NDA Draft Business Plan 2023 to 2026 - html version
Updated 21 April 2023
Preface
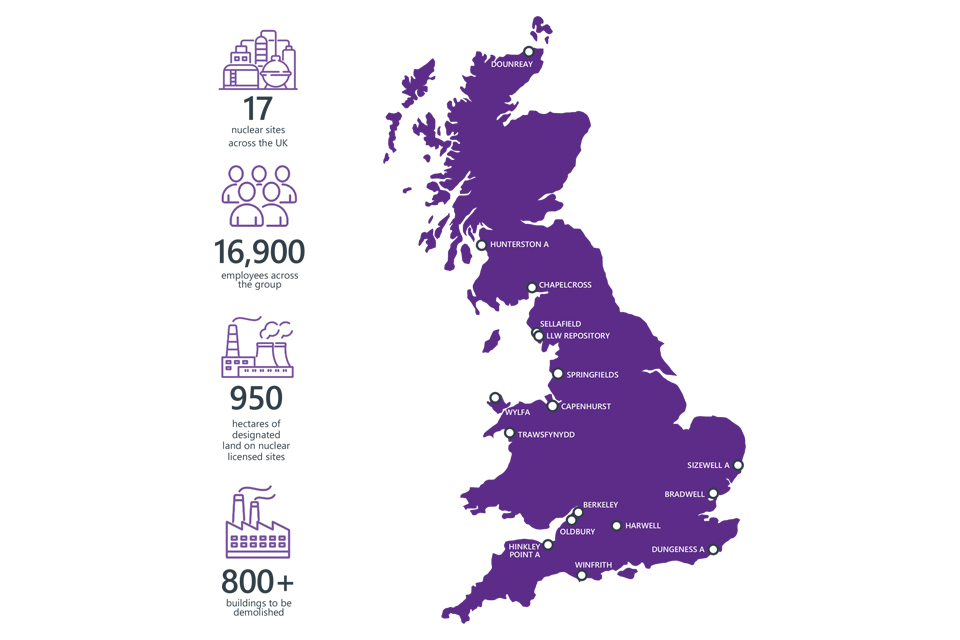
The NDA is charged, on behalf of Government, with the mission to clean up the UK’s earliest nuclear sites safely, securely and cost effectively. We’re committed to overcoming the challenges of nuclear clean-up and decommissioning, leaving the 17 nuclear sites ready for their next use. We do this work with care for our people, communities and the environment, with safety, as always, our number one priority.
Engaging openly and transparently on our work is important to us. This Business Plan is one of several publications which we create and consult on every year. In line with Energy Act requirements, it sets out the activities that will take place over the next three years to advance our important clean-up and decommissioning work and operate our facilities safely and securely. It shows anticipated funding for each of the businesses for 2023/24 and outline total funding for the following year. We show how the activities are helping to deliver our mission by aligning them to the 47 Strategic Outcomes identified in our Strategy and Mission Progress Report. We also include key work across our range of critical enablers vital to the delivery of the mission.
How we communicate our strategy and report progress
Engage with our stakeholders
NDA Strategy
Twelve week public consultation every five years. Describes how we will deliver our mission, ensuring that the UK’s nuclear legacy sites are decommissioned and cleaned up safely, securely, cost-effectively and in ways that protect people and the environment.
Energy Act requirement. Covers 100+ years.
Published every five years.
Report progress
Mission Progress Report
Provides our stakeholders with a clear and concise story of NDA mission progress since 2005, that demonstrates delivery of our strategic themes and outcomes as explained in our Strategy. Covers 100+ years.
Published every year.
NDA Business Plan
Eight week public consultation every year.
Describes key activities across the group over the next three years that align to our strategic outcomes and details the funding available for the next year.
Energy Act requirement. Covers three years (the first year in more detail).
Published every year.
NDA Mid-Year Performance Report
Provides a progress update against Business Plan activities and incorporates the NDA group targets.
Published every year.
NDA Annual Report and Accounts
Describes achievements and spending. Reports against Business Plan activities and contains an overall progress update against our mission.
Published every year.
A message from our Chief Executive David Peattie
Welcome to the NDA’s Business Plan, setting out our plans to 2026.
A simplified, stronger group
Last year I reported that all parts of the group had become NDA subsidiaries and that Nuclear Transport Solutions and Nuclear Waste Services had been formed. Preparations are now underway for Magnox Ltd and Dounreay Site Restoration Ltd to join together in 2023, subject to regulatory approval, as we continue to maximise the way that the NDA group works together.
The benefits of this simplified, stronger group are already clear. This plan highlights areas where our new operating model is making a difference, including the development of group-wide strategies on topics such as sustainability, innovation, asset management and digital. We’ve also agreed an operating framework that confirms the responsibilities held by all parts of the group and how we’ll work together to deliver best value for taxpayers.
I am acutely aware of the economic challenges facing the country and continue to welcome Government’s support for our nationally important work, mindful that there is a very clear need for us to spend money wisely and provide maximum value for the UK.
Progressing our mission
We organise our work into five themes and 47 strategic outcomes, providing a clear view of progress towards our mission. Many outcomes are long-term, delivered over many years. As a result, it’s rewarding to see some major milestones completed in the last year.
The Magnox Reprocessing Plant at Sellafield closed in July after 58 years, having handled around 55,000 tonnes of spent fuel during its lifetime. This enables the site to fully focus on decommissioning, with the recent start of waste retrievals from the Magnox Swarf Storage Silo a sign of that. Around two decades in the planning, it’s a significant moment to see material removed from one of our highest hazard facilities. Retrievals continue to be a focus for Sellafield, along with receiving and dismantling fuel from EDF Energy’s advanced gas-cooled reactors (AGRs).
Waste management is important across the estate, including at Magnox where a modular encapsulation plant recently went into service at Berkeley, helping to make intermediate level waste safe and generate learning that will shape plans at other sites. High hazard reduction also continues at Dounreay, in areas such as the Dounreay Fast Reactor and Prototype Fast Reactor, while the team develops an updated lifetime plan following its move to be an NDA subsidiary.
The work by Nuclear Waste Services (NWS) to find a suitable location for a geological disposal facility (GDF) has now seen four Community Partnerships established. Geophysical investigations have been completed off the Cumbrian coast, with geological analysis beyond the Lincolnshire coast due next year. This will enable site specific designs and safety assessments, providing communities with a better understanding of what hosting a GDF would mean for them.
NWS also manages an Integrated Waste Management Programme on behalf of the wider group. A five-year delivery plan has been developed, with innovative treatment, packaging and disposal solutions being considered that could lead to more sustainable outcomes.
Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS) is taking that learning and creating an Integrated Transport Management Programme, ensuring the NDA group’s transport requirements are joined up. It’s also progressing important work on the global stage, transporting mixed oxide (MOX) fuel from France to Japan and delivering vitrified high level waste and conditioned intermediate level waste to international customers.
Of course it’s not just what we do, but how we do it that is important and sustainability is now a critical enabler of our mission. Pioneering and innovative steps are being taken across our estate as we maintain our commitment to become carbon net zero by 2050, and 2045 in Scotland, with carbon management plans expected to be implemented in each part of the group during the next three years.
Trusted to do more
Our mission is growing, with preparations underway for EDF Energy to transfer seven AGR stations to the NDA, for decommissioning by Magnox. This is the most significant increase to the NDA’s portfolio since our creation, with each site moving across when defueling is complete. Strategies are being aligned and assumptions agreed before Hunterston B is expected to become the first site to transfer.
We’re also working with the Ministry of Defence to consider the potential for the NDA group to decommission its Vulcan site which sits next to Dounreay in Caithness. In addition, the UK Government has asked us to support its Energy Security Strategy and we recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Cwmni Egino. This will see us share information and expertise on the characteristics of land around our Trawsfynydd site to support the development of a new small-scale nuclear project.
While exploring and progressing these opportunities, our core mission remains unchanged.
Attracting and retaining skills to deliver our mission
With a complex range of skills needed to deliver this crucial and growing mission, our ambition to create great places to work has never been more important. This is particularly true as we face a so-called ‘war for talent’.
I’m pleased that our Leadership Academy and other development activities, such as a bespoke women’s development programme, are exceling. Attracting new people to the industry is also important and we’re set to launch a new NDA group graduate scheme that will see us do more to develop professional pathways in a number of areas, helping us to meet our requirements and importantly offering a fantastic way for graduates to start a career.
Working with stakeholders
An important part of my role is to engage with stakeholders and representatives of the communities in which we operate. This year has seen us get back together in person after many pandemic-related delays, welcoming hundreds of companies to our supply chain event and around 200 community representatives to our stakeholder summit in Edinburgh. These events were truly valuable, listening to views and understanding different perspectives.
In Edinburgh we signed an agreement to create a non-governmental organisation, or NGO, forum. The first meeting will soon take place, providing an important channel for dialogue about our future work.
We’ve also recently completed a stakeholder survey, with 829 individuals taking the time to provide us with detailed feedback on our progress, transparency and leadership. I’m happy to say the results are extremely encouraging, with community stakeholders underlining their positive perceptions of the NDA group, the importance of our strong relationships, and the robust platforms for dialogue and engagement.
Thank you
This Business Plan sets out a challenging programme of work, reducing hazards while contributing to a globally significant sustainability agenda, developing our people and supporting our communities. I remain proud of colleagues across the group who continue to safely progress our nationally important mission and together I’m confident we can deliver our mission, create great places to work and be trusted to do more.
David Peattie CEng HonFNucl
NDA Group Chief Executive Officer
The NDA and our mission
What we do
As owners of one of the largest nuclear decommissioning and remediation programmes in Europe, we develop the strategy for how work should be carried out. We also play an important role in supporting Government’s aspiration for the UK to be a leader in the civil nuclear sector within our remit and areas of expertise. Our strategy is continually evolving and is updated every five years. Our fourth iteration was published in March 2021. We strive to deliver best value for the UK taxpayer by focusing on reducing the highest hazards and risks, while ensuring safe, secure, and environmentally responsible operations at our sites. We seek ways to reduce the level of public funding by generating revenue through our commercial activities.
How we’re set up
We’re a non-departmental public body created by the Energy Act 2004 to clean-up and decommission our 17 sites. We’re sponsored and funded by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). Our plans for cleaning up the sites are approved by BEIS and Scottish ministers, who provide a framework for us. We have offices across the UK, in Cumbria, Warrington, Dounreay, Harwell and London and employ just over 380 permanent staff.
