impositions made in Q2 2023 was £159.9 million, down slightly on Q1 2023 (£164.1m) but up 20% on the previous year (£132.8m).
The total value of outstanding financial impositions was £1.51 billion in Q2 2023, up by 3% on the previous quarter (£1.47 billion).
Financial impositions and amounts paid by imposition type
Following the impacts of the COVID-19 response the overall value of impositions has tended to increase from series lows in Q2 2020.
In Q2 2023 the total value of impositions fell slightly on the previous period (down 3%). The latest imposition figure is 20% above that seen in the previous year, with increases seen across all imposition types – most notably a more than doubling in the amount imposed for victim surcharge, up from £12.5m in Q2 2022 to £27.2m in Q2 2023.
Outstanding financial impositions
In Q2 2023, the total value of financial impositions outstanding in England and Wales was £1.51 billion, up 3% on the previous quarter and 11% on the previous year.
The amount of outstanding financial impositions has more than doubled since Q1 2015 (£571m). A change in policy regarding the collection of financial impositions is partially behind this cumulative increase – unpaid accounts are no longer routinely closed and therefore, more outstanding impositions are carried over from previous periods.
6. Experimental statistics: Language interpreter and translation services
The number of completed language service requests remained close to the series high while the success rate increased to 97%.
There were 46,187 completed requests in Q2 2023, down 3% on the series peak seen in the previous quarter. The success rate increased back to 97% - back to levels seen in Q3 2022.
Completed service requests
The volume of completed service requests increased markedly and the latest levels represent a series peak. There were 46,187 completed requests in Q2 2023, a 3% fall on the series peak seen in the previous quarter (47,585).
Figure 10: Number of completed language service requests and overall success rate, Q1 2014 – Q2 2023 (Source: Table L1)
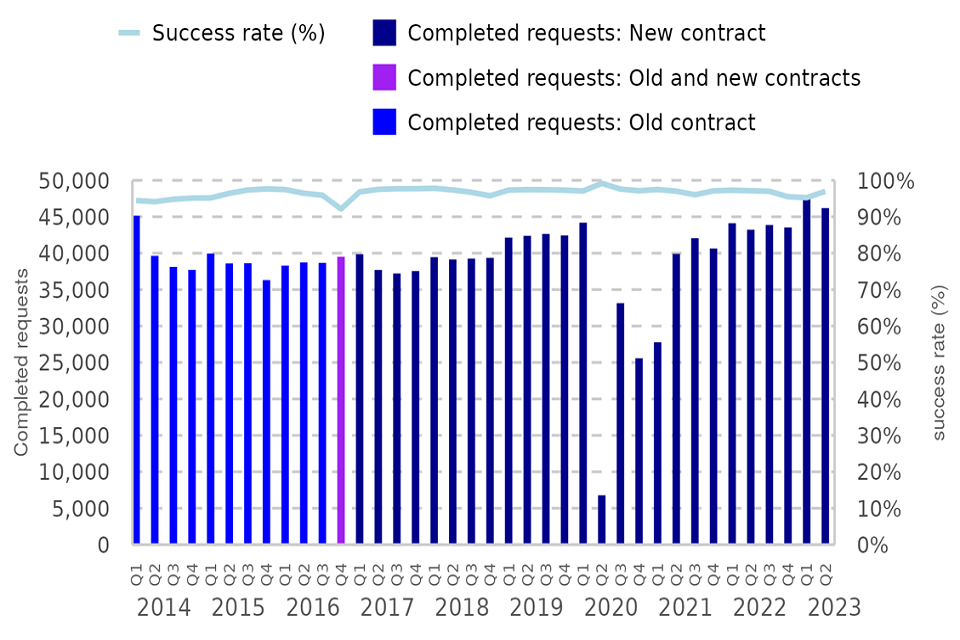
Success rate
The overall success rate in Q2 2023 was 97% - this increased from 95% in Q1 2023 and is back to levels seen in Q3 2022. This shift reflects a sharp decrease in the volume of unfulfilled requests, down 37% from 1,763 in Q1 2023 to 1,102 in Q2 2023.
