Direct Research Portfolio Annual Report 2017 to 2018
Published 27 March 2019

Graphene with R&D text superimposed
Introduction
The Nuclear Decommissioning Authority (NDA) is responsible for cleaning up the legacy from the UK’s pioneering post-war nuclear programme.
From the late 1940s onwards, the country’s smartest scientists led the world with ground-breaking discoveries, gradually building a diverse collection of experimental facilities for the UK’s defences and, later, to provide electricity for its citizens.
Their work spanned 17 locations across the UK and included:
- dozens of prototype reactors
- 11 nuclear power stations
- scores of research labs
- fuel-manufacturing and enrichment facilities
- spent fuel reprocessing plants
Many of the designs were unique; producing radioactive wastes and spent fuel that no-one had ever dealt with before. Structures, pipework, container vessels and land became contaminated and were mostly left for a future generation to clean up.
Many years later, the NDA is dismantling this historical legacy, demolishing structures and preparing sites for future uses. The mission will stretch for another 100-plus years and cost more than £100 billion.
Dealing with such a range of complexities and uncertainties requires fundamental science, innovative thinking and novel engineering. Progress depends on clearly understanding the problems, finding solutions and ensuring the cost for taxpayers remains acceptable. Research & Development (R&D) is therefore an essential part of decommissioning programme. The aim is to solve the challenging technical problems more effectively, more efficiently, more safely and, where possible, for less cost.
A total of approximately £101 million was spent on R&D during 2017 to 2018.
The bulk of this forms part of the budget allocated to our Site Licence Companies (SLCs) and subsidiary organisations, and is aimed at addressing specific on-site challenges identified during decommissioning activities. The work is carried out by SLCs, the subsidiaries and through contracts awarded to their supply chain.
Separately, the NDA also funds a strategic portfolio to commission projects directly, particularly in areas with potential to have an impact across a number of sites, or to develop our overall strategy. This kind of research may help shape and develop our strategy, encourage early innovation or maintain key technical skills. This portfolio is called the NDA Direct Research Portfolio (DRP).
About DRP
The DRP is a key component of the overall R&D programme. It accounts for approximately £5 million of the annual investment and represents an important area of overall support for R&D across the group’s 17 sites and subsidiary organisations.
The DRP is made up of projects that:
- help shape and underpin NDA’s overall strategy for the UK
- deliver innovation across multiple sites
- develop vital technical expertise for the future
DRP projects are aligned against NDA’s 4 driving strategic themes:
- Integrated waste management
- Site decommissioning and remediation
- Spent fuel management
- Nuclear materials
DRP projects are contracted through framework contracts that last up to 4 years. The current contracts, awarded in 2016, involve 3 framework contracts:
- Lot A: University interactions
- Lot B: Integrated waste management and Site decommissioning and remediation
- Lot C: Spent fuel management and Nuclear materials
Overall, 9 consortia comprising around 70 organisations are involved in the DRP, ranging from UK universities and research bodies to global corporations and small businesses.
Topics for individual projects are identified either by NDA’s internal technical experts or through the members of the Nuclear Waste and Decommissioning Research Forum (NWDRF), a cross-industry forum which promotes collaboration across the UK on nuclear decommissioning R&D.
This report outlinesthe projects funded through the DRP during 2017 to 2018, with case studies on some key projects. Some are ongoing from earlier contracts, but all have potential for a significant impact across the NDA group of businesses.
Further information on NDA’s R&D programme can be found in our 5-year R&D plan.
DRP spend and key facts
£5.7 million spent during 2017 to 2018
Spend on each Lot
| Lot | 2017 to 2018 Spend |
|---|---|
| Lot A | £1,500,326 |
| Lot B | £3,392,937 |
| Lot C | £880,276 |
Other key facts