Our sites
The UK’s nuclear landscape began to take shape in the post-war period and has evolved over many decades. The focus during the Cold War arms race was on producing material for Britain’s nuclear deterrent. When the nation’s priorities shifted, facilities were turned into nuclear power stations, and, from 1956 onwards, the UK’s first nuclear power stations began generating electricity for homes and businesses. Fuel fabrication and reprocessing plants were built from the 1970s to 1990s. Our 17 sites reflect this legacy and include the first fleet of nuclear power stations, research centres, fuel-related facilities, and Sellafield, which has the largest radioactive inventory and the most complex facilities to decommission. Current plans indicate it will take more than 100 years to complete our core mission of nuclear clean-up and waste management. The goal is to achieve the end state at all sites by 2130s, with all land on Scottish sites expected to be de-designated by 2333.
The NDA group
Accomplishing this important work requires the best efforts of the entire NDA group.
Cleaning up and decommissioning the UK’s nuclear legacy is a complex undertaking and relies on the full range of expertise and skills within the NDA group. Over the last few years, important decisions have been taken about how the organisations delivering our mission are managed, with the intention of simplifying structures and creating a stronger NDA group.
Last year we took the final steps to move to a group (subsidiary) operating model, away from the previous contractual, parent body organisation approach. Dounreay Site Restoration Limited (DSRL) became an NDA subsidiary in April 2021, followed by Low Level Waste Repository Limited (LLWR) in July. These follow similar changes for Sellafield in 2016 and Magnox in 2019.
Moving to a group model has enabled us to make further improvements and simplify structures. In January 2022 Radioactive Waste Management (RWM) and LLWR came together into one waste organisation, Nuclear Waste Services (NWS). We have also announced our intention to join Dounreay with Magnox in 2023, subject to regulatory agreement.
The NDA group will then be made up of the NDA and operating companies: Sellafield, Magnox with Dounreay, Nuclear Waste Services and Nuclear Transport Solutions. Our other subsidiaries include Rutherford Indemnity, NDA Archives, NDA Properties and Energus.
With the finalisation of this structure comes the ability to introduce group-wide policy statements in a number of areas.
There are nine policy statements and the NDA and its operating companies will meet the requirements of these through their individual arrangements:
- Ethics
- Sustainability
- Socio-economics
- Health and safety
- Environment
- Security
- Accounting
- Value for money*
- Diversity and inclusion*
The scope of the NDA group is set to grow, following arrangements agreed by the Government and EDF Energy for decommissioning Britain’s seven advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) stations.
The AGRs will reach the end of their operational lives over the next 10 years and, as they come offline, their ownership will transfer to the NDA for decommissioning, utilising the expertise of our group and significantly, Magnox and its experience in decommissioning the older Magnox stations.
*Still under development
Our vision
- Deliver our mission together safely, securely and more creatively, transparently and efficiently
- Create great places to work and take pride in what we do
- Trusted to do more in the UK and globally
Our funding
We are publicly funded through the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). Our total planned expenditure is voted upon annually by Parliament in line with the Spending Review.
Funding framework
Government has shown continued support for the NDA mission over recent years with increased grant funding offsetting the decline in commercial revenue. Spending Review 2021 (SR21) set funding for three financial years from 2022/23 to 2024/25. Funding for the final year of this plan (2025/26) has not yet been established and will be set as part of a future Spending Review process.
Commercial income
We maximise revenue from our existing assets and operations to help fund decommissioning and clean-up, in order to reduce the level of public funding needed to meet the scope of our plans and delivery of the NDA mission.
Our commercial operations are primarily spent fuel and nuclear materials management with additional opportunities identified in providing transportation services.
We will pursue all commercial opportunities using our existing assets, operations and people where they do not materially impact on our core mission or increase our liabilities.
Prioritisation and allocation of funding
Within affordability constraints, we will seek to maintain progress and maximise value for money through the effective implementation of our strategy. This means focusing on reducing our highest hazards and risks, whilst ensuring that safe, secure and environmentally responsible site operations are maintained.
Planned income and expenditure in 2023/24
This Business Plan sets out our anticipated income and expenditure for 2023/24. High inflation has placed significant cost pressure on many areas of our spend, but has also resulted in an expected increase in our income.
Our total planned expenditure for 2023/24 is £4.133 billion, of which £2.963 billion will be funded by UK Government and £1.170 billion from internally generated revenue.
Planned expenditure on site programmes will be £3.948 billion, while non-site expenditure is expected to be £0.185 billion.
This non-site expenditure includes skills development, socio-economic, research and development, insurance and pension costs, implementing geological disposal and the NDA operating costs.
- £4.133bn total planned expenditure 2023/2024
- £2.963bn funded by UK Government
- £3.948bn planned site expenditure
- £0.185bn planned non-site expenditure
| £m Businesses/Sites | Decom and Clean-up Costs | Total Operations Costs: Running Cost (B) | Total Operations Costs:Capex (C) | 2023/24 Plan Total (A+B+C) | 2022/23 Plan Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sellafield Limited | 1,462 | 731 | 607 | 2,800 | 2,345 |
| Magnox Limited | 530 | - | - | 530 | 515 |
| Dounreay Site Restoration Limited | 221 | - | - | 221 | 205 |
| Nuclear Waste Services | 240 | - | - | 240 | *202 |
| Nuclear Transport Solutions | - | 111 | - | 111 | 86 |
| Springfields Fuels Limited | 22 | - | - | 22 | 30 |
| Capenhurst | 24 | - | - | 24 | 31 |
| Non-site expenditure | 185 | - | - | 185 | *231 |
| Total | 2,684 | 842 | 607 | 4,133 | 3,645 |
| Income | - | - | - | 1,170 | 820 |
| Net (grant funded) | - | - | - | 2,963 | 2,825 |
Notes:
- Numbers may not cast due to rounding
- Final Annual Site Funding Limits issued in March 2023 may be adjusted to reflect efficiency,
performance and portfolio pressures. - The NDA reserves the right to reallocate funding to meet prioritised programme needs.
*2022/23 figures differ from that disclosed in last year’s plan as some waste-related expenditure previously shown in non-site expenditure is now shown under Nuclear Waste Services
Summary of NDA funding 2023/24 onward
| Summary of NDA funding | 2023/24 £m | 2024/25 £m | 2025/26 £m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Income | 1,170 | 1,338 | tbc |
| Government funding | 2,963 | 2,940 | tbc |
| Expenditure | (4,133) | (4,278) | tbc |
| Net | - | - | - |
2023/24 breakdown of non-site expenditure
| Non-site expenditure | 2023/24 Plan £m | 2022/23 Plan £m |
|---|---|---|
| NDA operating costs | 38 | *37 |
| Critical enablers | 74 | 71 |
| Estate insurance | 12 | 11 |
| Other central spend | 61 | **110 |
| Total | 185 | 229 |
*figure differs from that shown in last year’s plan due to a reclassification of costs to ‘Other central spend’ ** figure differs from that shown in last year’s plan due to i) a reclassification of costs from ‘NDA operating costs’ and ii) a reclassification of certain waste-related costs now shown under Nuclear Waste Services
2023/24 breakdown of planned income by category
| Income source | 2023/24 Plan £m | 2022/23 Plan £m |
|---|---|---|
| Reprocessing and fuel management services | 906 | 548 |
| NDA – INS transport | 73 | 51 |
| NDA-generated revenue | 152 | 177 |
| Intra-site services | 39 | 44 |
| Total | 1,170 | 820 |
Current plans indicate it will take 100+ years to complete our core mission of nuclear clean-up and waste management
Our strategic approach and themes
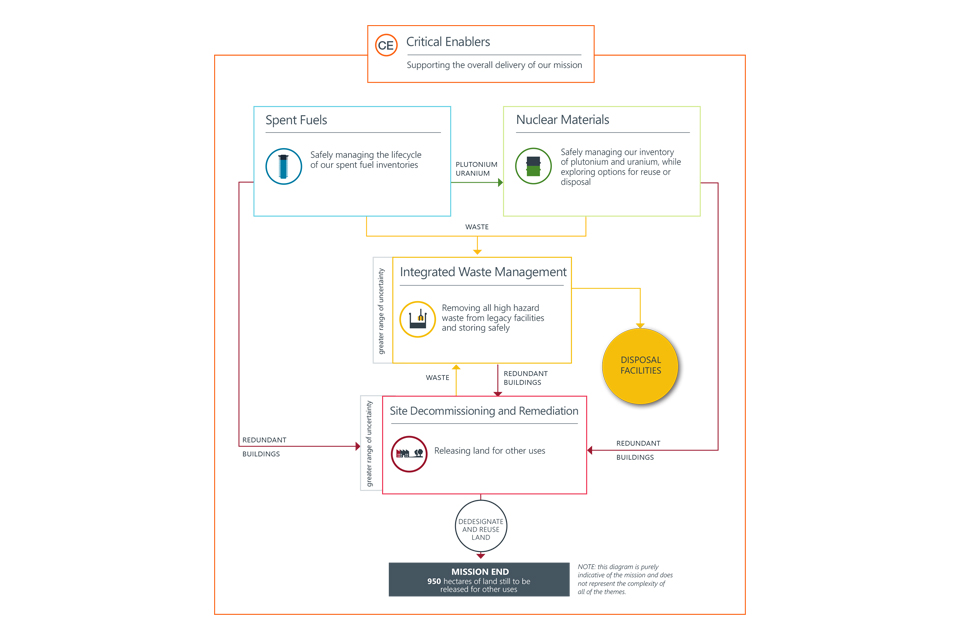
We use five strategic themes to describe all the activities needed to deliver the NDA’s mission.
The first four strategic themes, Spent Fuels, Nuclear Materials, Integrated Waste Management and Site Decommissioning and Remediation relate directly to our clean-up and decommissioning work and are known as driving themes.
The fifth theme describes the important activities needed to support the delivery of our mission and is known as Critical Enablers. The diagram below demonstrates how they interplay.
Currently, the most urgent task is dealing with our sites’ highest-hazard materials, spent fuel, nuclear materials and highly-radioactive wastes. Once the inventory has been made safe, the redundant nuclear facilities can be dismantled and demolished.
Our five themes
Spent Fuels
Our strategy defines our approach to managing the diverse range of spent fuels for which we are responsible, which are divided into Magnox, Oxide and Exotic. Once spent fuel is removed from a reactor, it is stored in a pond or dry store until it can be dispatched to Sellafield.
Reprocessing extracts materials (plutonium and uranium) that could potentially be re-used and also generates highly radioactive wastes, or fission products. The NDA’s strategy is to bring the reprocessing programme to an end. The THORP reprocessing plant and the Magnox reprocessing plant have now closed. All remaining spent fuel will be safely stored until a permanent solution for disposal is available. Our spent fuel work is separated into fifteen strategic outcomes that we must deliver.