Complaints and complaint rate
The number of complaints has remained low since Q2 2020, with 201 complaints made in Q2 2023. This has decreased on the previous quarter (230) and remains well below levels seen pre-COVID (436 complaints in Q1 2020). The overall complaint rate was 0.4% in Q2 2023 and has remained below 1% since Q3 2020.
‘Off-contract’ requests
The number of ‘off-contract’ requests in Q2 2023 fell back following a sharp increase in the previous quarter, falling from 2,015 to 1,626 in Q2 2023 – this remains well above the average seen across the series (around 672 requests per quarter).
7. Further information on criminal courts data
The latest data presented in this publication are provisional. Final data for each calendar year is published in June, following further data cleaning and the incorporation of additional cases not available in our original extracts.
Accompanying files
As well as the bulletin, the following products are published as part of this release:
-
Two technical guides providing background information and standalone quality guide.
-
A set of overview tables, covering each section of this bulletin.
-
Pivot tools and underlying data which feature further breakdowns of published data.
National Statistics status
National Statistics status means that official statistics meet the highest standards of trustworthiness, quality and public value. This bulletin recently underwent a compliance check with the Office for Statistics Regulation and retained its National Statistics status in January 2019. All official statistics should comply with all aspects of the Code of Practice for Statistics. They are awarded National Statistics status following an assessment by the Authority’s regulatory arm which considers whether the statistics meet the highest standards of Code compliance, including the value they add to public decisions and debate. It is the Ministry of Justice’s responsibility to maintain compliance with the standards expected for National Statistics. If we become concerned about whether these statistics are still meeting the appropriate standards, we will discuss any concerns with the Authority promptly. National Statistics status can be removed at any point when the highest standards are not maintained, and reinstated when standards are restored.
Experimental Statistics status
Experimental statistics are produced under the remit of the Code of Practice for Statistics. They are also produced impartially and are free from political influence[footnote 13].
Future publications
Our statisticians regularly review the content of publications. Development of new and improved statistical outputs is usually dependent on reallocating existing resources. As part of our continual review and prioritisation, we welcome user feedback on existing outputs including content, breadth, frequency and methodology. Please send any comments you have on this publication including suggestions for further developments or reductions in content to the contacts listed below.
Contact
Press enquiries should be directed to the Ministry of Justice press office:
Tel: 020 3334 3536
Email: newsdesk@justice.gov.uk
Other enquiries and feedback about these statistics should be directed to the ‘Data & Analysis: Courts and People’ division of the Ministry of Justice:
Criminal Courts and Sentencing Data and Statistics,
Ministry of Justice, 10 South Colonnade, London, E14 4PU
Email: statistics.enquiries@justice.gov.uk
Next update: 14th December 2023
URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/criminal-court-statistics
© Crown copyright
Produced by the Ministry of Justice
Alternative formats are available on request from statistics.enquiries@justice.gsi.gov.uk
-
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/common-platform-system-tested-in-criminal-courts/ ↩
-
https://www.gov.uk/guidance/hmcts-common-platform-participating-criminal-courts/ ↩
-
https://www.judiciary.uk/announcements/message-from-the-lord-chief-justice-latest-covid-19-restrictions/ ↩
-
https://www.judiciary.uk/announcements/review-of-court-arrangements-due-to-covid-19-message-from-the-lord-chief-justice/ ↩
-
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/more-face-to-face-hearings-as-courts-reopen ↩
-
https://www.judiciary.uk/announcements/jury-trial-sites-4/ ↩
-
https://questions-statements.parliament.uk/written-statements/detail/2022-10-12/HCWS317 ↩
-
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/crime-news-extension-of-fee-rises-after-moj-and-cba-deal ↩
-
Guilty plea rate is the number of defendants pleading guilty to all counts as a proportion of those with a plea. ↩
-
The waiting time is the duration between a case being sent to the Crown Court and the first main hearing. ↩
-
The hearing time is the time a case spends being heard in the Crown Court, including preliminary hearings, main hearings, and hearings where a sentence is given to a defendant. ↩
-
https://www.statisticsauthority.gov.uk/monitoring-and-assessment/code-of-practice/ ↩