Graphic shows: £5.7 million spent 2017 to 2018, more than 30 companies involved and 37 projects started
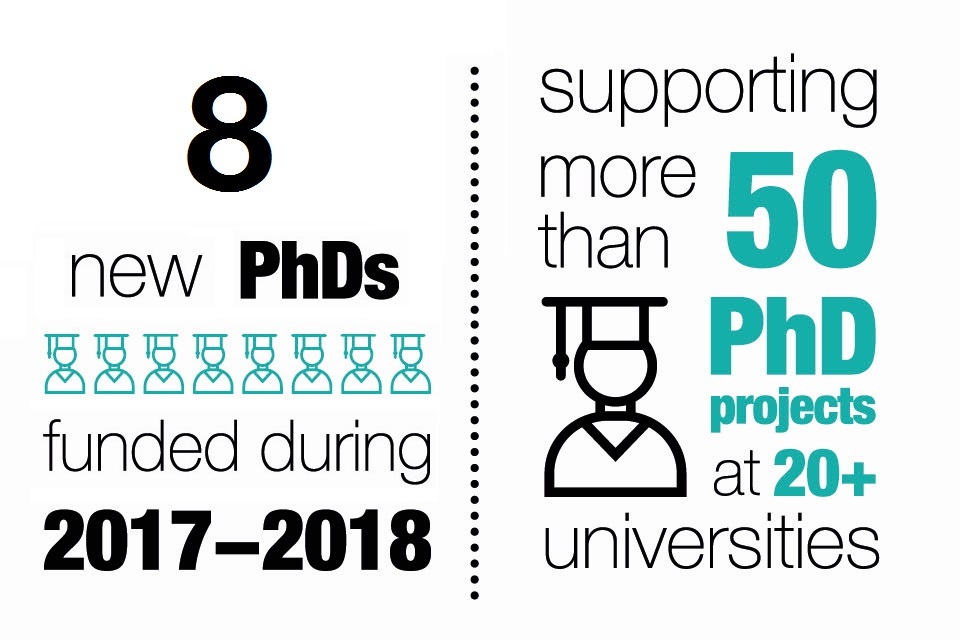
Number of academic studies supported: 8 new PhDs and more than 50 in total, across 20-plus universities
New projects
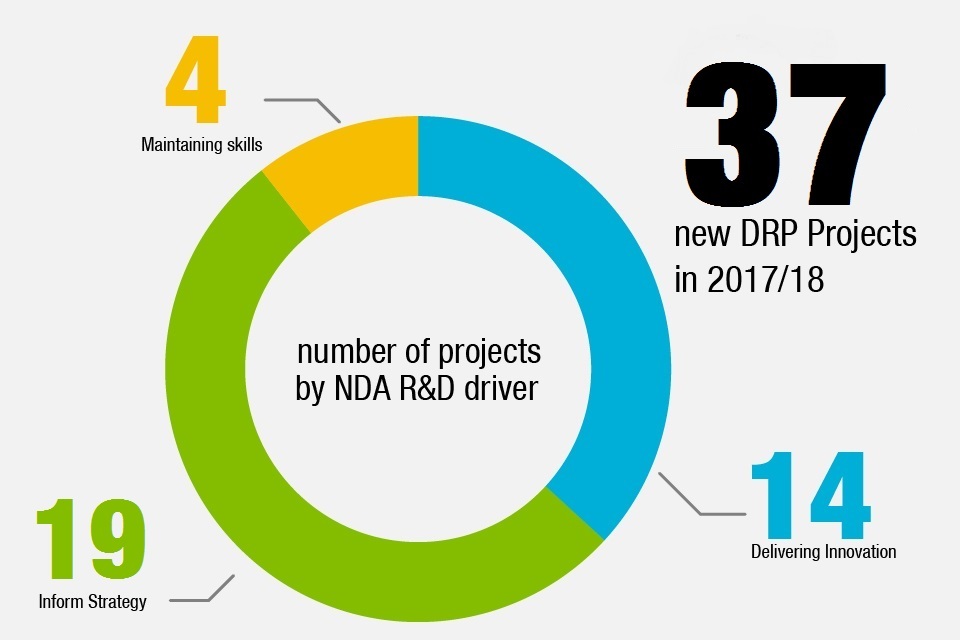
Graphic shows: 37 new porjects started. Of these, 4 relate to skills, 19 to informing strategy and 14 to delivering innovation
| NDA R&D Driver | Number of New DRP projects (FY2017/18) |
|---|---|
| Delivering Innovation | 14 |
| Inform Strategy | 19 |
| Maintaining Skills | 4 |
Lot A: University Interactions
Delivering innovation
| PhD title | University |
|---|---|
| Development of novel radiochemical methods for the analysis of challenging nuclides in nuclear decommissioning samples | University of Birmingham /University of Surrey / National Physical Laboratory |
| Radiochemistry Sensors for use on Robotic Inspection Vehicles | University of Manchester |
| Experimental and modelling approaches to support the management of radioactive discharge pipelines | University of Manchester |
| In-situ non-contact pressure measurement in sealed cans using acoustic methods | University of Warwick |
| Measurement of waste package dimensions and deformations using robotically deployed optical methods | University of Strathclyde |
| An Efficient One-Pot Process for Conditioning and Encapsulation of Contaminated Mercury Waste | University of Sheffield |
| Atomic scale insights into the mobility of radionuclides in the plasma vitrification simulant plutonium contaminated materials | University of Liverpool |
| Cements of the future, and future nuclear cements | University of Sheffield |
Lot B: Integrated waste management and site decommissioning and remediation
| Project title | Lead organisation | R&D driver |
|---|---|---|
| Briefing notes on emerging issues in Land Quality Management for the Nuclear Industry | Arup | Maintaining Key Skills |
| Creation of guidance to SLCs to assist them in determining optimum end state associated with off-site structures | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Developing standardised conditioning factors and packaging factors for Intermediate Level Waste (ILW) and Low Level Waste (LLW) streams | Galson Sciences | Inform Strategy |
| Development of an improved rapid methodology for the analysis of Carbon-14 in solid decommissioning waste | NSG Environmental | Delivering Innovation |
| Evaluation of characterisation approaches for populations of small-volume / high number redundant laboratory chemicals | Arup | Delivering Innovation |
| Identification and implementation of treatment technologies for ion exchange materials | NSG Environmental | Delivering Innovation |
| Identification and implementation of treatment technologies for sludges, oily sludges and oily wastes | NSG Environmental | Delivering Innovation |
| Problematic waste packaging and transport study | Eden Nuclear and Environment | Inform Strategy |
| Real world behaviour of artificial radionuclides in near surface hydrogeological environments | Wood | Maintain Skills |