Nuclear Materials
Our strategy defines our approach to dealing with the inventory of uranics and plutonium currently stored on some of our sites. These nuclear materials are by-products from different phases of the fuel cycle, either manufacturing or reprocessing. All nuclear materials must be managed safely and securely, by either converting them into new fuel or immobilising and storing them until a permanent UK disposal facility is available.
All of our plutonium is stored at Sellafield. Our uranium is located at a number of our sites and we are continuing to consolidate it at sites which we consider are best suited to its management.
Our nuclear materials work is separated into ten strategic outcomes that we must deliver.
Integrated Waste Management
Our strategy considers how we manage all forms of waste arising from operating and decommissioning our sites, including waste retrieved from legacy facilities. Managing the large quantities of radioactive waste from electricity generation, research, the early defence programme and decommissioning is one of the NDA’s biggest challenges. Some of this radioactive waste is in a raw (untreated) form, some has been treated and is being interim stored and, in the case of low level waste, some has already been permanently disposed of.
Retrieving, treating and interim storing the radioactive waste from Sellafield’s four legacy ponds and silo facilities is the NDA’s highest priority.
Our integrated waste management work is separated into fourteen strategic outcomes that we must deliver.
Site Decommissioning and Remediation
Our strategy defines our approach to decommissioning redundant facilities and managing land quality in order that each site can be released for its next planned use. After the buildings on our sites have been decommissioned, decontaminated and dismantled the land will be cleaned up to allow it to be released for other uses. At that point, its ownership would transfer to the new user of the land.
The NDA is currently assessing alternatives for the final stages of decommissioning that could lead to earlier release of land, continued employment and opportunities to reuse the land.
Our site decommissioning and remediation work is separated into eight strategic outcomes that we must deliver.
Critical Enablers
Some of the work we do, we describe as ‘critical enablers’. Critical enablers cover the important activities needed to support the overall delivery of our mission.
Work featuring in 2023-2026
This Business Plan covers the work we will do over the next three years to progress or complete activity across our five strategic themes. You can find the 2023-2026 plans for each of the NDA group operating companies in the next sections.
The next sections present in more detail examples of some of the important work that will either be completed or advanced in the next three years. This near-term activity is mapped against our strategic themes and specifically to the 47 outcomes* that make up our mission.
*Our 47 outcomes cover all our strategic themes except ‘critical enablers’.
Spent Fuels 2023-2026
Spent Magnox Fuel
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | All sites defueled | Completed |
| 2 | All legacy Magnox fuel retrieved | 2039 |
| 3 | All Magnox fuel reprocessing completed | Completed* |
| 4 | All remaining Magnox fuel in interim storage | 2042 |
| 5 | All remaining Magnox fuel disposed | 2125 |
Spent Oxide Fuel
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | All EDFE Oxide fuel received | 2035 |
| 7 | All legacy oxide fuel retrieved | Completed |
| 8 | All oxide fuel reprocessing completed | Completed |
| 9 | All remaining oxide fuel in interim storage | 2035 |
| 10 | All remaining oxide fuel disposed | 2125 |
Spent Exotic Fuel
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | All exotic fuel defueled | 2024 |
| 12 | All exotic fuel consolidated | 2028 |
| 13 | All exotic fuel reprocessing completed | Completed* |
| 14 | All remaining exotic fuel in interim storage | 2028 |
| 15 | All remaining exotic fuel disposed | 2125 |
*Completed subject to final date verification.
Case study - Magnox Reprocessing Plant completes mission
Sellafield’s Magnox Reprocessing Plant ceased operations this year, completing a mission spanning almost six decades.
The plant handled around 55,000 tonnes of spent fuel during its lifetime from the UK’s fleet of 11 Magnox plants as well as reprocessing Magnox fuel from Italy, Japan, and fast breeder fuel from Dounreay. In total, it returned over 15,000 tonnes of uranium back into the fuel cycle. All Magnox reactors have stopped generating and completed final defuelling, with the last load of burnt-up Magnox fuel arriving at Sellafield in 2019.
Fewer than 250 tonnes of fuel is now left for interim storage on the site before eventual final storage in a geological disposal facility.
Case study - Preparations for AGR stations to transfer
Arrangements have been agreed by the UK Government and EDF Energy for Britain’s seven advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) stations to be decommissioned by the NDA group.
The first site to transfer is likely to be Hunterston B in 2026, with exact timescales to be determined by factors including defueling progress. The final AGR station will likely transfer in the early 2030s.
Preparations are underway, including collaborative work to align decommissioning strategies and plans and the development of key strategic assumptions which will determine the position the first site will be in when it transfers after final defueling is completed. This will act as a template and learning basis for subsequent station transfers.
Nuclear Materials 2023-2026
Plutonium
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | All plutonium produced | 2023 |
| 17 | All plutonium consolidated | Completed |
| 18 | A: All plutonium repacked in long-term storage B: All cans not suitable for extended | |
| storage repackaged | 2060 | |
| 19 | All plutonium in modern interim storage | 2060 |
| 20 | All plutonium reused or disposed | 2120 |
Uranium
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | All uranium produced | 2023 |
| 22 | All uranium consolidated | 2025 |
| 23 | All uranium treated | 2055 |
| 24 | All uranium in interim storage | 2055 |
| 25 | All uranium reused or disposed | 2120 |
Case study - Uranium consolidation programme
Reprocessing spent nuclear fuel separates uranium, plutonium and other fission products. Large quantities, approximately 70,000 tonnes of uranium, in various forms, have been generated as a legacy of the UK’s civil nuclear programme. The NDA is responsible for safely managing this inventory of uranic material.
81% of this uranic material has now been consolidated at the Capenhurst site in Cheshire, where it is safely stored pending a decision on future use or disposition.
Approximately 2,900 tonnes of uranium still need to be consolidated:
- 2,000 tonnes in the form of uranium hexafluoride at Springfields fuel manufacturing site in Lancashire
- 200 tonnes of uranium produced from reprocessing operations at Sellafield
- The remainder is held in various sites across the NDA group
Good progress continues to be made as part of the consolidation programme with over 100 tonnes of uranic material consolidated from across the NDA group to Capenhurst in 2022, including ongoing monitoring and assessment to ensure the material continues to be stored safely.
Integrated Waste Management 2023-2026
Low Level Waste
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 26 | All LLW produced | 2127 |
| 27 | All LLW treated - to enable diversion or reuse | 2127 |
| 28 | All waste suitable for disposal in NDA facilities | 2127 |
| 29 | All waste suitable for permitted landfill disposed | 2127 |
Intermediate Level Waste
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | All ILW produced | 2120 |
| 31 | All ILW waste retrieved | 2048 |
| 32 | All ILW treated | 2120 |
| 33 | All ILW in interim storage | 2120 |
| 34 | All ILW disposed | 2125 |
High Level Waste
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 35 | All HLW produced | 2030 |
| 36 | All HLW treated | 2030 |
| 37 | All HLW waste in interim storage | 2030 |
| 38 | All overseas HLW exported | 2025 |
| 39 | All HLW disposed | 2104 |
Case study - First waste removed from legacy silo at Sellafield
The first waste has been retrieved from Sellafield’s Magnox Swarf Storage Silo (MSSS). It’s part of work to progress the retrieval of high hazard waste from Sellafield’s four legacy ponds and silos and place it in modern facilities at the site.
It represents a significant step in the site’s decommissioning and is a milestone that’s involved around two decades of planning and preparation. This achievement is the result of a significant effort by Sellafield Ltd, the supply chain and key stakeholders such as regulators and Government.
Retrieval of material from the Pile Fuel Cladding Silo was also expected to commence in 2022, but a number of operational challenges mean this is now expected in 2023. It will mean that all four legacy facilities have then commenced the process of retrievals.
Case study - A solution for the future
Delivering a geological disposal facility (GDF) to dispose of higher activity radioactive waste is an important project for the UK. It’s a key focus for the recently formed Nuclear Waste Services, an NDA group company responsible for managing radioactive waste.
Significant progress has been made in finding a willing community this year. Four communities have formed Community Partnerships, three in Cumbria, Mid-Copeland, South-Copeland and Allerdale, and one in Theddlethorpe in Lincolnshire.
As well as progressing with community engagement, the first phase of site evaluation has taken place with geophysical investigations off the coast of Cumbria conducted over the summer.
Further geological analysis beyond the Lincolnshire coast will take place next year. This will allow us to develop site specific designs and safety assessments providing local communities with a better understanding of what hosting a GDF would mean for them.
Site Decommissioning and Remediation 2023-2026
Operational and planned
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 40 | All planned new buildings Operational | 2090 |
| 41 | All buildings primary function completed | 2127 |
Decommissioning and demolition
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 42 | All buildings decommissioned | 2131 |
| 43 | All buildings demolished or reused | 2133 |
Sites
| Outcome number | Activity | End date |
|---|---|---|
| 44 | All land delicensed or relicensed | 2135 |
| 45 | All land in End State - all planned physical work complete | 2134 |
| 46 | All land delicensed or relicensed | 2135 |
| 47 | All land in End State - all planned physical work complete | 2333 |
Case study - Establishing site end states
Dounreay, Hunterston A, LLW Repository, Trawsfynydd and Winfrith sites have taken the lead in developing preferred end state assumptions.
We have a responsibility to propose end states for each of our sites - defined as the physical condition to which the site will be taken at the end of the decommissioning process.
It will vary between sites, taking into account factors such as safety, community requirements and environmental sensitivities. Given most end states will not be achieved for decades, the focus is on developing credible options to set direction.
Work at these lead sites is an example of collaboration across the NDA group, alongside wider engagement with regulators and local authorities as well as UK and international good practice forums.
A delivery schedule for the remaining Magnox sites has also been agreed alongside the establishment of an end state enabling programme at Sellafield.
Case study - Trawsfynydd looks to reduce reactor height
Magnox has taken an important step towards its goal of reducing the height of the reactor buildings at Trawsfynydd, which is a major milestone it its programme to decommission the site.
The former nuclear power plant is nestled in Snowdonia National Park, so the aesthetics of the site are considered alongside safe and sustainable decommissioning. The project will reduce the height of the reactors and soften the skyline whilst addressing structural and safety deficiencies associated with the full height structure.
An outline business case was approved this year enabling detailed development to begin. The project will go out to tender next year, providing opportunities for suppliers and the local economy.
Completion of the project will see the volume of the building diminish by 96,000m3, the height reduce by 29 metres and 30,000 tonnes of concrete removed, crushed and reused on the site.
Critical Enablers 2023-2026
Socio-Economic
Investing in our communities
The NDA has a legal duty set out in the Energy Act to have regard for the impact of our activities upon those communities living near our sites. In addition, we share the same responsibilities all public bodies have under the Public Services (Social Value) Act to secure wider social, economic and environmental benefits from how we undertake our work.
Our approach towards fulfilling these responsibilities can be found in the NDA Local Social and Economic Impact Strategy and this informs our social impact programme.
The NDA Group Social Impact programme invests approximately £15 million per year in those communities where we are progressing our nuclear decommissioning mission, leveraging millions more in the process.
This programme addresses the key, structural economic challenges facing our site communities and is delivered by local social impact teams working in our operating companies and living in those communities where we are working to achieve change.
By building partnerships, leveraging funding, and attracting investment, we are building a lasting social and economic legacy for future generations beyond the completion of our mission.
Case study - Morlais Tidal Energy Project, Ynys Môn
Working with social enterprise Menter Môn, a £900,000 investment from the NDA and Magnox Ltd has leveraged £39 million from the Welsh Government to develop Morlais - a 240 megawatt tidal energy project off Holy Island, creating at least 100 new jobs in the area with the potential for many more.
Menter Môn works across north Wales to deliver a range of regeneration, environmental and cultural projects by working in partnership with Government, the third sector and business.
Still in the development process, the Morlais project supports local businesses and has taken on eight new local apprentices to date. All profits will be reinvested locally through a new community benefit fund and through Menter Môn community projects. As a renewable energy project, providing clean energy, new jobs and economic diversification, the Morlais project is the definition of ‘green growth’.
Case study - iSH - The Industrial Solutions Hub, Cleator Moor
With an investment of over £10 million from the NDA and Sellafield Ltd, the Industrial Solutions Hub (iSH) will unlock millions more funding as part of a £22.5 million Town Deal for Cleator Moor.
iSH is a social enterprise, owned by Copeland Borough Council with the aim of growing and diversifying the economy of West Cumbria away from an over-dependency upon Sellafield. It brings together Sellafield Ltd, its supply chain, academia and research facilities into a business cluster focused on industrial problem solving and practical applications, creating an ecosystem to encourage and foster successful business start-ups and nurture small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) development.
The iSH campus aims to create around 700 new job opportunities and is set to generate an additional £40 million per year of revenue for local businesses.
Group strategies
Case study - Group-wide Digital and Innovation strategies launched
Group-wide digital and innovation strategies have been developed and published this year.
Everyday lives have become increasingly digitally enabled, with the pandemic leading to a significant change in working processes and practices, facilitated by technology.
Our Digital Strategy enables better collaboration, and freeing up time to be spent on delivery at all levels of the organisation.
Meanwhile innovation, alongside research and development, is a critical enabler of the NDA’s Strategy 4. The Innovation Strategy draws heavily upon collective knowledge, capabilities and information infrastructure.Essential to successful implementation will be enabling a culture where innovation can thrive.
Change extends beyond technology and engineering. It includes our approach to project management, finance, risk, contracting, skills development, assurance, and approvals.
Research, Development and Innovation
Case study - NDA and National Decommissioning Centre launch research partnership
The NDA and the National Decommissioning Centre (NDC) have signed a three-year collaborative research agreement - the first of its kind between the nuclear and oil and gas decommissioning sectors.
The unique strategic partnership, supporting research with a potential value of up to £900,000, will see us work with researchers from the University of Aberdeen in areas of mutual interest to both the nuclear and oil and gas sectors.
These will include decarbonisation of decommissioning activities, economic impacts, cost benchmarking and remote operations in hazardous environments.
The partnership will draw on current research taking place at the NDC and the University of Aberdeen as well as harnessing the capabilities of the NDC’s £1.6 million simulation suite, to enable operational scenarios related to nuclear decommissioning activity to be trialled in a safe, virtual environment.
This will allow users to reduce the risks in operations such as the removal or moving of infrastructure, or deployment of new technologies to understand which are best suited to a task.
People
Case study - Launching an NDA group graduate programme
NDA needs the right people, with the right skills, in the right place, at the right time to deliver our mission. Ensuring that we have a pipeline of future talent is one of the most important investments we make.
The Nuclear Graduates programme, established by NDA in 2008, is an award-winning two-year programme playing a key role in attracting diverse, critical skills and talent into the sector.
More than 400 graduates have so far been recruited by the programme, working across the NDA group and wider industry.
We have also recently invested in specialist programmes to meet head on some of the skills challenges we face. These include cyber, radiation protection and finance, audit and risk.
Building on that success, we’re preparing to launch an NDA group graduate scheme, complementing the existing Nuclear Graduates programme and enabling us to bring together professional pathways in a way which not only enables us to meet our skills needs, but offers a unique and rich experience for our successful graduates.
Stakeholder Relations
Case study - Public and Stakeholder Engagement as a key enabler
Around 170 representatives of communities and organisations from across the UK gathered in Edinburgh for the NDA group’s stakeholder summit in September.
It was the first time in three years that stakeholders have gathered in person due to the pandemic. The event covered updates on the decommissioning mission, social value, skills and sustainability.
The event supports the NDA’s objective of building better understanding and support of our mission with stakeholders and the general public, maintaining their support, confidence, and trust through consultation, engagement and outreach.
The summit also saw an agreement signed to create an NDA/non-governmental organisation (NGO) forum underpinning NDA’s commitment to openness and transparency, by encouraging wider scrutiny of activities. Stakeholder feedback received during engagement on NDA’s latest strategy and regular surveys highlighted a request to broaden engagement to include more young people and also pressure groups and NGOs, to allow greater inclusivity of viewpoints, and challenge.
Asset Management
Case study - Digital transformation is the future of asset management
NDA group colleagues have been actively working together to understand how best we can manage the multiple assets we have across the estate.
Our sites have facilities that are 50-70 years old. They are well beyond their design life and, in many cases, destined for deactivation and decommissioning. Other facilities are needed to support the continuing missions, such as the retrieval, treatment and stabilisation of legacy waste and environmental remediation efforts, missions which are expected to last for many years. It’s an extremely complex picture.
The key to managing these assets sustainably, balancing cost, risk and performance is to have reliable, consistent data. Efficient data and information management are essential to allow for better informed decision-making, ultimately leading to greater longevity for assets and improved process performance.
The group has been collaborating on a joint Asset Management Strategy. This sets out an agreed approach by which we can drive towards achieving the best industry standards in asset management.
Teams are looking at how we can move from a situation where there is heavy reliance on manual processes, inconsistent data sets and join up systems that need to talk to each other, standardising diagnostic information from plants and facilities across sites. It’s work that has the potential to achieve multi-million pound efficiency savings.
Beginning with pilot schemes at Dounreay and Sellafield, teams will be working together to achieve the bridging of the gap between IT/OT (Information Technology and Operational Technology) so that the estate will be able to create connected infrastructure.
Magnox is being supported through its Enterprise Asset Management transformation program to bring on board the NDA Asset Information Strategy. This will transform the way work is delivered and asset risk is managed while readying Magnox to integrate the AGR fleet successfully.
Diversity and Inclusion
Case study - Passports help diversity and inclusion journey
Our employee-led disability network, known as Enable, has sponsored and championed a group-wide initiative to introduce workplace adjustment passports.
They can be used by all employees and not just those with recognised disabilities, long-term illnesses or caring responsibilities.
The passport records any agreed reasonable adjustments, changes to work schedules, role and responsibilities, working environments, provision of specialist technology and other support and assistance as may be required. If employees move roles within the group, the passport can be taken with them to support conversations about adjustments in the new workplace.
Enable is just one of our employee-led networks, with gender balance, menopause, LGBT+ and race equality groups also helping to connect with colleagues and support our diversity and inclusion journey.
Sustainability
The NDA group has a legal, moral and ethical responsibility to deliver our mission sustainably, with care for our people, communities and the environment. Demonstrating its importance, sustainability was introduced as a critical enabler to our mission in the NDA Strategy 4, published in 2021.
A resulting Sustainability Strategy has been launched this year with a focus on delivering sustainable outcomes through decommissioning practices, with care for the environment through positive and sustainable socio-economic outcomes for nuclear communities.
The strategy links with other wider considerations including achieving carbon net zero by 2050 in England and Wales and 2045 in Scotland, Government’s Nuclear Sector Deal and Ten Point Plan for Green Industrial Revolution, as well as adopting the United Nations 17 sustainable development goals.
Case study - CO2 shipping improvement
Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS) has improved its carbon footprint and reduced fuel usage in its shipping operations as the business works to reduce CO2 output.
With transportation heavily reliant on fuel, shipping operations at NTS have focused on new ways to sail differently, using less fuel and reducing exhaust emissions.
On a voyage earlier this year, NTS put a number of techniques into practice, saving over 14% of fuel and 19% in CO2 emissions in comparison to original estimates. This meant an overall saving of 918 tonnes of CO2.
The fuel-saving techniques included:
- Planning more efficient voyages and, where possible, using economical speeds
- Strategic weather routing by the ship’s Master using currents, tidal streams and weather windows
- Single engine operations used where possible
- At the ships’ home port of Barrow, a link to mains power has been installed meaning ships no longer have to run their generators. Solar panels have also been installed to provide electricity to the site.
Case study - Introducing supplier carbon reduction plans
Dounreay now requests that carbon reduction plans are submitted when suppliers bid for work at the site through Contracts Finder. This is encouraging companies to think about how they help the UK to be net carbon zero by 2050. Around 60% of companies bidding for work since the request was introduced have submitted plans, while a quarter don’t have plans, they have alternative polices in place and the remaining companies don’t yet have any arrangements in place.
Case study - Restoring a local environment in Snowdonia
When trees in a conifer plantation near Magnox’s Trawsfynydd site were damaged in recent storms, the NDA and Magnox looked for a sustainable solution. The existing conifers, planted several decades ago, are not native to the area.
So, the decision was taken to replace the damaged plantation with native deciduous trees in keeping with the natural vegetation of this part of Wales. This means that the local environment is protected, providing a more appropriate habitat for local wildlife and giving the local community a more natural and sensitive landscape.
The replanting scheme is just one small part of a programme to understand and improve the local environments across the NDA group – some 4,500 hectares of land in all.
In this part of Snowdonia, these activities are already having an effect. Having seen what the NDA has been doing, a neighbouring farmer is in the process of planting native trees on three hectares of his own land.