| Review of management approaches and treatment technologies used for the treatment of smaller volume problematic radioactive wastes | Galson Sciences | Inform Strategy |
| Solid Waste Characterisation Guidance Document | Wood | Maintaining Skills |
| Technical secretary for National inventory Forum (NIF) | Wood | Inform Strategy |
Lot C: Spent fuel management and nuclear materials
| Project title | Lead organisation | R&D driver |
|---|---|---|
| Attendance at Radiation Induced Segregation (RIS) workshop to present and discuss results | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Attendance at Radiation Induced Segregation (RIS) workshop to present and discuss results | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Attendance at the AGR Technical Forum 2018 to present work and discuss results and strategy development | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Attendance at the AGR Technical Forum 2018 2018 to present work and discuss results and strategy development | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Desktop review of the techniques available for characterisation of AGR cladding composition, microstructure and corrosion behaviour | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Desktop study - Information on in-pond caesium detector for locating failed fuel | Wood | Deliver innovation |
| Desk-top study into the variations in Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR) cladding specifications and manufacturing processes | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Desktop study on Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Can Filling Methodology - Options Assessment | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Desktop study on horizon scanning of alternative approach to plutonium immobilisation | National Nuclear Laboratory | Deliver Innovation |
| Literature review of AGR-relevant corrosion modelling and simulation [footnote 1] | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Literature review of AGR-relevant corrosion modelling and simulation [footnote 1] | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Literature review of dry storage conditions and impact on AGR fuel behaviour | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Literature review on effects of aging on plutonium powder characteristics | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Review of next steps in the development of an Radiation Induced Segregation model for AGR fuel cladding | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Review of the potential contribution of Post Storage Examination (PSE) to the NDA Oxide Fuel Strategy | National Nuclear Laboratory | Inform Strategy |
| Role of niobium carbide (NbC) precipitates on corrosion mechanisms of AGR cladding | Wood | Inform Strategy |
| Support to Horizon 2020 project: GENIORS (GEN IV Integrated Oxide fuel Recycling Strategies) [footnote 2] | National Nuclear Laboratory | Maintaining Skills |
Case studies
Lot A case study