NDA group key activities
All activities and dates shown in the subsequent pages represent the latest emerging information and are subject to change.
Where we expect an activity to complete during the Business Plan period, this is clearly stated. All other activities will continue into the following year.
NDA
Important milestones 2023-2026
- Continue preparations for the transfer of Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR) stations to the NDA group for decommissioning
- Continue to embed our Sustainability Strategy to support the NDA’s carbon net zero commitment
- Continue to support the maintenance of sustainable local economies for communities living near NDA sites and contribute to regional economic growth where possible
- Continue to work with group businesses to explore alternative disposal options for Higher Activity Waste
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £38 million
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Spent Fuels | ||
| Spent Oxide Fuel | ||
| Continue to work with EDF Energy and our subsidiaries on the integrated and collaborative delivery programme for the safe and cost-effective defueling of AGR power stations, the AGR Operating Programme | 2023-2026 | 6, 9 |
| Spent Exotic Fuel | ||
| Work with our group businesses to optimise the strategy for the consolidation of exotic fuels from Dounreay to Sellafield | 2023-2026 | 12, 14 |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Plutonium | ||
| Work with the UK Government on a disposition solution that puts the UK’s plutonium beyond reach | 2023-2026 | 20 |
| Implement a programme of research and development to mature the credible options for plutonium disposition | 2023-2026 | 20 |
| Uranium | ||
| In line with our Strategy, and following business case approval, implement the preferred approach to dealing with the NDA owned uranium hexafluoride at Capenhurst | 2023-2026 | 22, 23, 24, 25 |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Make more use of a risk informed approach for waste management and to seek solutions that help to optimise the lifecycle of both radioactive and non radioactive wastes | 2023-2026 | 26 - 39 |
| Work with group businesses to explore alternative disposal options for Higher Activity Waste | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Plutonium | ||
| Work with the UK Government on a disposition solution that puts the UK’s plutonium beyond reach | 2023-2026 | 20 |
| Implement a programme of research and development to mature the credible options for plutonium disposition | 2023-2026 | 20 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Work with our operating companies to support the continued optimisation of our strategies for decommissioning and clean-up, embedding a rolling programme of decommissioning across Magnox reactor sites and planning for the integration of AGRs | 2023-2026 | 42, 43, 44, 45, 46 |
| Reviewing and establishing new guidance on the selection of decommissioning strategies, including our approach to prioritisation | 2023-2026 | 42, 43 |
| Dedesignate or reuse | ||
| Work with Government, regulators and our operating companies to support continued development of more proportionate regulatory arrangements for final stage decommissioning and clean-up and the timely delivery of these | 2023-2026 | 45, 46, 47 |
| Continue to lead the NDA group Remediation Forum, helping embed approaches to the determination and delivery of site end-states across our sites, and sharing our learning through the wider Nuclear Industry Group on Land Quality | 2023-2026 | 45 |
| Review opportunities available under our Group Operating Framework to make better use of our land, across the NDA-owned estate, to support delivery of our decommissioning and clean-up mission and also ensuring we deliver relevant long term controls and stewardship of our sites | 2023-2026 | 46, 47 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Develop strategic opportunities that optimise delivery of the mission | 2023-2026 | - |
| Active participation in the British Energy Security Strategy to help achieve HMG deliverables | 2023-2026 | - |
| Provide support to Government on nuclear new build decommissioning plans | 2023-2026 | - |
| Develop a group-wide accommodation strategy (including welfare, warehousing, transport and logistics) allowing effective re-use of the operational land and creating great places to work | 2023-2026 | - |
| Effective and efficient management and assurance of retained landholding consisting of 2,110 hectares across 81 properties | 2023-2026 | - |
| Proactively dispose/release surplus assets no longer required by the NDA group or wider parts of Government, including those that have high socio-economic value | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continuing to engage with UK and international bodies and partners to share our learning and knowledge, learn from others, and support development of improved approaches to decommissioning and clean-up | 2023-2026 | - |
| Reviewing our ways of working, including our decision-making tool, the Value Framework, to better monitor and deliver sustainability outcomes through our decommissioning and clean-up activities | 2023-2026 | - |
| Reviewing opportunities to embed principles of Circular Economy and Environmental Stewardship into our approaches to site decommissioning and clean-up activities | 2023-2026 | - |
| Sustainability and health, safety, environment and wellbeing | ||
| Ensure that our mission outcomes and the journey to deliver them are sustainable | 2023-2026 | - |
| Having established our group carbon footprint, group carbon policy and a roadmap to net zero by 2050, develop and implement carbon reductions through carbon management plans at each operating company | 2023-2026 | - |
| Build on our natural capital baseline assessment of our NDA owned land and develop a plan to improve the environmental value of this land where this aligns with other strategic land use opportunities | 2023-2026 | - |
| Contribute to environmental sustainability performance and meet Greening Government Commitment | 2023-2026 | - |
| Lead in the area of mental health and wellbeing across the NDA group and further enhance the wellbeing community across the group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Security, resilience, ICT, information governance and digital | ||
| Implement new ICT programmes to allow smarter, flexible working across the NDA. To include digital transformation and Information Governance initiatives aimed at improving the way we work and collaborate, whilst maintaining information security and legislative compliance | 2023-2026 | - |
| Lead on the evolution of the Digital Vision and Strategy and the development of a Data Strategy and Target Operating Model for the NDA group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Support implementation of forthcoming new nuclear emergency preparedness standards across the NDA group, as part of the UK’s implementation of the Basic Safety Standards Directive 2013 | 2023-2026 | - |
| Improved intelligence sharing capabilities with national intelligence service providers and the NDA group | - | |
| Cyber security | ||
| Proactively deter, detect, defend against, recover from and be resilient to both current and evolving cyber threats | 2023-2026 | - |
| Research, development and innovation | ||
| Work with other nuclear and non-nuclear organisations to encourage and leverage cross-sector investment in research, development and innovation and foster technology transfer between sectors and internationally | 2023-2026 | - |
| Lead the promotion and adoption of technology and innovation across the NDA group, developing an environment where innovation can thrive | 2023-2026 | - |
| Work collaboratively across the NDA group to embed good practices in Technology and Innovation Management and Technical Assurance | 2023-2026 | - |
| People | ||
| Enable and drive the delivery of our mission through our people by attracting, retaining and developing a high performing, highly skilled, talented and motivated workforce and creating a culture in which they can thrive. We will continue our commitment to apprentices, graduates and developing the leaders and experts for the short, medium and long term as well as addressing the key skills gap to support delivering our mission | 2023-2026 | - |
| Lead the diversity and inclusion strategy across the NDA group ensuring effective governance and co-ordination to drive a One NDA Inclusion approach, including achieving sector targets, strategy goals and commitments supporting our vision to create great places to work | 2023-2026 | - |
| Implement Government led reforms of public sector pensions across the NDA group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Asset management | ||
| Secure safe, reliable, maintainable and sustainable asset performance and optimise through life cost of assets | 2023-2026 | - |
| Supply chain | ||
| Build commercial capability which maintains a resilient, sustainable, diverse, ethical and innovative supply chain that optimises value for money for the UK taxpayer when sourcing goods and services | 2023-2026 | - |
| Socio-economics | ||
| Support the maintenance of sustainable local economies for communities living near NDA sites and, where possible, contribute to regional economic growth | 2023-2026 | - |
| Public and stakeholder engagement | ||
| Provide opportunities for the public and stakeholders to better understand our mission, comment on and influence NDA planning and decision making, and draw on the knowledge and experience of stakeholders | 2023-2026 | - |
| International relations | ||
| Be a world leader in facilitating international collaboration in nuclear decommissioning | 2023-2026 | - |
| Transport | ||
| Ensure the effective, safe and secure transportation of materials to enable the successful delivery of the NDA mission | 2023-2026 | - |
Sellafield Limited
Sellafield Limited is an NDA subsidiary, responsible for delivering the NDA mission, through operating and decommissioning Europe’s largest and most complex nuclear site. This includes cleaning up nuclear facilities and safeguarding nuclear fuel, materials, and waste.
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £2,800 million
Site in Cumbria
276 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares
All 276 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
The portfolio of work is balanced around the following priorities:
- Safeguarding and keeping secure special nuclear material
- Reducing risk and hazard in high hazard areas
- Support the nation’s civil nuclear programme by:
- The safe management and storage of Advance Gas cooled Reactor (AGR) fuel
- Facilitating the effective defueling of the AGR reactors
- Ongoing safe storage of Magnox remnant fuel
- Ensuring the infrastructure is resilient
- Progressing risk and hazard reduction in other site areas
- Supporting NDA group material consolidation
Important milestones 2023-2026
- Continue to receive and dismantle AGR spent fuel from EDF
- Continued and sustained retrievals from Magnox Swarf Storage Silo (MSSS)
- Continue to retrieve materials from the First Generation Magnox Storage Pond (FGMSP)
- Implement a revised strategy for Magnox remnant fuel
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- All buildings decommissioned - TBD
- All land remediated - 2125
- All land dedesignated - 2125
TBD is shown when the date for completing the strategic outcome is not sufficiently clear for a specific date to be given at this time.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Spent Fuels | ||
| All spent fuels discharged from the operating Advanced Gas-Cooled Reactor (AGR) power stations and defueling of all Magnox power stations reactors are sent to Sellafield for management. The receipt of AGR fuels will continue until the end of the AGR electricity programme, whilst all the Magnox fuel has now been received at Sellafield. The management of AGR fuel under contracts with EDF Energy provides a significant income stream to NDA. | ||
| Spent Magnox Fuel | ||
| Continue to interim store in the Fuel Handling Plant (FHP) remnant Magnox fuel and fuels recovered from the First Generation Magnox Storage Pond (FGMSP) | 2023-2026 | 4 |
| Continue to retrieve fuels from FGMSP | 2023-2026 | 2 |
| Implement a strategy for all of the fuel and fuel bearing materials in FHP | 2023-2024 | 4 |
| Completion of Programme Studies including pre-treatment in FHP for remnant Magnox Fuel | 2023-2025 | 2 |
| Spent Oxide Fuel | ||
| Enhance the capacity to receive/manage and interim store AGR spent fuel from EDF energy to support bulk defueling | 2023-2026 | 6, 8 |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| The various activities across the site produce wastes in many forms. These require varying degrees of treatment and onward processing. The site continues to focus on safe, efficient management of these wastes, including: the conversion of Highly Active Liquor (HAL) into passively safe vitrified waste; the return of vitrified material overseas; and the management of on-site intermediate and low level wastes. The areas of principal focus are the redundant Legacy Ponds and Silos facilities, made up of the Pile Fuel Storage Pond, Pile Fuel Cladding Silo, First Generation Magnox Storage Pond and Magnox Swarf Storage Silo. These facilities supported the development of the nuclear programme in the UK from the early 1950s. Subsequently, they supported electricity generation from the fleet of Magnox power stations. The programmes include the removal of nuclear fuel, sludge and solid material which require the provision of equipment to retrieve the various wastes and then treat and store them. This process needs to take into account the role of integrated waste management in achieving hazard reduction and long-term safety, security and environmental protection requirements. | ||
| Low Level Waste | ||
| Continue to generate savings and preserve capacity at the Low-Level Waste Repository (LLWR) by enhancing capability to divert waste from LLWR and into the supply chain | 2023-2026 | 27 |
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Support risk reduction from Legacy Ponds through continued removal of fuel and waste from the facilities | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Magnox Swarf Storage Silo (MSSS) • Continue retrievals from MSSS • Progress the capability required for bulk retrievals | 2023-2026 | 31, 31 |
| Commence retrievals from Pile Fuel Cladding Silo (PFCS) | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Support the NDA’s strategy by continuing the programmes to receive and treat waste materials from Harwell and AWE Aldermaston | 2023-2025 | 32 |
| Support future waste treatment through implementing the capability to actively demonstrate characterisation, size reduction and decommissioning | 2023-2026 | 32 |
| Support risk reduction by developing additional capability for treatment of intermediate level liquid wastes (Site Ion Exchange Effluent Plant (SIXEP) Continuity Plant (SCP)) | 2023-2026 | 32 |
| Continue to support industry and health care in the management of used radioactive sources | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Ensure continued storage capacity in the SIXEP facility, including the identification of alternative treatment options | 2023-2025 | 33 |
| High Level Waste | ||
| Continue the programme to repatriate overseas-owned vitrified waste to its country of origin | 2023-2026 | 38 |
| Support risk reduction through the continued vitrification of highly active liquor | 2023-2026 | 36 |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Sellafield is the custodian of the majority of the UK’s inventory of separated plutonium which is held in safe and secure storage. | ||
| Plutonium | ||
| Continue the safe and secure storage of plutonium by developing the capability to repack plutonium in line with UK policy | 2023-2026 | 18, 19 |
| Continue to progress NDA disposition residues to waste | 2023-2026 | 20 |
| Uranium | ||
| Support future decommissioning by implementing plans for consolidated storage of Sellafield uranics | 2023-2026 | 22, 24 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and demolition | ||
| Commence post operational clean-out (POCO) of Magnox Reprocessing Plant | 2023-2024 | 42 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| A number of key enabling activities require specific focus, ranging from infrastructure refurbishment or replacement projects, through to key change programmes which aim to improve operational delivery and efficiency on site. | ||
| Continue to support future business requirements including the development and embedding of a value-led culture | 2023-2026 | - |
| Develop and embed the long-term partnership with the supply chain | 2023-2026 | - |
| Progress the transformation of project delivery on site and continue to embed the benefits of the Programme and Project Partnership | 2023-2026 | - |
| Support small and medium enterprise organisations by increasing overall spend with them in line with the Government growth agenda | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to embed the Sellafield security enhancement programme | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue with improvements to the site utilities infrastructure | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue the programme to ensure the analytical services capability is available to support the mission | 2023-2026 | - |
| Working to embed the capability to proactively protect, detect, respond, and recover against current and evolving cyber threats | 2023-2026 | - |
| Manage and deliver asset management and continuous improvement capability and performance to support mission delivery | 2023-2026 | - |
| Implementation of an overarching Infrastructure Strategy which supports and enables delivery of the future mission | 2023-2025 | - |
| Continue to progress the land programme to ensure SL has the land and property available to deliver the mission | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to explore the opportunity for thermal treatment | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to progress and embed sustainability through the key areas identified within the NDA Sustainability Policy | 2023-2026 | - |
| 2023 Corporate Plan development | 2023-2025 | - |
| Continue to embed the One NDA approach and comply with the Group Operating Framework (GOF) model | 2023-2026 | - |
| Regulatory engagement | ||
| Ensure discharges are in line with UK discharge strategy | 2023-2026 | - |
| Reduce environmental risk (including retrieval and treatment of legacy wastes, reduction of HAL stocks) | 2023-2026 | - |
Magnox Limited
Magnox is an NDA subsidiary, responsible for 12 nuclear sites across the UK: Berkeley, Bradwell, Chapelcross, Dungeness A, Harwell, Hinkley Point A, Hunterston A, Oldbury, Sizewell A, Trawsfynydd, Winfrith and Wylfa. Magnox also generates electricity at the Maentwrog hydroelectric plant.
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £530 million
A change in decommissioning strategy to Site Specific Strategies (SSS) is being developed which takes into account all contributing factors for that site as well as the strategic and funding pressures on the Magnox Portfolio. The Rolling Programme of Decommissioning (RPD) strategy, which approaches decommissioning in a phased way, aims to reduce the overall cost, duration and uncertainty of the Magnox mission, enabling further beneficial re-use of some of our land for other purposes.
The RPD is the basis for the NDA Strategy 4 for Magnox. This will maximise the opportunity for sharing any lessons learned, developing and implementing new innovative technologies, and strengthening wider capability. The programme will collectively be geared towards reducing risk, reducing lifetime costs, and growing skills and knowledge to deliver benefits both nationally and to local communities. The site-specific decommissioning and end state strategies will be continually reviewed and optimised using the learning obtained from across the estate and other influencing factors such as Government policy and funding.
We will support economic growth and job creation by continuing to drive progress against a short-term plan with clear milestones. Each site will also have long-term options identified and decision points on both the decommissioning strategy and the end state. This will allow us to consider opportunities for more innovative approaches, based on the technology and external factors of the time, and provide a basis for ongoing engagement and consultation on our strategies for site decommissioning. In order to recognise the uncertainties in the long term, we have chosen to set out approximate dates that our best estimates of the earliest available options encompass rather than setting out specific dates for our milestones. The current best estimates for end state dates have been included in the 2023-2026 NDA Business Plan and reflect the work done to date on near-term plans and medium-term plans. These estimates are subject to change as we develop our plans and take account of contributing factors including HMG priorities, funding and approvals.
For example, further changes, as we develop our RPD plans, are liable to arise as we seek to integrate and optimise the Magnox plans with those of the AGRs and indeed any other future missions which Magnox may be asked to support in due course.
Key activities
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Uranium | ||
| Continue the programme for the transfer of nuclear materials including regulatory permissioning | 2023-2026 | 22 |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Low Level Waste | ||
| Delivery of the Magnox elements of the estate-wide LLW Management Plan including diversion to alternative treatment including development of updated Integrated Waste Strategy | 2023-2026 | 26, 27, 28, 30 |
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Continue to pursue opportunities to consolidate ILW to interim stores | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and demolition | ||
| Continue estate decommissioning and demolition activities in line with individual site strategies | 2023-2026 | 42, 43 |
| Continue reactor decommissioning | 2023-2026 | 43 |
| Continue to manage and remove asbestos | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue development of site specific strategies as part of a rolling programme of decommissioning | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Dedesignate or Reuse | ||
| Continue working with regulators to ensure appropriately scaled management arrangements and permissioning for Interim States and Interim End States are determined and agreed | 2023-2026 | 44, 45 |
| Development of Interim State approaches, utilising revised management arrangements | 2023-2026 | 44 |
| Monitoring of management and maintenance arrangements for sites in Care and Maintenance | 2023-2026 | 44 |
| Progress land quality activities to support suitability for reuse | 2023-2026 | 44, 46 |
| Progress land dedesignation and release to support reuse | 2023-2026 | 47 |
| Provision of support to nuclear new build | 2023-2026 | 47 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Support Government in activities to deliver preparations for decommissioning the Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor fleet | 2023-2026 | - |
| Prepare Magnox for the joining of Dounreay and each AGR as they reach fuel free state. Develop and deliver the joint programmes with DSRL and EDF | 2023-2026 | - |
| Support small and medium enterprise organisations by increasing overall spend with them in line with the Government growth agenda | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue enhancement of Cyber Security Capability and IT infrastructure | 2023-2026 | - |
| Optimise Asset Management capability and performance to support mission delivery | 2023-2026 | - |
| Progress development of workforce capability and skills for decommissioning in Magnox and the supply chain | 2023-2026 | - |
| Develop and deliver to the sustainability agenda | 2023-2026 | - |
| Identify and realise opportunities in research, development and innovation | 2023-2026 | - |
Berkeley
Site in Gloucestershire
27 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
11 hectares - 16 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2060s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2025 | 31 |
| Complete design and build of the Gravel and Amalgum Retrieval Plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW wastes | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Commence the deplant and demolition of the Caesium Removal Plant | 2023-2026 | 42, 43 |
| Continue to progress the asbestos and plant removal from the blower houses | 2023-2026 | 42, 43 |
Bradwell
in care and maintenance
Site in Essex
20 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 20 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2080s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Dedesignate and Reuse | ||
| Ongoing management of site during Care and Maintenance period | 2023-2026 | 44 |
Chapelcross
Site in Dumfries and Galloway
96 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 96 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2060s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW wastes | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Progress preparations for pond draining and stabilisation including waste retrievals | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Prepare and execute land remediation of the cooling tower basins | 2023-2025 | 46 |
| Commence and progress turbine hall asbestos removal | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Dungeness A
Site in Kent
20 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 20 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2050s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW wastes | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Continue to progress activities supporting consolidated ILW storage | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Commence and progress decommissioning the Active Effluent Treatment facilities | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Prepare and progress the demolition of the boilers and associated buildings | 2023-2026 | 43 |