Poster and PhD students
We need to maintain and develop sufficient high-level expertise to support decommissioning as the mission moves forward over the next 100-plus years. We therefore invest in a range of university research programmes targeted at decommissioning, and fundamental supporting topics, while supporting wider collaborative research programmes that align with industry requirements.
Read more: Investing in technical expertise for the future of nuclear decommissioning
Lot B case studies
Graphene
Graphene
We are looking to understand how graphene, an emerging technology, could improve delivery of NDA’s mission, and have therefore commissioned a review of graphene properties, the latest associated developments and areas for potential deployment in decommissioning.
Read more: Graphene, one for the future
Thermal treatment

Geomelt
We’re always seeking alternative, as well as cost-efficient, solutions for immobilisation of large quantities of mixed, diverse radioactive waste. An integrated project team has been working on adapting existing thermal treatment technology to produce stable, passively safe material that can be disposed of in a Geological Disposal Facility.
Read more: Thermal solution can reduce waste volumes
Emerging issues

Emerging issues brief
NDA has developed an information resource to share among all professionals involved in land remediation, including site employees and contractors. This is aimed at ensuring the latest techniques and regulatory guidance is adopted and the latest techniques are shared.
Read more: Land remediation specialists embrace e-sharing
Cement encapsulation

Cement encapsulation
A continued supply of cement powders is vital for encapsulating UK higher activity radioactive wastes before packaging, storage and eventual disposal. However, supplies depends on by-products from UK industries that are in decline. We have therefore carried out a review into current issues and outlined options for managing future risks.
Read more: Forward planning to ensure cement supplies
Lot C case study
Hot isostatic pressing

Hot isostatic pressing
Some UK plutonium stocks are unsuitable for re-use as a component of new fuel and we require a different way to deal with these stocks. We’re working to identify and develop immobilisation technologies, which include refinement of an existing thermal treatment process: hot isostatic pressing.
Read more: Pressure treatment for plutonium stockpile
Framework contractors
Lot A: University interactions
| Lead organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| National Nuclear Laboratory | Frazer-Nash Consulting |
Lot B: Integrated waste management and Site decommissioning and remediation
| Lead organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| Wood | Brenk Systemplanung, Jülich Research Centre, Andra, Cogentus Consulting, DAS, Imperial College London, Longenecker & Associates, MMI Engineering, NuVision, OC Robotics, Fortum, University of Birmingham, University of Bristol, University of Cambridge, University of Manchester. |
| Arcadis | AdvanSci, Applied Photonics, Areva RMC, Aurora, ESI, MDecon, Pöyry, ProNu-Dec, Tradebe Inutec, TWI, University of Liverpool, Dalton Nuclear Institute, University of Surrey. |
| Arup | Costain, Pöyry, Studsvik, James Fisher Nuclear, SN3, AdvanSci, MCM, Bilfinger GVA, Pinsent Masons, CL:AIRE, r3 Environmental Technology, Dalton Nuclear Institute. |
| Eden Nuclear and Environment | Cavendish Nuclear, DBE TECHNOLOGY GmbH, Golder Associates, Tradebe Inutec, Project Time and Cost International. |
| Galson Sciences | National Nuclear Laboratory, Frazer-Nash Consulting, Advansci, Amphos 21, Cogentus Consulting, Integrated Decision Management, Jacobs, Kurion, Rodgers Leask, VTT, University of Bristol, Lancaster University, University of Leeds, University of Manchester, University of Sheffield. |
| NSG Environmental | AECOM, ARC, Oxford Technologies, NPL, ESG, Quintessa, React Engineering, KDC, Tradebe Inutec, Synergy Health, Nuclear AMRC, Loughborough University, University of Manchester, University of Surrey. |
Lot C: Spent fuel management and Nuclear materials
| Lead organisation | Consortia |
|---|---|
| Wood | Andra, Brenk Systemplanung, Jülich Research Centre, Imperial College, DAS Ltd, Fortum, MMI Engineering, NPL, NRG, OC Robotics, Studsvik, University of Birmingham, University of Manchester, University of Bristol, University of Cambridge, Loughborough University. |
| Orano | NSG Consultancy, MDecon, Quintessa, University of Liverpool, University of Sheffield. |
| National Nuclear Laboratory | Frazer-Nash Consulting, Galson Sciences, ALD France, Aquila Nuclear Engineering, DBD, DAS, IDM, Jacobs, Kurion, Rodgers-Leask, University of Bristol, Lancaster University, University of Leeds, University of Manchester, University of Sheffield, Imperial College. |
-
NDA received two acceptable bids for this work from NNL and Wood respectively. The bids were complementary and therefore there was merit in commissioning both pieces of work. ↩ ↩2
-
This project involves NDA providing leveraged funding to NNL to facilitate its participation in this EU Horizon 2020 project. NNL’s participation in the project will develop and maintain skills in the area of fuel recycling. ↩