Harwell
Site in Oxfordshire
107 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
23 hectares - 84 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - 2025
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2050s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Uranium | ||
| Continue the programme for the transfer of nuclear materials | 2023-2026 | 22 |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue preparations for decommissioning of the Radiochemistry Facility (B220) | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue decommissioning, demolition, land remediation, reinstatement and delicensing of the Liquid Effluent Treatment Plant (LETP) | 2023-2026 | 42, 43, 44 |
| Continue preparations for the decommissioning of the British Experimental Pile Zero reactor (BEP0)) | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue preparations and planning for the decommissioning of the Active Waste Handling facility (B459) | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Dedesignate or Reuse | ||
| Continue incremental release of land to the Harwell campus through targeted demolitions, remediation and clearance of land tracts | 2023-2026 | 42, 43, 47 |
Hinkley Point A
Site in Somerset
19 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 19 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2060s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue and complete asbestos removal from the reactor building | 2023-2025 | 42 |
| Continue to progress the de-planting of the reactor building | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Hunterston A
Site in Ayrshire
15 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 15 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2050s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Commissioning of the solid ILW encapsulation plant | 2023-2026 | 32 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue the decommissioning of the Active Effluent Treatment facilities | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue to progress the deplanting of the cooling pond overbuilding | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Oldbury
Site in South Gloucestershire
47 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
32 hectares - 15 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2080s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities supporting consolidated ILW storage | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Commence the design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW (at Berkeley) | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue to progress the decommissioning of the Active Effluent Treatment facilities | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Commence and progress the asbestos removal, deplant and demolition of the turbine hall | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Commence the asbestos removal from the reactor building | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Sizewell A
Site in East Suffolk
14 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 14 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2070s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to support consolidation of ILW storage | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Commence design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Commence and progress the decommissioning of the Active Effluent Treatment facilities | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Progress and complete the asbestos removal, deplant and demolition of the turbine Hall | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Commence and progress the asbestos removal from the boiler houses | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Trawsfynydd
Our lead and learn site for rolling decommissioning
Site in North Wales
15 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 15 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2050s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue and complete activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2025 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue and complete reactor height reduction enabling activities | 2023-2024 | 42 |
| Commence, prepare, and progress reactor building height reduction | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue deplanting, decommissioning and demolition of the ponds complex facility | 2023-2026 | 42 |
Winfrith
Site in Dorset
81 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
10 hectares - 71 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2036s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Low Level Waste | ||
| Complete shipments of LLW drums from Treated Radwaste Store to LLWR | 2023-2025 | 28 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue DRAGON reactor decommissioning, including the completion of the construction and installation of the core segmentation equipment | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue SGHWR decommissioning, including the completion of the construction and installation of the core segmentation equipment | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Commence and progress the removal of the discharge pipelines | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Continue land remediation activities and end state development | 2023-2026 | 46 |
Wylfa
Site in Anglesey
21 hectares
Hectares dedesignated
0 hectares - All 21 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Free from Spent Fuel - Achieved
- Free from Nuclear Materials - Achieved
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All land in End State - all planned physical work complete - c.2080s*
*This is our best estimate of the earliest date to achieve milestones but is based on a number of dependences, assumptions, risks and exclusions and is subject to site specific strategy development and approval.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Continue to progress activities to retrieve, treat and store ILW | 2023-2026 | 31, 32, 33 |
| Continue to progress design and build of ILW retrieval plant | 2023-2026 | 31 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue and complete asbestos removal from the de-aerator floor of the turbine hall | 2023-2024 | 42 |
| Commence and progress the isolation, asbestos removal, deplant and demolition of the turbine hall | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| Commence and progress asbestos removal from the reactor building | 2023-2024 | 42 |
Dounreay Site Restoration Limited
Dounreay Site Restoration Limited (DSRL) is an NDA subsidiary responsible for decommissioning and cleaning up the Dounreay site in the north of Scotland. It also operates a Low Level Waste (LLW) disposal facility to deal with waste from the site.
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £221 million
Site in Northern Scotland
60 hectares (plus 12 hectares designated for LLW facility) in Caithness.
Hectares Dedesignated
0 hectares - 60 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence, the 12 for the LLW facility are designated but not licensed.
Important milestones 2023-2026
The activities below are extracted from the current site Lifetime Plan and are subject to change. A revised Lifetime Plan is in development following the transition to an NDA subsidiary.
- All fuel in long-term storage or shipped off site.
- Dounreay Fast Reactor (DFR) dismantled
- Prototype Fast Reactor (PFR) dismantled
- Shaft and silo encapsulation complete
- Site clearance and environmental restoration phase 3 complete
- Interim end state achieved
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- Defueled - TBD
- Free from Nuclear Materials - TBD
- All Radioactive Waste Disposed - TBD
- All Buildings Decommissioned or Relicensed - TBD
- All Land Demonstrated as Suitable for Reuse - TBD
- All Land Dedesignated or Reused – TBD
TBD is shown when the date for completing the strategic outcome is not sufficiently clear for a specific date to be given at this time.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Spent Fuel | ||
| Spent Exotic Fuel | ||
| Complete removal of in reactor DFR breeder fuel and transfer to interim storage | 2023-2026 | 12 |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Low Level Waste | ||
| Continue transfer of LLW to LLW facility | 2023-2026 | 27 |
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Complete construction of Dounreay Cementation Plant (DCP) Store Extension | 2023-2024 | 32 |
| PFR raffinate immobilisation complete | 2023-2025 | 32 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| PFR - complete reactor vessel residual sodium treatment operations - turn reactor vessel atmosphere from nitrogen to air | 2023-2026 | 42 |
| PFR raffinate immobilisation complete | 2023-2025 | 32 |
| Dedesignate or Reuse | ||
| NDA and regulatory permissioning in support of the Interim End State definition and arrangements for Dounreay | 2023-2026 | 46 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Support small and medium enterprise organisations by increasing overall spend with them in line with the Government growth agenda | 2023-2026 | - |
| Prepare Dounreay for joining with Magnox. Develop and deliver the joint programme | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue enhancement of Cyber Security Capability and IT infrastructure | 2023-2026 | - |
| Optimise Asset Management capability and performance to support mission delivery | 2023-2026 | - |
Nuclear Waste Services
Nuclear Waste Services (NWS) launched in January 2022. This new organisation brings together the long-established expertise of site operator Low Level Waste Repository Limited (LLWR), Geological Disposal Facility (GDF) developer Radioactive Waste Management (RWM) Limited and the NDA’s Integrated Waste Management Programme. The NWS vision is to make nuclear waste permanently safe as soon as possible. It is focused on managing UK nuclear waste safely, innovatively, and sustainably, while driving value for money.
NWS is not a legal entity but provides strategic oversight over the operation and development of these businesses through a management board governance structure. The legal entities of LLWR and RWM will endure, although the intention is to move to a single legal entity operating under the NWS brand at an appropriate point in the future.
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £240 million
Site in Cumbria
100 hectares
Hectares Dedesignated
0 hectares - All 100 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Important milestones 2023-2026
- 2023 - Repository Development Programme (RDP) Tranche 1 design complete (*)
- 2024 - RDP commence main construction (*)
- 2026 - Environmental Safety Case (ESC) submitted to the Environment Agency (*)
- 2026 - Decision to Government on communities to progress to deep borehole investigation and increased community investment
- 2026-2027 - RDP Vault 8 closure (*)
- 2029 - Start site characterisation deep borehole investigations
- 2029 - RDP final capping of Vault 8 (*)
Site progress (achieved and expected)
- All Buildings Decommissioned or Relicensed - TBD
- All Land Demonstrated as Suitable for Reuse - TBD
- All Land Dedesignated or Reused - 2135 (*)
TBD is shown when the date for completing the strategic outcome is not sufficiently clear for a specific date to be given at this time.
(*) indicates activities related to specific work at NWS Low Level Waste Repository site
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Integrated Waste Management | ||
| Low Level Waste | ||
| Deliver the National LLW Programme to optimise LLW Strategy implementation. Work with consigning SLCs to improve waste forecast and inventory and continue segregated waste, treatment, and disposal services (*) | 2023-2026 | 26, 27, 28, 29 |
| Intermediate Level Waste | ||
| Through activity and enabling partners – deliver a robust technical programme, support the GDF Programme and Waste Management | 2023-2026 | 32, 33, 34 |
| Work with NDA to support innovation in approaches to integrated waste management | 2023-2026 | 33 |
| Type B packaging capability to support NDA and MOD customers | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Implement Government policy on geological disposal of higher activity waste to deliver a suitable site and willing community | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Through activity and enabling partners – Deliver a robust technical programme, support the GDF Programme and Waste Management | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Establish an innovation partnership for asbestos | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Establish a standard group-wide service including a characterisation infrastructure plan | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Establish thermal treatment as a proven technology for the group | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Delivery of thermal treatment Plutonium Contaminated Material design and build | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Deliver initial Near Surface Disposal capability subject to appropriate Government policy | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Complete the Near Surface Disposal at surface and at depth optimisation works | 2023-2026 | 34, 39 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Site End State Gate B paper delivered (*) | 2023-2026 | 44, 45, 47 |
| New Build and Operations | ||
| Complete enabling works for phased construction of the final capping for trenches 1 to 7 and Vault 8 (*) | 2023-2026 | 41 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Support hazard reduction across the NDA group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Deliver LLW packaging and transport services (*) | 2023-2026 | - |
| Manage and operate LLWR site safely to provide an effective UK disposal service (*) | 2023-2026 | - |
| Consider options to further optimise operations at the LLWR site (*) | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to pursue overall cost savings in delivery of the Lifetime Plan | 2023-2026 | - |
| Support small and medium enterprise organisations by increasing overall spend with them in line with the Government growth agenda | 2023-2026 | - |
| Active participation in the British Energy Security Strategy and the North West Nuclear Arc to help achieve HMG key deliverables | 2023-2026 | - |
| Mature and deliver asset management and continuous improvement capability and performance to support mission delivery | 2023-2026 | - |
| Ensure that NWS has willing communities – working closely with our Community Partnerships and interested parties to build understanding of the GDF Programme and maintain community participation | 2023-2026 | - |
| Ensure that NWS can put forward two best and suitable sites for detailed investigation in Tranche 3 – underpinned through site evaluation activities | 2023-2026 | - |
| Complete the transition to become a single legal entity | 2023-2026 | - |
| Optimise NWS business delivery efficiency and capability commitments including a new IT platform | 2023-2026 | - |
| Regulatory engagement | ||
| Contribute to sustainability performance under the Greening Government Commitments (GGC) | 2023-2026 | - |
Nuclear Transport Solutions
Nuclear Transport Solutions (NTS) provides the NDA group with specialist transport and logistics capabilities.
Delivering our mission relies on being able to transport radioactive materials and other freight safely and sustainably. NTS supports this by transporting spent nuclear fuel from UK power stations to Sellafield, returning reprocessed products to customers overseas, and providing packaging and licensing solutions to the NDA group.
It also generates revenue through commercial opportunities in the UK and overseas – offsetting the cost of delivering decommissioning and clean-up work at the UK’s oldest nuclear sites.
NTS operates Direct Rail Services (DRS) and Pacific Nuclear Transport Limited (PNTL) to deliver rail and shipping services for customers, building on decades of experience of providing safe, secure and reliable transport solutions.
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £111 million
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Spent Fuels - Spent Oxide Fuel | ||
| Support AGR fuel movements by rail for EDF from stations to Sellafield, including preparations for the AGR defueling programme | 2023-2026 | 6 |
| Nuclear Materials - Plutonium and Uranium | ||
| Support national nuclear material rail movements for Harwell, Winfrith and DSRL | 2023-2026 | 22 |
| Integrated Waste Management - High Level Waste | ||
| Continue to deliver important international transports of vitrified High Level Waste (HLW) and conditioned Intermediate Level Waste (ILW) | 2023-2026 | 16, 17 |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Establish and implement an Integrated Transport Programme to identify opportunities and realise benefits from better coordination and optimisation of NDA group transports | 2023-2026 | - |
| Seek opportunities for new business within nuclear shipping, rail, packaging and design by providing transport enabling solutions to UK and international markets | 2023-2026 | - |
| Undertake appropriate non-nuclear business to maintain and enhance the skills and capabilities required to support the core nuclear mission | 2023-2026 | - |
| Maintain and operate a fleet of specialist transport assets which meet the highest standards of quality, safety and security in order to support NDA operations | 2023-2026 | - |
| Attract and retain the necessary skills, capability and diversity of talent to deliver business in a safe, secure and reliable manner | 2023-2026 | - |
| Support the discharge of NDA obligations with respect to MOD nuclear rail transportation | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to deliver NDA’s contractual obligations for transport of mixed oxide (MOX) fuel from France to Japan | 2023-2026 | - |
| Develop and implement a carbon reduction plan to successfully achieve carbon net zero aspirations | 2023-2026 | - |
NDA Archives Limited
NDA Archives is an NDA subsidiary, responsible for Nucleus (the Nuclear and Caithness Archives) and related operational activities across the NDA group. The Nucleus facility is currently operated by a commercial partner and provides the centre of excellence for long-term records management, archive services, digital preservation and heritage management.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Re-competition of the commercial partner contract | 2023-2024 | - |
| Continuing development of the Hub and Spokes delivery model – centralised inventory and management with dispersed, off-site storage where appropriate | 2023-2024 | - |
| Working with stakeholders to continue the development and implementation of the NDA’s heritage strategy | 2023-2024 | - |
| Continuing to meet the environmental targets set across the NDA group in alignment with our obligations under the Greening Government Commitments Scheme | 2023-2026 | - |
| Development of accommodation options, including strategies/proposals for dealing with increased capacity needs at Nucleus and the NDA group’s material and samples management and storage requirements | 2023-2026 | - |
| Magnox collection sift completed and ready for accession | 2024-2025 | - |
| Sellafield offsite collection sift completed and ready for accession | 2024-2025 | - |
NDA Properties Limited
NDA Properties Ltd is an NDA subsidiary, holding and managing the majority of the non-nuclear property assets within the NDA group.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Effective and efficient management and assurance of retained landholding consisting of 640 hectares across 85 properties | 2023-2026 | - |
| Review and deliver progressive environmental stewardship across the portfolio estate | 2023-2026 | - |
| Proactively dispose/release surplus assets no longer required by the NDA group or wider parts of Government, including those that have high socio-economic value | 2023-2026 | - |
| To engage and collaborate with NDA group and stakeholders to target carbon net zero objectives | 2023-2026 | - |
Rutherford Indemnity Limited
Rutherford Indemnity Ltd provides insurance cover for the NDA group. The company is a wholly-owned subsidiary, managed for the NDA by Marsh Management Services Guernsey Limited, and has no direct employees.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Provide optimal insurance coverage to the NDA to support its NDA group-wide insurance programme, exploiting opportunities to reduce overall cost of insurance risk and offering insurance solutions (including support for claims handling enhancements) to meet the evolving needs of the group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to deliver the target return on the investment portfolio, protecting Rutherford’s ability to offer insurance on a cost-effective basis, maintaining liquidity in order to be able to respond promptly to a major loss | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to use a prudent proportion of Rutherford’s assets to support infrastructure investment within the NDA group | 2023-2026 | - |
| Maintain capability for payment of dividends to the shareholder | 2023-2026 | - |
Energus
Energus is an NDA subsidiary offering conference and events facilities and a range of training, education and business support services geared to providing and enhancing skills within both the local and national nuclear workforce.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Critical Enablers | ||
| Continue to work closely with the NDA and stakeholders across the nuclear sector to upskill and develop the workforce of today and tomorrow | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to manage and facilitate a range of training opportunities for the NDA group and wider nuclear sector, including: • Nuclear Graduates • functional programmes for both graduates and apprentices including cyber security, finance, audit and risk, radiation protection, commercial, business and civil engineering • bespoke programmes to support the NDA People Strategy and the British Energy Security Strategy Support the development of the NDA group Graduate Scheme | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to work in partnership with the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) and NDA Cyber Security Resilience Programme (CSRP) to deliver a pipeline of cyber security young talent into the sector including: • CyberFirst • Level 3 programme to Energy Coast UTC • Apprentices • Graduates and be the venue of choice for Cyber Security training in the North West | 2023-2026 | - |
| Provide a range of managed services within the people and skills arena including recruitment programmes, work experience and STEM engagement – supporting the NDA commitment to ED&I and achieving greater levels of social value and socio economic benefit to our communities and broader stakeholders | 2023-2026 | - |
| Provide a high quality training environment for all Sellafield apprentices, working with a range of education partners and suppliers | 2023-2026 | - |
| Continue to be a Cumbrian venue of choice for the NDA group’s events, conferences and delivery of training and education | 2023-2026 | - |
Springfields
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £22 million
81 hectare site in Lancashire.
All 81 hectares remain covered by the nuclear site licence.
Owned by Westinghouse Electric UK Holdings Limited.
Springfields is a nuclear fuel manufacturing site and is located near Preston in Lancashire. The site is operated by Springfields Fuels Limited (SFL) and is used to manufacture a range of fuel products for UK and international customers, the processing of historic uranic residues and decommissioning of redundant facilities.
From April 2010, the NDA permanently transferred ownership of the company to Westinghouse Electric including the freedom to invest for the future under the terms of a new 150-year lease. SFL is contracted to provide decommissioning and clean-up services to the NDA to address historic liabilities.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Uranium | ||
| Continue to appropriately manage, care and maintain NDA stock of uranic materials | 2023-2026 | 23, 25 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition |
Capenhurst
Planned expenditure for 2023/24 - £24 million
30 hectare site in Cheshire
17 hectares have been dedesignated
Modification of Designating Direction signed by the Minister in May 2010 and July 2012. Remaining 13 hectares are covered by the nuclear site licence.
Owned by URENCO
The NDA Capenhurst site is located near Ellesmere Port in Cheshire.
In 2012, the site was transferred to URENCO, owners of the adjacent licensed site, and was amalgamated into a single nuclear licensed site. As part of this transfer, URENCO established Urenco Nuclear Stewardship (UNS), formerly known as Capenhurst Nuclear Services, to provide responsible management of uranic materials and carry out remediation work on behalf of the NDA.
UNS manages a large proportion of the NDA’s uranic inventory and also provides broader decommissioning and demolition works for redundant facilities, in order to reduce liability and optimise space utilisation on site.
| Key activities | Timescale | Strategic outcome |
| Nuclear Materials | ||
| Uranium | ||
| Continue the safe storage and management of uranic materials, including uranium hexafluoride tails prior to processing through the Tails Management Facility | 2023-2026 | 22, 23, 24, 25 |
| Site Decommissioning and Remediation | ||
| Decommissioning and Demolition | ||
| Continue decommissioning of key facilities | 2023-2025 | 41, 42, 43, 47 |
Delivery of our mission up to 2040 - Spent Fuels and Nuclear Materials
Useful links
- Nuclear Decommissioning Authority www.gov.uk/nda
- Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy www.gov.uk/beis
- Sellafield Ltd www.gov.uk/government/organisations/sellafield-ltd
- Magnox Ltd www.gov.uk/government/organisations/magnox-ltd
- Dounreay Ltd www.gov.uk/government/organisations/dounreay
- Nuclear Waste Services www.gov.uk/government/organisations/nuclear-waste-services
- Nuclear Transport Solutions www.nucleartransportsolutions.com
- URENCO Ltd www.urenco.com
- Springfields Fuels Ltd www.westinghousenuclear.com
Useful documentation
- The NDA group Sustainability Strategy 2022 - GOV.UK (www.gov.uk/nda)
- NDA Strategy - March 2021 (www.gov.uk/nda)
- NDA Business Plan 2021 to 2024 and NDA Business Plan 2022 to 2025 (www.gov.uk/nda)
- NDA Mid-Year Performance Report 2020 to 2021 (www.gov.uk/nda)
- NDA Research and Development 5 year plan: 2019 to 2024 (www.gov.uk/nda)
- Nuclear Decommissioning: attracting and retaining skills (brochure) Nov 2016 (www.gov.uk/nda )
- NDA Corporate Centre: gender pay gap report, 2021 (www.gov.uk/nda)
- Register of Director’s Interests and associated procedure (www.gov.uk/nda)
- NDA: working with our communities (www.gov.uk/nda)
Glossary
AGR Advanced Gas-Cooled Reactor
BEIS Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy
CAPEX Capital expenditure
DFR Dounreay Fast Reactor
DRS Direct Rail Services Ltd
DSRL Dounreay Site Restoration Ltd
EDFE EDF Energy
ED&I Equality, Diversity and Inclusion
FGMSP First Generation Magnox Storage Pond
FHP Fuel Handling Plant
GDF Geological Disposal Facility
HAL Highly Active Liquor
ILW Intermediate Level Waste
INS International Nuclear Services Ltd
LETP Liquid Effluent Treatment Plant
LLW Low Level Waste
LLWR Low Level Waste Repository
MOD Ministry of Defence
MOX Mixed Oxide Fuel
MSSS Magnox Swarf Storage Silo
NDA Nuclear Decommissioning Authority
NDAPL NDA Properties Ltd
NTS Nuclear Transport Solutions
NWS Nuclear Waste Services
POCO Post Operational Clean Out
PFR Prototype Fast Reactor
PFSP Pile Fuel Storage Pond
PPP Programme and Project Partners
RD&I Research, Development and Innovation
RWM Radioactive Waste Management Ltd
SGHWR Steam Generating Heavy Water Reactor
SLC Site Licence Company
SME Small and Medium Enterprise
THORP Thermal Oxide Reprocessing Plant
UKGI UK Government Investments

